Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
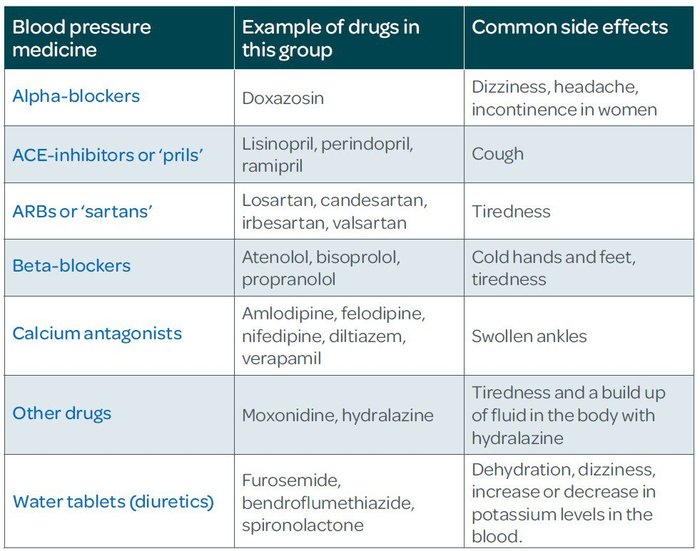
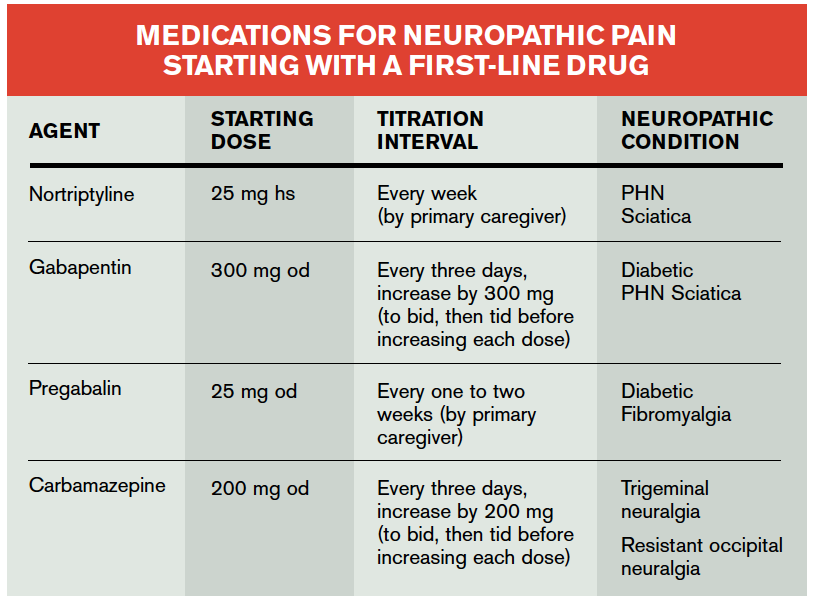
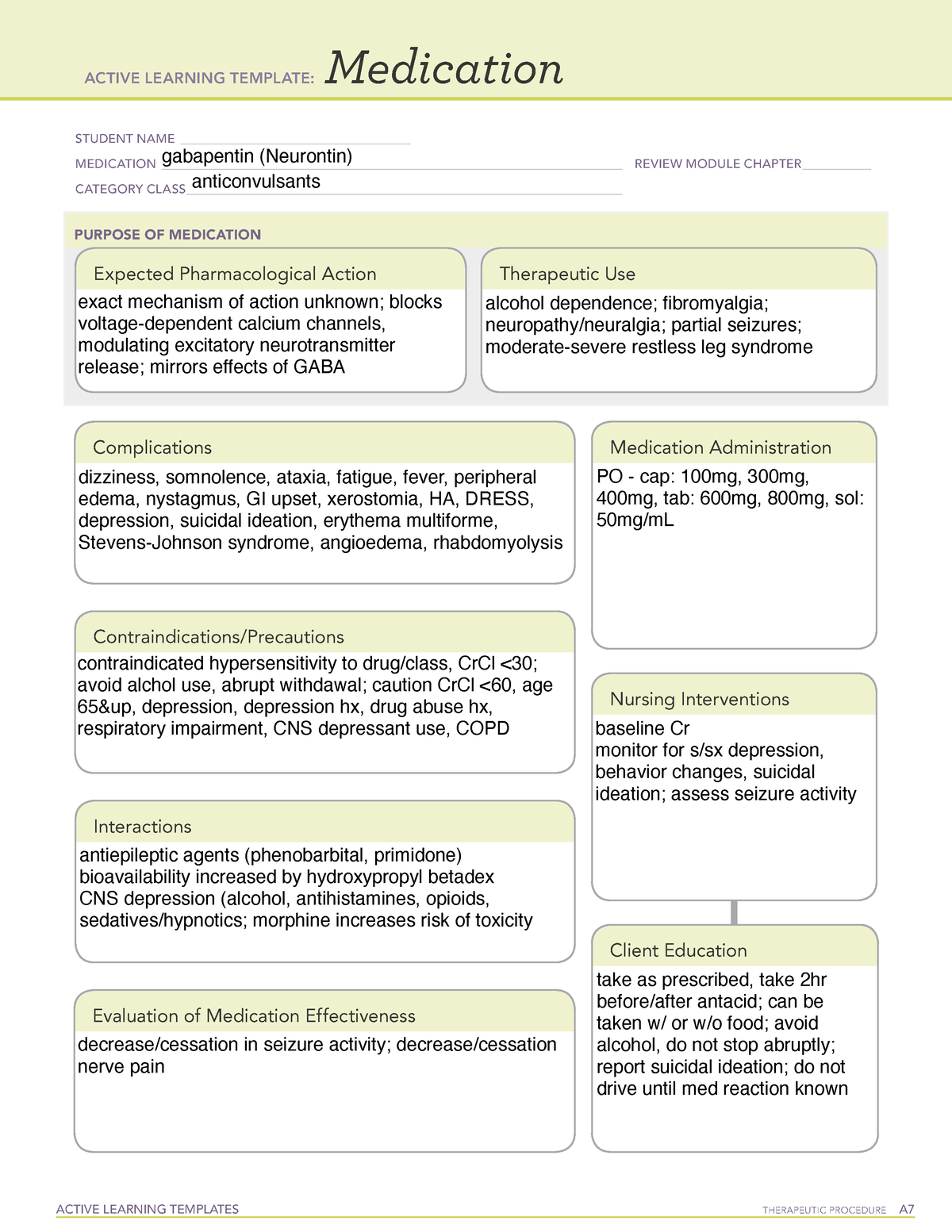
This narrative review provides an overview on cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular medications potentially impairing orthostatic blood pressure. This review may be helpful to guide medical therapy optimization in patients with an abnormal orthostatic blood pressure response, to minimize the risk of drug-related orthostatic hypotension. losartan, which is a medication for high blood pressure; magnesium oxide, (2019). Gabapentin reduces blood pressure and heart rate through the nucleus tractus solitarii. https: "Calcium channel blockers are used to treat high blood pressure and may also be prescribed to mitigate symptoms of coronary artery disease, arrhythmia, angina, high cholesterol and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease," Dunn says. Medications are a common reason for swollen ankles and feet, also called pedal edema. Amlodipine (Norvasc), gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise), and pregabalin (Lyrica) can cause puffy legs and ankles. Birth control pills, certain over-the-counter pain medications, and steroids are a few other culprits. Hypertension (high blood pressure) Anxiety; Insomnia; Sweating; Seizures; This rebound hypertension poses a significant risk, particularly for those with pre-existing high blood pressure. If gabapentin needs to be discontinued, it should always be done under medical supervision, with gradual tapering to minimize withdrawal effects. To review the blood pressure (BP) effects of pain and analgesic medications and to help interpret BP changes in people suffering from acute or chronic pain. Acute pain evokes a stress response which prompts a transient BP increase. Chronic pain is High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin may interact with certain medications or supplements. Because of drug interactions, using gabapentin with certain medicines is typically not recommended, but may be required in some cases. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. I am also dealing with high blood pressure, and currently take 50 mg of Losartan in the morning and, for the past two months, 5 mg of Amlodipine Bensylate at bedtime. Two nights ago, because of the hot temps, I added a 10 mg Melatonin. Might I be making my balance trouble worse with this mix of meds and Melatonin? We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. The primary medications that should be avoided or used with extreme caution in combination with gabapentin include: Opioid Painkillers: Combining gabapentin with strong painkillers, such as morphine , can significantly increase the risk of drowsiness, dizziness , and respiratory depression . Meloxicam may make some blood pressure medications less effective. Taking meloxicam with certain blood pressure medications can also raise your risk of kidney damage. Meloxicam and other NSAIDs can restrict blood flow to the kidneys. Taking them with blood pressure medications that run through the kidneys may lead to acute (sudden) kidney injury. Research suggests that gabapentin can lower blood pressure by reducing the body’s production of certain hormones that can increase blood pressure. It may also help to relax blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through them. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: I suggest you contact your Dr. asap. Drugs that can cause high potassium levels (Hyperkalemia) Some medications cause the blood level of potassium to increase, which is known as hyperkalemia. It occurs when your blood serum level exceeds 5.0 mmol/L. Drugs used to treat high blood pressure, heart-related problems and kidney issues can cause high potassium. They include:
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |