Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
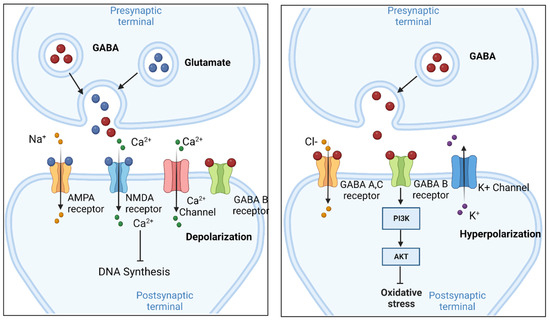 |  |
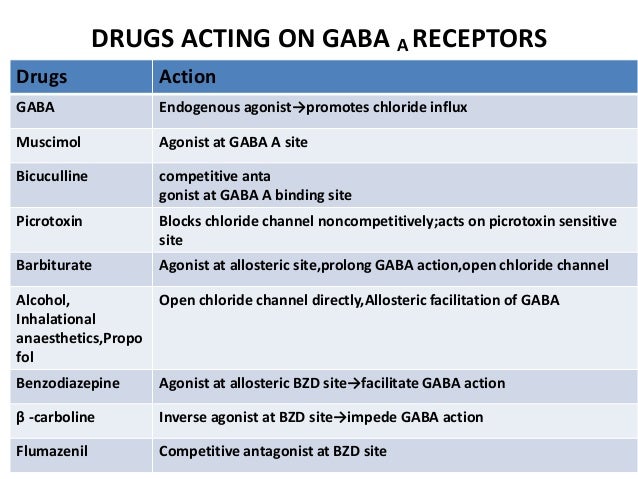
GABAGoodness is devoted to the discussion of all GABAergics, Gabapentnoids and VDCC inhibitors such as Pregabalin, Gabapentin, Phenibut, Carisoprodol, GHB, Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates, and more! This is a great place to ask general or recreational questions, get harm reduction advice, or share your experience with withdrawal syndromes. Not enough is known about how GABA may interact with drugs, foods, or other herbs and supplements, but use with caution if taking with blood pressure medications. GABA supplements are classified as dietary supplements and can be purchased over-the-counter, while gabapentin requires a doctor's prescription and medical oversight due to its potential side effects and interactions with other medications. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medications called anti-epileptics. It can be used to treat seizures and nerve pain associated with shingles. Magnesium is a mineral that our bodies rely on, and it can be found in foods, drinks, and certain medications. When gabapentin and magnesium-containing medications or supplements are combined, they may Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. But sublingual GABA is well absorbed by the body and should be given a thorough trial by every person with IPS. You can take 100 to 300mg sublingual GABA to treat pain flares, or 100 to 200mg of GABA simultaneously with an opioid medication or GABA surrogate for added pain relief. Take-home message: - gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major neurotransmitter that regulates much of our brain function. It was previously thought that ingested GABA could not cross the blood-brain barrier, but new research suggests that it may be able to. - Drugs that mimic the action of GABA are numerous, work in a variety of ways, and can have effects ranging from treating epilepsy to GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a neurotransmitter in the brain. Learn about the benefits of GABA supplements and its medical significance. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. The study uses data from the FDA. It is based on gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin (the active ingredients of Gaba and Gabapentin, respectively), and Gaba and Gabapentin (the brand names). Other drugs that have the same active ingredients (e.g. generic drugs) are not considered. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Both gabapentin and GABA supplements have been shown to be effective in reducing anxiety. However, it is important to note that gabapentin is a prescription medication and should only be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional. GABA supplements are available over-the-counter and can be purchased without a prescription. GABA reuptake inhibitors like Deramciclane have similar effects, as they help to keep GABA in the vicinity of the receptors for longer. When is the best time to take GABA? Consume the GABA on an empty stomach for better absorption. For split doses, take the supplement approximately 60 minutes before eating your next meal or two hours after a meal.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |