Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
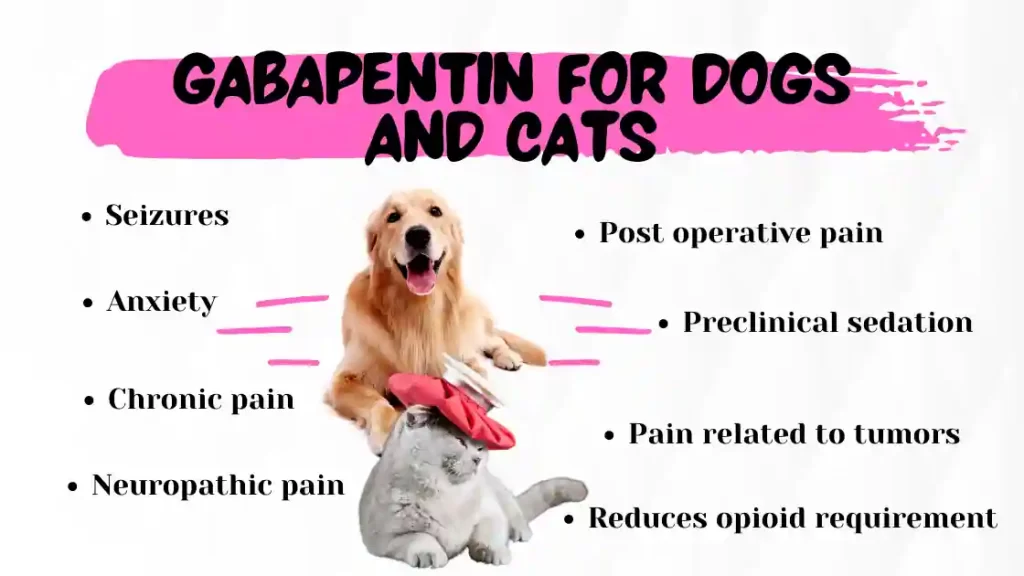
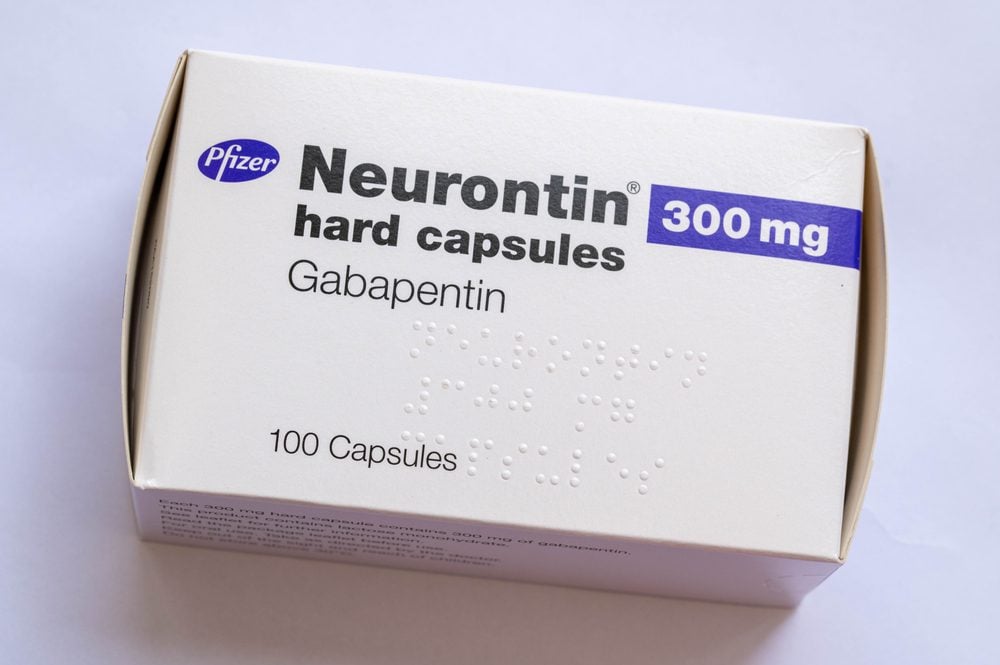
Gabapentin should only be given in tablet or capsule form because the human liquid version of gabapentin contains xylitol, which is highly toxic to dogs and can cause liver toxicity and death! Before giving your dog gabapentin, you should mention to your veterinarian any other medications that your dog is currently taking. 12. **Concern:** Can gabapentin be used in senior dogs? **Answer:** Gabapentin can be used safely in senior dogs, but it is important to monitor them closely for any signs of side effects, as older dogs may be more susceptible to certain side effects. 13. **Concern:** Can gabapentin be used in dogs with liver or kidney disease? With the reported exception of dogs, gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and it is normally excreted in its unchanged form in urine [25,100]. This kinetic behaviour could result in specific criticisms for certain categories of subjects (e.g., geriatrics, subjects with chronic hepatic and renal disease). What Is Gabapentin for Dogs? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug that is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. How gabapentin works is not completely understood; however, it is thought to block stimulation of the nerve cells. In dogs with kidney or liver diseases, gabapentin should be used with caution because it will take longer for them to metabolize the drug. Image Credit By: luchschenF, Shutterstock Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Most dogs are prescribed gabapentin to manage chronic pain associated with arthritis and cancer as well as neural and post-operative pain. It’s often prescribed alongside NSAIDs or opiates. It’s thought to amplify their effect on pain management despite potential side effects. The short answer is: While rare, gabapentin can potentially contribute to liver injury in dogs, though it’s not a common side effect. The relationship is complex and often involves multiple factors rather than being a direct cause-and-effect scenario. Is Gabapentin okay for dogs with liver disease? My dog took gabapentin for arthritis for a few days and it really helps. She barely moves without it. My dog has elevated liver enzymes (mild) but the vet isn’t sure if it’s mild or serious. She is taking supplements for this. 🩺 Does Gabapentin Affect the Liver or Kidneys in Dogs? Gabapentin is primarily processed by the kidneys , which means that in cases of long-term use, especially at high doses, there’s a slight risk of kidney strain or impairment. The question of whether gabapentin is harmful to a dog’s liver is a valid concern for pet owners, especially when considering long-term medication. In short, while gabapentin is not known to directly cause liver damage in most cases, the situation isn’t entirely black and white. Another serious side effect of gabapentin in dogs is liver damage. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause liver toxicity, which can lead to liver failure and death. This risk is higher in dogs with pre-existing liver disease or those taking other medications that can affect liver function. Lastly, because gabapentin also undergoes some liver metabolism, it should be used with caution in dogs with liver disease. Which Is the More Effective Analgesic in Dogs—Gabapentin or Tramadol? Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. Although gabapentin is only metabolized through the kidneys in humans, research shows that in dogs it’s metabolized through both the kidneys and liver. So dogs with kidney or liver Several case reports note analgesia when gabapentin was used for treatment of chronic pain. 14,15 And in a clinical study on postoperative pain in dogs undergoing mastectomy, although pain scores did not differ, dogs receiving NSAIDs plus gabapentin required fewer opioid rescue doses than dogs receiving NSAIDs alone; thus, the gabapentin did 1. Can Gabapentin cause liver damage in dogs? Quote from Veterinarian: “While Gabapentin is generally considered safe for dogs, there is a potential risk of liver damage with long-term use. It is important to monitor liver function tests periodically when a dog is taking Gabapentin to ensure that any potential issues are detected early.” 2. 9. Can gabapentin cause liver or kidney damage in dogs? Gabapentin does not typically cause direct liver or kidney damage. However, it’s metabolized by the kidneys, so dogs with kidney disease may require lower doses to avoid side effects. 10. What happens if you stop gabapentin suddenly in dogs? Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. 9. Can gabapentin cause liver or kidney damage in dogs? Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys in dogs, so it is important to monitor kidney function in dogs receiving long-term gabapentin therapy. Liver damage is rare but can occur in some cases. 10. Are there any alternative treatments to gabapentin for dogs? However, the effects may persist longer in dogs with liver and kidney disease. Therefore, Gabapentin should be used with caution in dogs with: Liver and kidney problems
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |