Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
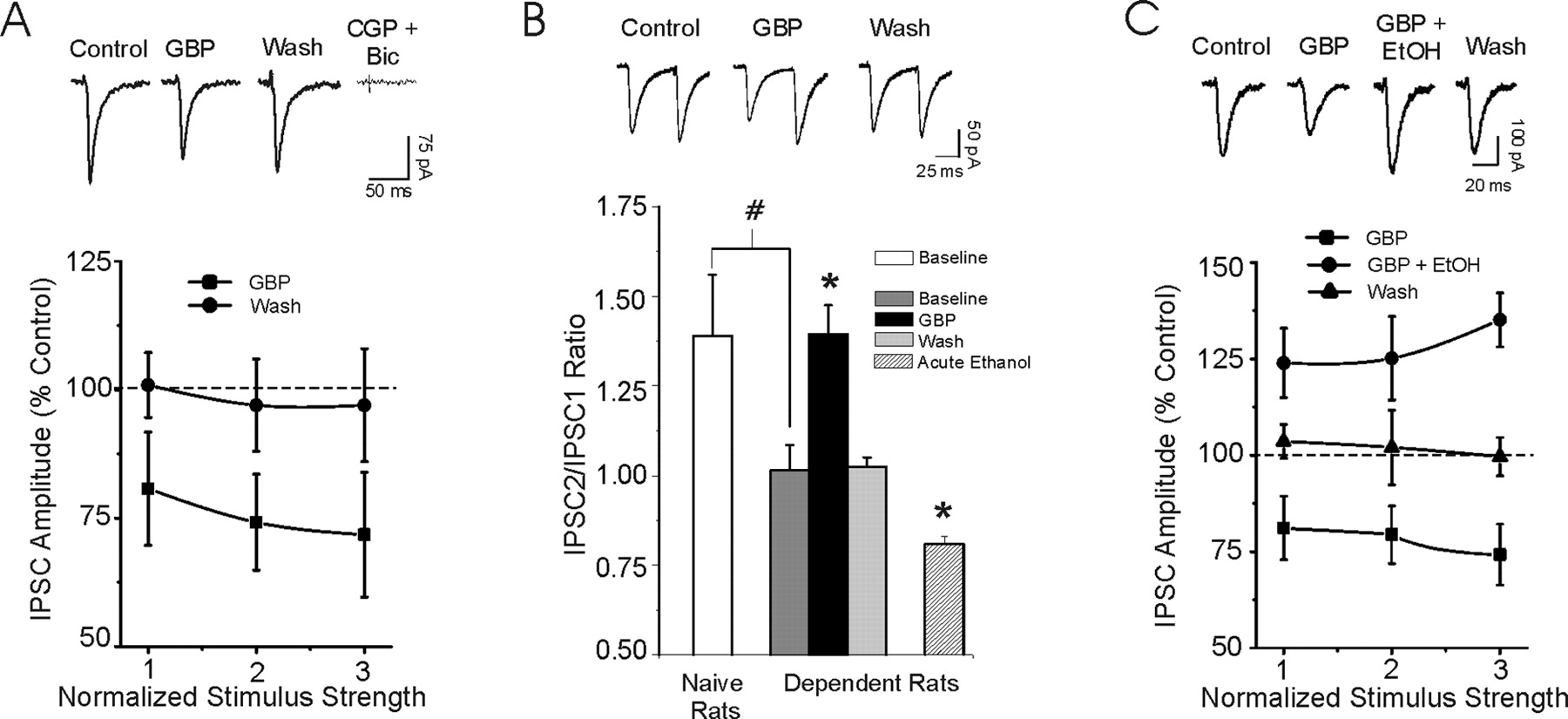 |  |
A hangover is the combined negative mental and physical effects you experience after drinking that occur as your blood alcohol concentration (BAC) approaches zero, according to the Alcohol Hangover Research Group (AHRG), an international team of experts and institutions that focuses on hangover research. Gabapentin is prescribed to aid against alcohol withdrawal anxiety, while the alcohol hangovers (withdrawals) create the anxiety to begin with. More importantly, talk to a doctor and be completely honest about your habit, they will set you on the right track to stop. Combining gabapentin with alcohol poses significant risks. Understanding these dangers is crucial for anyone considering using gabapentin alongside alcohol. The interplay between gabapentin and alcohol can amplify each other's effects, leading to heightened side effects. Is it possible to get an alcohol and Gabapentin hangover? Combining alcohol and Gabapentin can result in a more severe hangover. The interaction between the two substances can cause extreme drowsiness, dehydration, nausea, headaches, and cognitive fog the following day. Gabapentin is an off-label medication for alcohol use disorder, sold under the brand names Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant, among others. The medication was originally developed to treat epilepsy and is now FDA-indicated for a variety of additional uses, including the treatment of conditions like postherpetic neuralgia and restless leg syndrome. 6. Avoid Alcohol. While using Gabapentin for hangover relief, it is recommended to avoid consuming alcohol. Alcohol can interfere with the medication’s effectiveness and may also exacerbate hangover symptoms. 7. Monitor Your Symptoms. Pay attention to your body and monitor how Gabapentin is affecting your hangover symptoms. Gabapentin and Alcohol Memory Loss. Gabapentin and alcohol can impair memory formation. It is not well-known why these substances can impact memory. However, GABA appears to be related to memory formation, and both drugs can cause “blackouts.” Can You OD on Gabapentin and Alcohol? Gabapentin is thought to increase the risk of alcohol People use alcohol and gabapentin together increase both of their effects. They may feel relaxed, euphoric, and energized simultaneously. However, the combination of alcohol and gabapentin may be dangerous. According to the Epilepsy Foundation, anti-epileptic drugs like Gabapentin do not mix well with alcohol. While some people get away with a drink or two, doctors advise against this practice, especially if you struggle with AUD. Here are the reasons why Gabapentin and alcohol should not be taken together: Both substances have sedative effects. Combining gabapentin with alcohol can intensify CNS depression, increasing risks of dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired judgment. Healthcare providers advise against alcohol consumption during gabapentin treatment due to the potential for exacerbated side effects. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Gabapentin, a nonbenzodiazepine anticonvulsant GABA analog, has shown some recent promise in the treatment of alcoholism. Preliminary clinical data suggest that gabapentin may be effective in reducing symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal and some symptoms of protracted abstinence (Furieri and Nakamura-Palacios, 2007). The precise mechanism of Additionally, there is also an increased risk of seizures with alcohol abuse and withdrawals. So using alcohol with gabapentin can render the medicine useless for the treatment of epilepsy since it aggravates the medical condition for which the drug is being used. For all these reasons it is suggested to not take alcohol with gabapentin. A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of Gabapentin has been used effectively in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal in alcoholics (Bonnet et al., 1999, 2007; Bozikas et al., 2002; Gentry et al., 2002; Voris et al., 2003; Book and Myrick, 2005; Mariani et al., 2006; Myrick et al., 2007) and has a selective action in decreasing the convulsive and anxiety-related signs of ethanol The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) 3 times daily. Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. If you take an antacid containing aluminum and magnesium, such as Maalox®, Mylanta®, Gelusil®, Gaviscon®, or Di-Gel™, you should wait at least 2 hours before taking your Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem Studies suggest that gabapentin may be effective in treating alcohol withdrawal and promoting alcohol abstinence. 1,5 In a randomized clinical trial by a study published in the Journal of American Medical Association, 41% of gabapentin participants reached total abstinence. 1.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |