Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
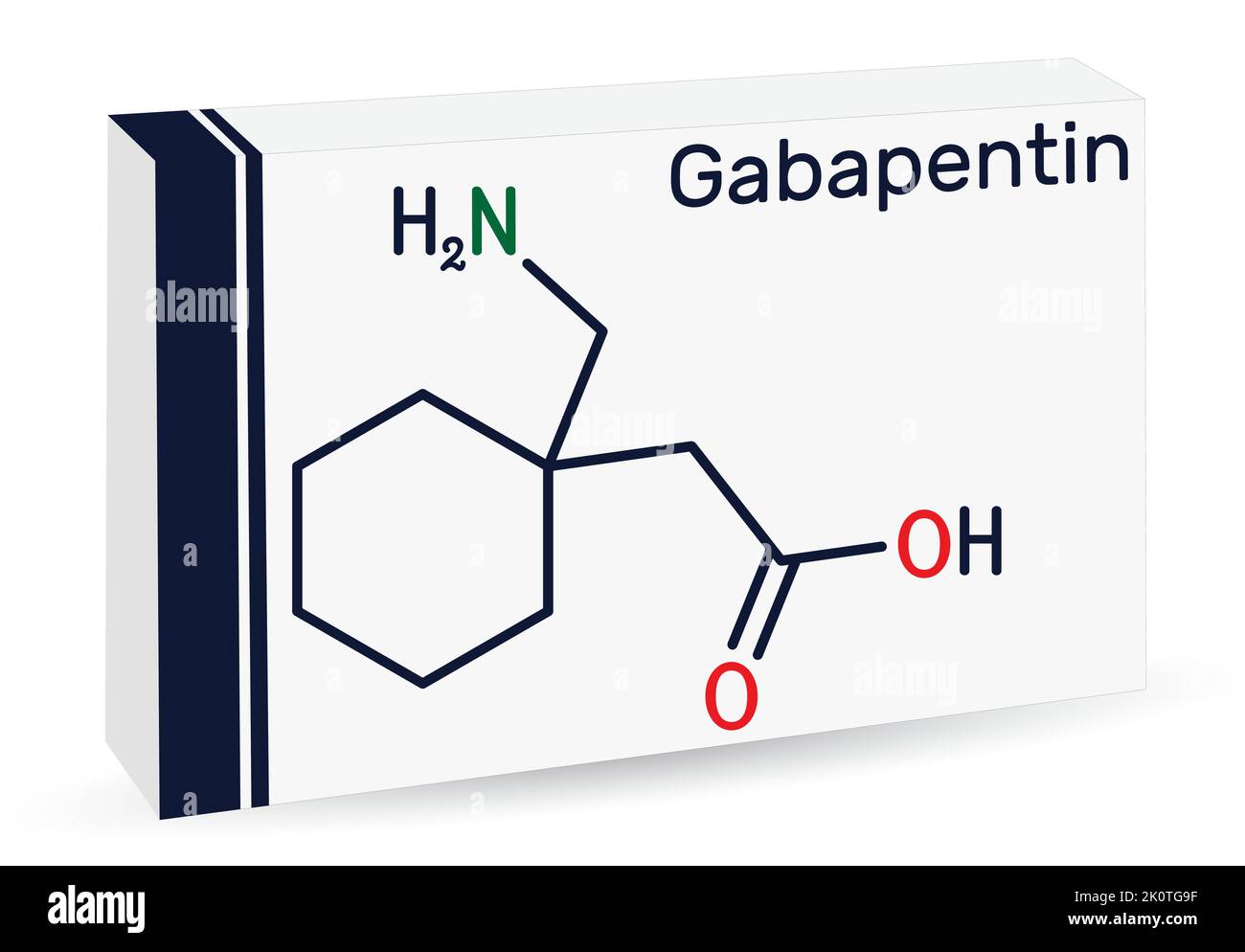
Gabapentinoids such as gabapentin are the molecules with the strongest evidence for chronic pain treatment, while carbamazepine is mainly effective in trigeminal neuralgia. It has been recently demonstrated that gabapentin can induce vasodepression and bradycardia acting through the nitric oxide pathway [ 80 ]. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: In clinical settings, gabapentin effectively attenuates the pressor response to surgical procedures, highlighting its potential utility in managing perioperative hypertension. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term cardiovascular implications of gabapentin use. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Hypertension (high blood pressure) Anxiety; Insomnia; Sweating; Seizures; This rebound hypertension poses a significant risk, particularly for those with pre-existing high blood pressure. If gabapentin needs to be discontinued, it should always be done under medical supervision, with gradual tapering to minimize withdrawal effects. Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. 1. Dizziness is the No. 1 side effect of gabapentin. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Dizziness is similarly common with Horizant. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Medications are a common reason for swollen ankles and feet, also called pedal edema. Amlodipine (Norvasc), gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise), and pregabalin (Lyrica) can cause puffy legs and ankles. Birth control pills, certain over-the-counter pain medications, and steroids are a few other culprits. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided These studies have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing significant reductions in blood pressure. However, more research is needed to fully understand the effects of gabapentin on high blood pressure. Potential Benefits of Gabapentin for High Blood Pressure. Gabapentin may offer several benefits for people with high blood In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of auxiliary α 2 δ subunit of VDCCs, in adult SHR with established neurogenic hypertension. The acute gabapentin administration lowered BP and heart rate more in conscious SHR than Wistar-Kyoto rats. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Results: Unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS produced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic effects in SHR rats. The cardiovascular Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. losartan, which is a medication for high blood pressure; magnesium oxide, which is a We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. In a recent study comparing 600 mg and 1000 mg doses of gabapentin, Bafna et al 10 found that gabapentin 1000 mg given before operation significantly attenuated the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation, whereas gabapentin 600 mg had no effect. Medicines for nerve (or neuropathic) pain such as gabapentin (Neurontin) or pregabalin (Lyrica) are now commonly prescribed for fibromyalgia, restless leg syndrome and neuropathy. They are moderately effective for these conditions. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |