Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
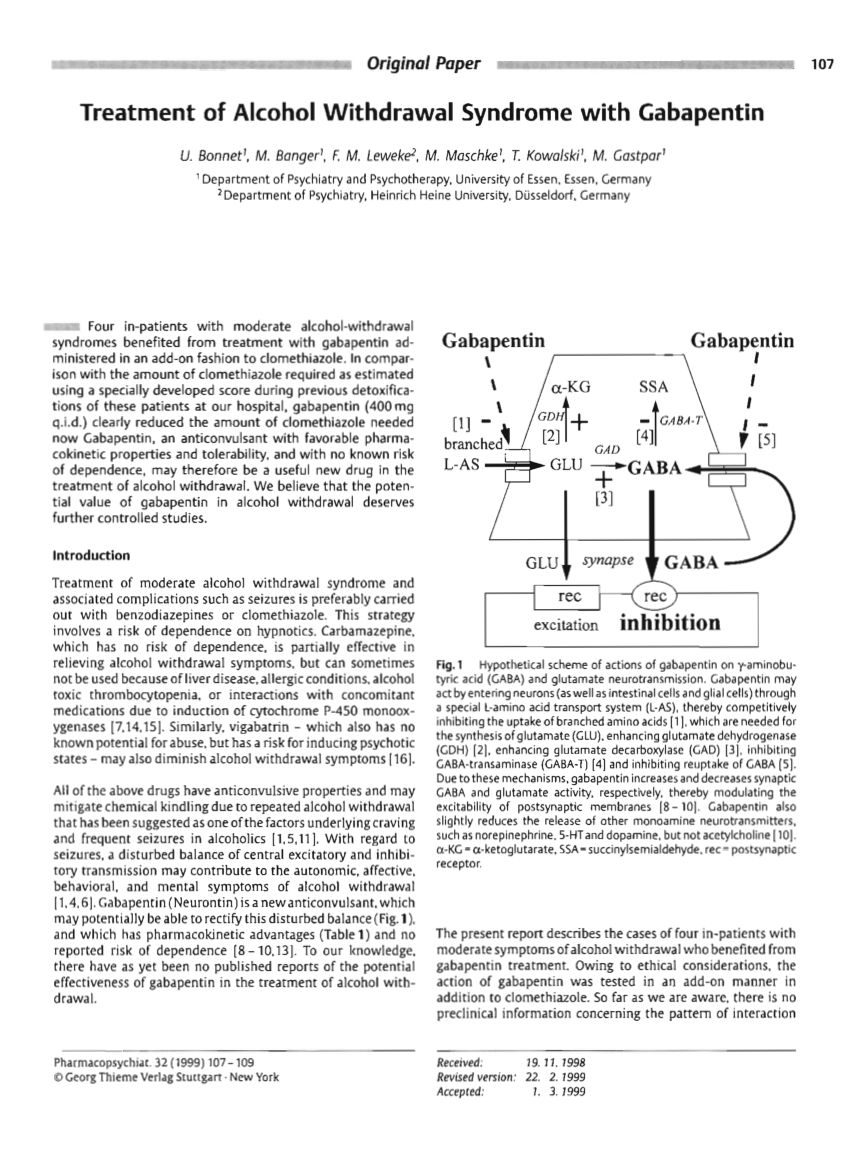 |  |
In ambulatory veterans with symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin treatment resulted in significantly greater reduction in sedation (ESS) and a trend to reduced alcohol craving (PACS) by the end of treatment compared to chlordiazepoxide treatment. Although limited by the small sample size, the Conclusions: Our analysis of pooled data provides evidence that the use of gabapentin to manage alcohol withdrawal symptomatology and related cravings is at least moderately effective. However, given the limited number of available well-designed studies, these findings require further support through more rigorously designed studies. The ambulatory management of mild alcohol withdrawal, the initial diagnosis and treatment of alcohol use disorder, and specific conditions due to alcohol-related organ damage (eg, cirrhosis, pancreatitis) are discussed separately. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The purpose of this article is to evaluate the impact of adding gabapentin to a symptom-triggered alcohol withdrawal protocol to better illuminate gabapentin's role in acute alcohol withdrawal management. Basic Biology of Alcohol Use and Withdrawal. Chronic/Heavy Use - New Homeostasis Abrupt cessation or significant change in drinking (e.g. hospitalization) disrupts homeostasis leading to overall GABA/glutamate imbalance - withdrawal Nejad (2013) Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, UpToDate Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with anxiolytic properties shown to have beneficial effects in a multitude of areas pertaining to optimal treatment of alcohol withdrawal, as well as alcohol dependence. 10, 12, 16, 17 It can be used in hepatic impairment, with fewer drug-drug interactions than previously studied anticonvulsants (carbamazepine Librium can slow or stop your breathing, especially if you have recently used an opioid medication or alcohol. A person caring for you should seek emergency medical attention if you have slow breathing with long pauses, blue colored lips, or if you are hard to wake up. Librium may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have: Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Objectives: Recent literature suggests that gabapentin may be an alternative treatment to standard management of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Gabapentin is one medication shown in small studies to reduce the need for benzodiazepines in the setting of alcohol withdrawal. The continuation of gabapentin after alcohol withdrawal appears to be safe during early sobriety and may aid in reducing alcohol-related cravings or returning to alcohol consumption. Chlordiazepoxide, sold under the brand name Librium among others, is a sedative and hypnotic medication of the benzodiazepine class. It is used to treat anxiety, insomnia and symptoms of withdrawal from alcohol, benzodiazepines, and other drugs. Chlordiazepoxide has a medium to long half-life, while its active metabolite has a very Gabapentin is a potentially efficacious treatment for reducing the risk of relapse to harmful drinking patterns in outpatient management of alcoholism. Gabapentin's ease of use, rapid titration, good tolerability, and efficacy in both the withdrawal and chronic phases of treatment make it particularly appealing. Librium (chlordiazepoxide) is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety disorders or alcohol withdrawal. Librium is available in generic form. What Are Side Effects of Librium? Librium may cause serious side effects including: severe drowsiness, unusual changes in mood or behavior, confusion, aggression, anger, sudden restless feeling or excitement, Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |