Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
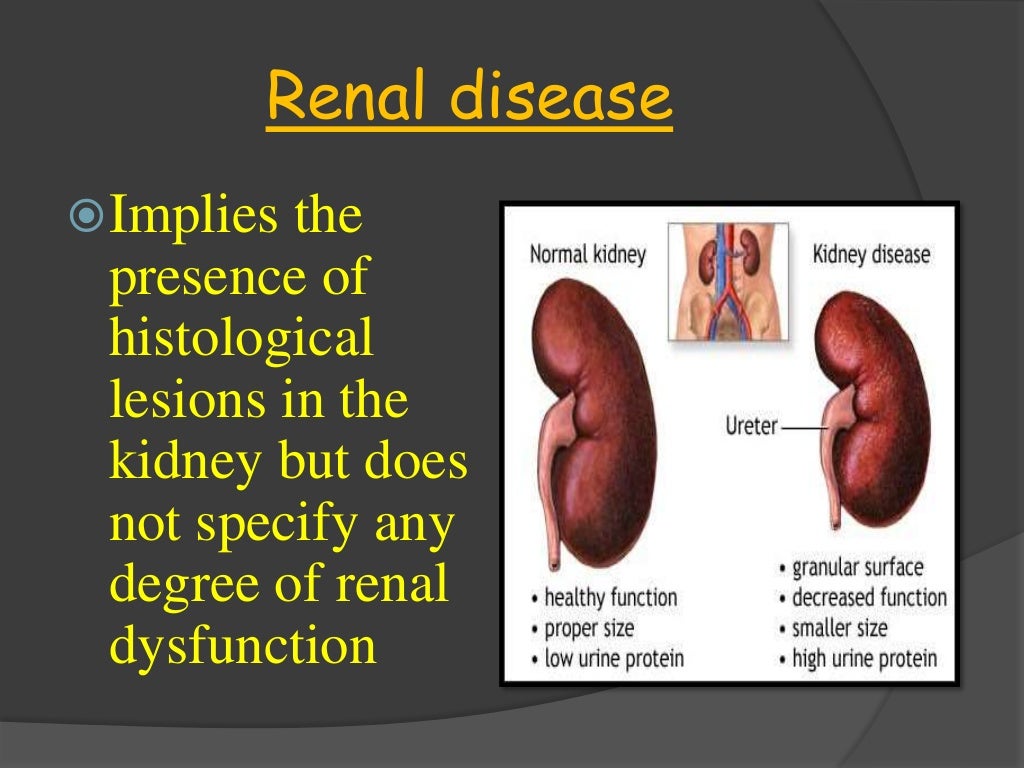 | 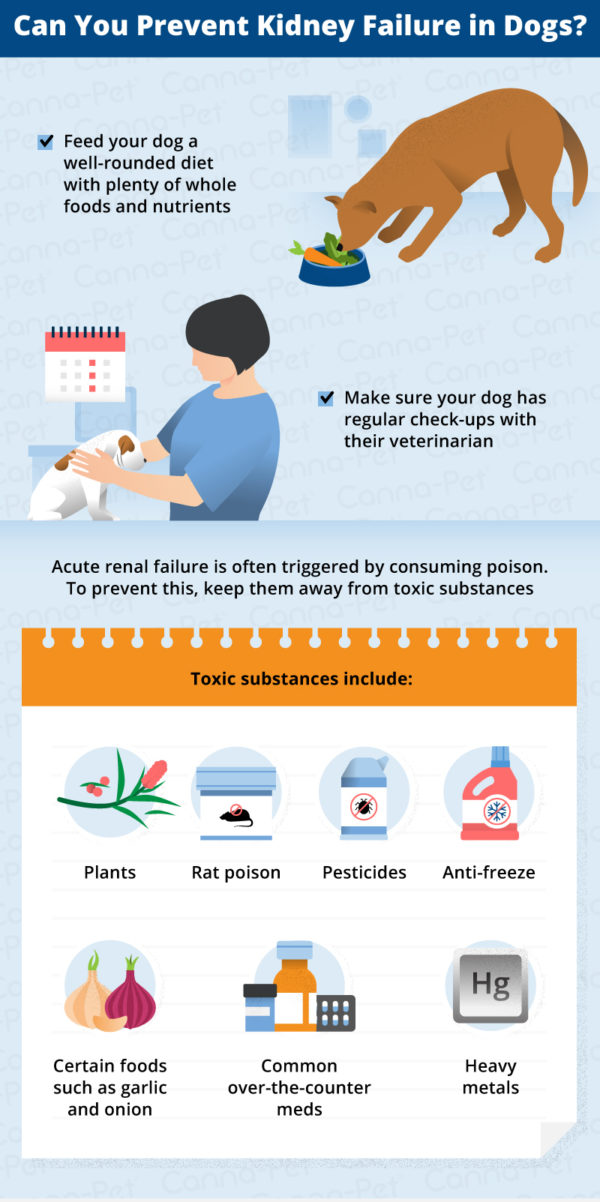 |
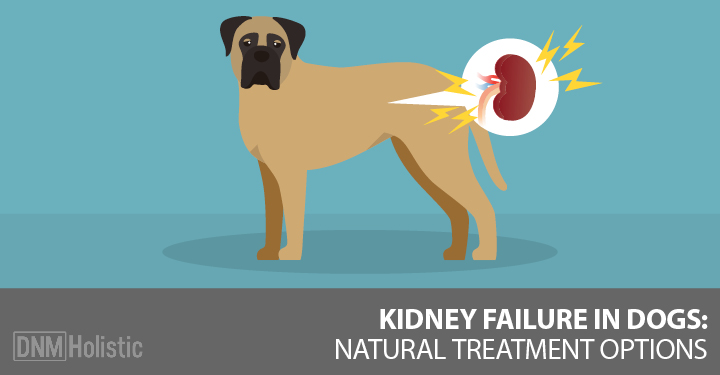
Gabapentin should be USED WITH CAUTION in pets that: have kidney disease; are pregnant and/or lactating ; Do not stop this medication abruptly in pets with epilepsy, as this can cause withdrawal seizures. Some liquid oral formulations contain xylitol, a sugar substitute that is toxic to dogs, so be cautious and read the label before administering. At normal prescribed doses, gabapentin is unlikely to cause kidney damage in dogs. However, it’s essential to administer the drug exactly as prescribed. Overdosing or combining it with other medications that can affect kidney function increases the risk of issues. Abstract Simple Summary. Adjusting drug dosages in dogs and cats with chronic kidney disease (CKD) can be challenging in clinical practice due to the lack of specific indications in the current literature; moreover, the evaluation of renal function through the measurement of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), which is unanimously considered as a requisite for most adjustment strategies, is The kidneys and liver are needed for the metabolism of gabapentin so it should be avoided by dogs with liver disease or kidney disease. Pregnant or nursing dogs, or dogs taking antacids, hydrocodone or morphine should not take it to avoid drug interactions. Although dogs with kidney disease may need a lower dose due to slower excretion, gabapentin does not seem to have adverse effects on the kidneys like NSAIDs do. One of the drawbacks to gabapentin as a pain medication, however, is that it does not have anti-inflammatory effects like NSAIDs do. Causes of Acute Kidney Failure in Dogs This is known as acute kidney failure or acute renal failure, and is most often related to infections or toxins. Dehydration or the bacterial infection leptospirosis (which is contracted by ingesting contaminated water) can cause acute kidney failure in dogs. However, the effects may persist longer in dogs with liver and kidney disease. Therefore, Gabapentin should be used with caution in dogs with: Liver and kidney problems ; Young puppies ; Pregnant and lactating female dogs; On the other hand, Gabapentin should not be used at all in dogs: Allergic to the active ingredient ; Receiving meds with Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. For instance, a smaller dog may exhibit more pronounced symptoms than a larger dog given the same dose, while a dog with liver or kidney disease might experience prolonged effects. It is worth noting that gabapentin is commonly prescribed “off-label” in veterinary medicine. When Is It Contraindicated to Use Gabapentin in Dogs? Because gabapentin is predominantly excreted by the kidneys, dogs with kidney disease should not be treated with gabapentin. Gabapentin should start to take effect fairly quickly, and relief should be noticed within one to two hours of administration. It’s a short-acting drug, and the effects will be gone in 24 hours. That said, the medication may last longer in dogs with kidney or liver impairment. Q: What Medications Should Be Used in Dogs With Elevated Liver Enzymes and Chronic Kidney Disease? Elevated Liver Enzymes It has been shown that, in the absence of liver dysfunction, elevated liver enzymes—serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and/or alanine aminotransferase (ALT)—are not necessarily a contraindication to the administration of Gabapentin is technically safe for use in animals with renal disease but we have to be careful with the dosage since the kidney clear the medication. Often, we need to reduce the dosage as it can have a more severe effect. So dogs with kidney or liver problems may have more prolonged side effects. Your veterinarian may want to monitor kidney and liver blood values when using gabapentin long-term. Recommended Gabapentin for dogs is an anti-seizure and pain medication commonly prescribed to dogs by veterinarians. Gabapentin for dogs may be helpful for treating chronic pain especially nerve pain that is secondary to neurological diseases such as slipped discs. The most common side effects of gabapentin in dogs include sedation and dizziness. Although dogs with kidney disease may need a lower dose due to slower excretion, gabapentin does not seem to have adverse effects on the kidneys like NSAIDs do. One of the drawbacks to gabapentin as a pain medication, however, is that it does not have anti-inflammatory effects like NSAIDs do. Dogs with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, may require a lower dose or should not take gabapentin at all. Additionally, gabapentin should not be abruptly discontinued, as this can cause withdrawal seizures in dogs with epilepsy. Kidney Failure in Dogs. Also referred to as renal failure, kidney failure can be caused by a number of diseases that may affect the kidneys and related organs. Healthy kidneys regulate hydration, maintain a normal electrolyte balance, release hormones needed to produce red blood cells, and remove toxins. Specific COX-2 inhibitor approved for use in dogs. No safer in renal compromise. Gabapentin 3–10 mg/kg PO q 24 hrs. The best effects are seen when used in combination with other analgesics such as NSAIDs or paracetamol (acetaminophen). Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate 13–15 mg/kg chondroitin sulfate PO q 24 hrs. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is often used for nerve pain and is safe for dogs with kidney disease. It is typically used to manage conditions like arthritis, spinal issues, and post-surgical pain. It does not have significant effects on kidney function, making it a reliable option.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |