Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
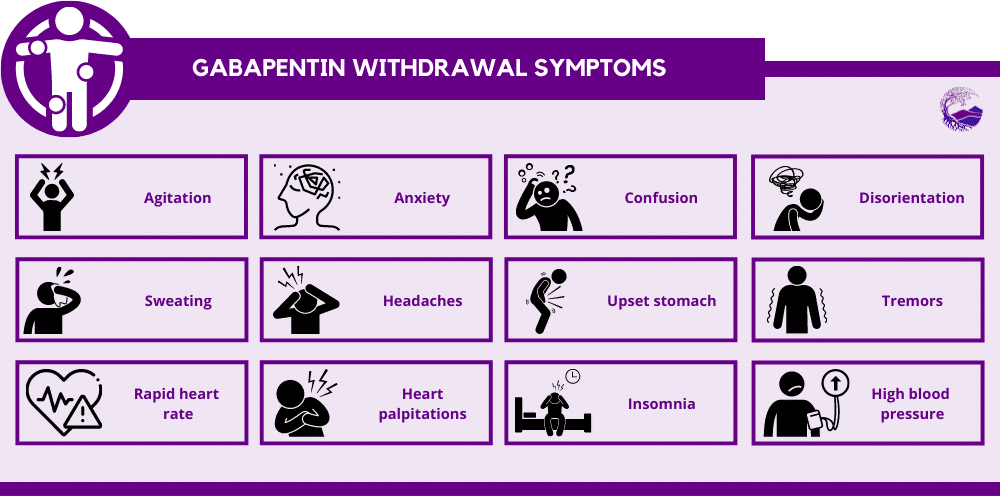 |  |
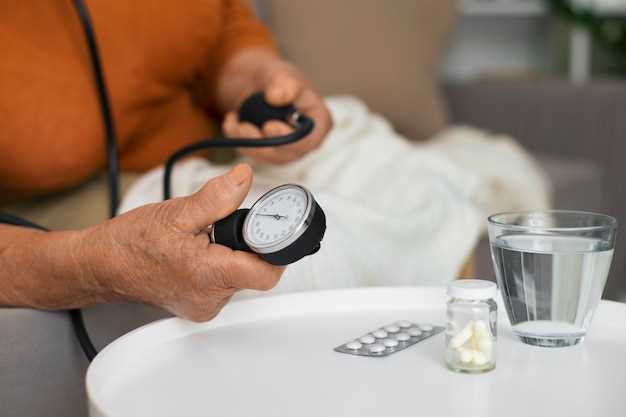
Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Hypertension (high blood pressure). Sweating. Confusion. Incoherent speech. Impaired ability to pay attention. Nausea. Pain. Insomnia. Restlessness. Anxiety. Agitation. Tremors. Seizures. Someone using gabapentin to control seizure activity should not stop using gabapentin suddenly without talking to their physician. High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. What are the brand names of gabapentin? Gabapentin is available as both a brand name product and a generic product (chemically the same, usually lower cost than the brand name product). Brand names of gabapentin include Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Research on rats has shown that gabapentin may lower blood pressure in those with high blood pressure (hypertension). Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension , a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. 2. Can Gabapentin cause high blood pressure? While some studies suggest gabapentin may have therapeutic benefits for individuals with hypertension, it does not typically cause high blood pressure. It is important to monitor blood pressure when taking gabapentin, especially in patients with a history of hypertension, but gabapentin is not a The relationship between gabapentin and blood pressure is complex, as the drug may exert both hypertensive and hypotensive effects depending on the patient’s clinical context and individual response. In some cases, gabapentin has been reported to cause a decrease in blood pressure, particularly in patients with autonomic dysfunction or those When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding These studies have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing significant reductions in blood pressure. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of gabapentin on high blood pressure. Potential Benefits of Gabapentin for High Blood Pressure. Gabapentin may offer several benefits for people with high blood Gabapentin is a drug for nerve pain regulation that can cause high blood pressure when withdrawn abruptly or cause insomnia. Learn about other factors that increase blood pressure risk and how to recognize the signs of hypertension. Abstract. Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |