Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
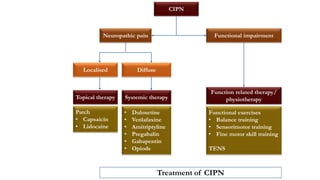 |  |
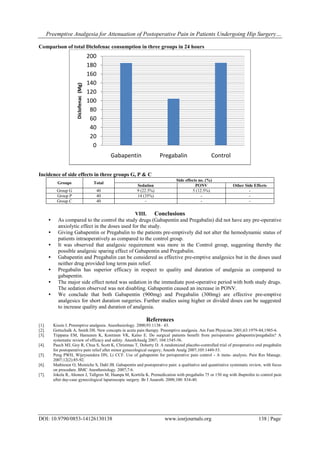
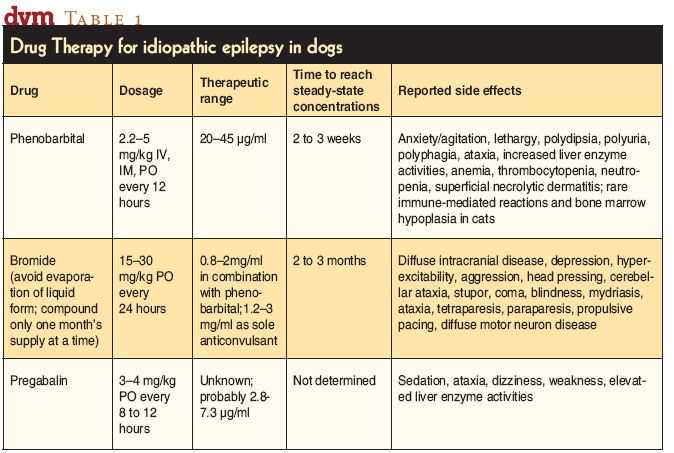
Gabapentinoids, such as gabapentin and pregabalin, are first- and second-generation α2δ inhibitor ligands, respectively, and both are approved for use as adjunctive therapy in pain control. Gabapentin (Neurontin 1 ) and pregabalin (Lyrica 2 ) are first- and second-generation α2δ ligands, respectively, and are both approved for use as adjunctive therapy in pain control. Although they do not bind to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors they have been successfull In a partial spinal nerve injury model, combination therapy with subeffective doses of gabapentin and pregabalin potentiated the therapeutic efficacy of spinal cord stimulation, a tool used for neuropathic pain relief, as evaluated via the von Frey test . Extracellular recordings confirmed that this low-dose combination enhanced the suppression Pregabalin/gabapentin vs. placebo: nonopioid pharmacologic therapies are preferred and should be combined with nonpharmacologic therapy to reduce chronic pain and improve function. 4 This report not only focuses on the issue of therapeutic duplication, CNS depressant adverse effects, and consequences of potential combined gabapentin and pregabalin therapy but also highlights the importance of responsible prescribing particularly with centrally acting/psychoactive medications. The patient improved following initiation of 100 mg of gabapentin and gradual reduction of pregabalin to 150 mg per day. The pain subsided completely with additional downward adjustments of pregabalin. After low levels of pain returned, gabapentin was boosted to 100 mg twice a day, with pregabalin at 25 mg. We describe here a case of a female patient with a history of diabetes, diabetic neuropathy, and hypertension being prescribed both gabapentin and pregabalin concomitantly which led to adverse effects like drowsiness, dizziness, fatigue, and ataxia. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Pregabalin (Lyrica) are first and second-generation α2δ [1,2] ligands, respectively, and are both approved for use as adjunctive therapy in pain control. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Because some compounds may have potential supra-additive (synergistic) effects (e.g., gabapentin and opioid analgesic), both the dose-sparing effect and potential enhancement of therapeutic efficacy associated with a drug combination may be substantial 33, 40. Toth C. Substitution of gabapentin therapy with pregabalin therapy in neuropathic pain due to peripheral neuropathy. Pain Med. (2010) 11(3):456–65. 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00796.x [Google Scholar] 38. Rickels K, Shiovitz TM, Ramey TS, Weaver JJ, Knapp LE, Miceli JJ. A study by Tesfaye et al, found no significant effect of the moderate-dose combination (300 mg pregabalin plus 60 mg duloxetine) therapy on peripheral NeP compared with high-dose monotherapy (600 mg pregabalin or 120 mg duloxetine). 12 However, this combination therapy was considered to be potentially effective, safe, and well tolerated and if Oxcarbazepine, gabapentin, zonisamide, and eslicarbazepine acetate have been reported to be effective as add-on therapy for refractory partial seizure. However, the short duration of studies makes it difficult to extrapolate to long-term treatment [ 62-65 ]. Since both agents have the same mechanism of action and pharmacodynamic targets, reviews do not routinely recommend dual gabapentinoid therapy. A proposed mechanism of action of pregabalin and gabapentin is antagonism of NMDA receptors. Both drugs can also antagonize calcium channels in the central nervous system. dverse effects. [5] Gabapentin and pregabalin may have a synergistic effect in the treatment of neuropathic pain that could lead to lower doses needed with less a. dverse effects. [6] However, there is no literat. Two such medications are gabapentin and pregabalin, which were originally developed to treat epilepsy and nerve pain. Though not officially approved for the treatment of anxiety disorders, both gabapentin and pregabalin have been increasingly studied and prescribed off-label due to their potential anxiolytic effects. What are Gabapentinoids? 12 South Recovery offers therapy, medication-assisted treatment, and holistic support for individuals struggling with gabapentin or Lyrica misuse. Contact us today for help. At 12 South Recovery, we aim to help restore balance to every area of life – treating the mind, body and spirit so our clients are able to find lasting recovery from Recommended first-line treatments are the gabapentinoids (gabapentin, pregabalin), and antidepressants (duloxetine, amitriptyline). It is important to recognise when treatment is not successful and switch medication early, rather than up-titrating. It should be borne in mind that patients may benefit from combination therapy. When failed to relief the PHN with pregabalin or gabapentin, doctor will turn to gabapentin and pregabalin combination therapy. The current study concluded that gabapentin and pregabalin have the same mechanism of action, so the guidelines do not recommend their combined use. Gabapentin and Lyrica (pregabalin) generally aren't used together due to their numerous similarities. Taking both gabapentin and Lyrica together would generally be considered a 'therapeutic duplication', but there is some evidence of the potential positive benefits of this.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |