Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
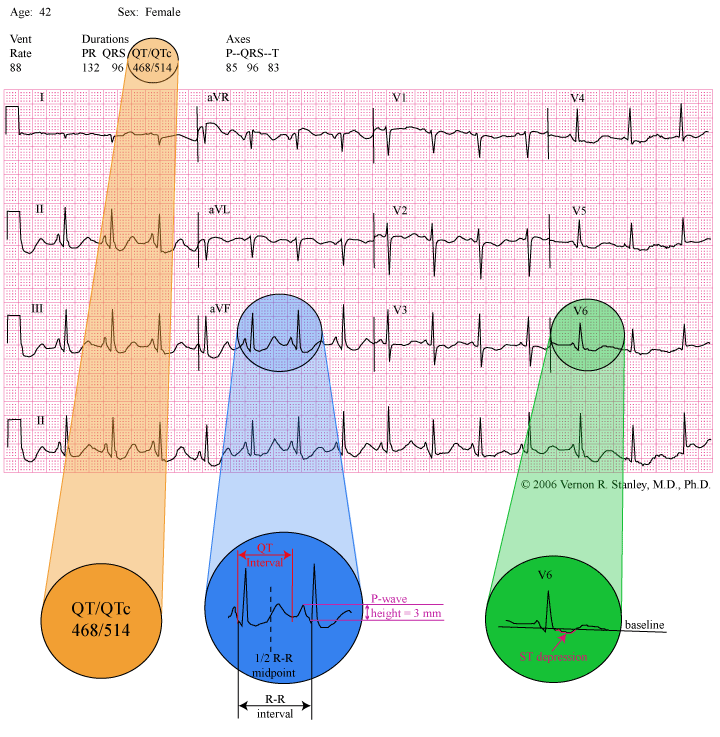
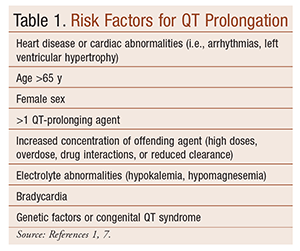
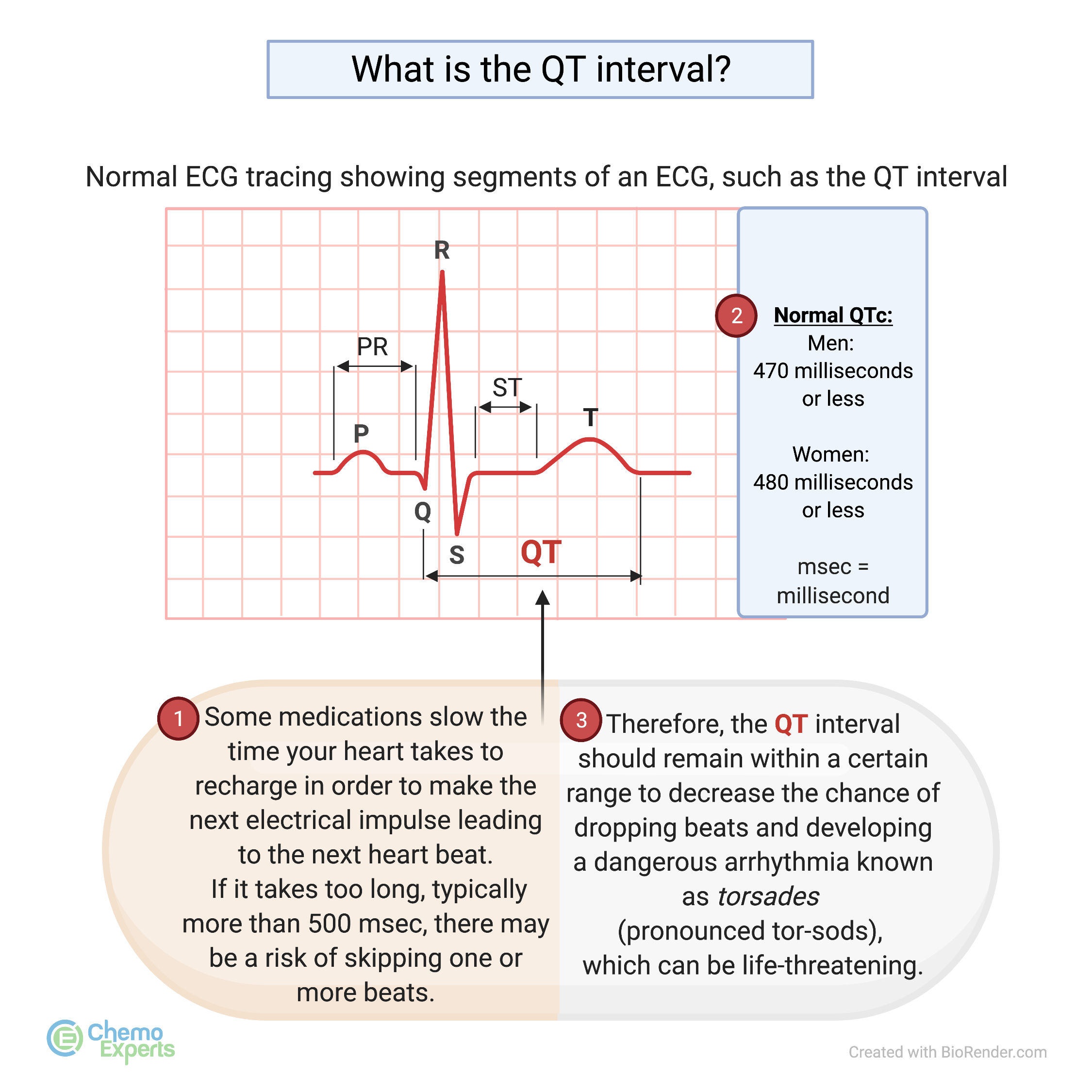
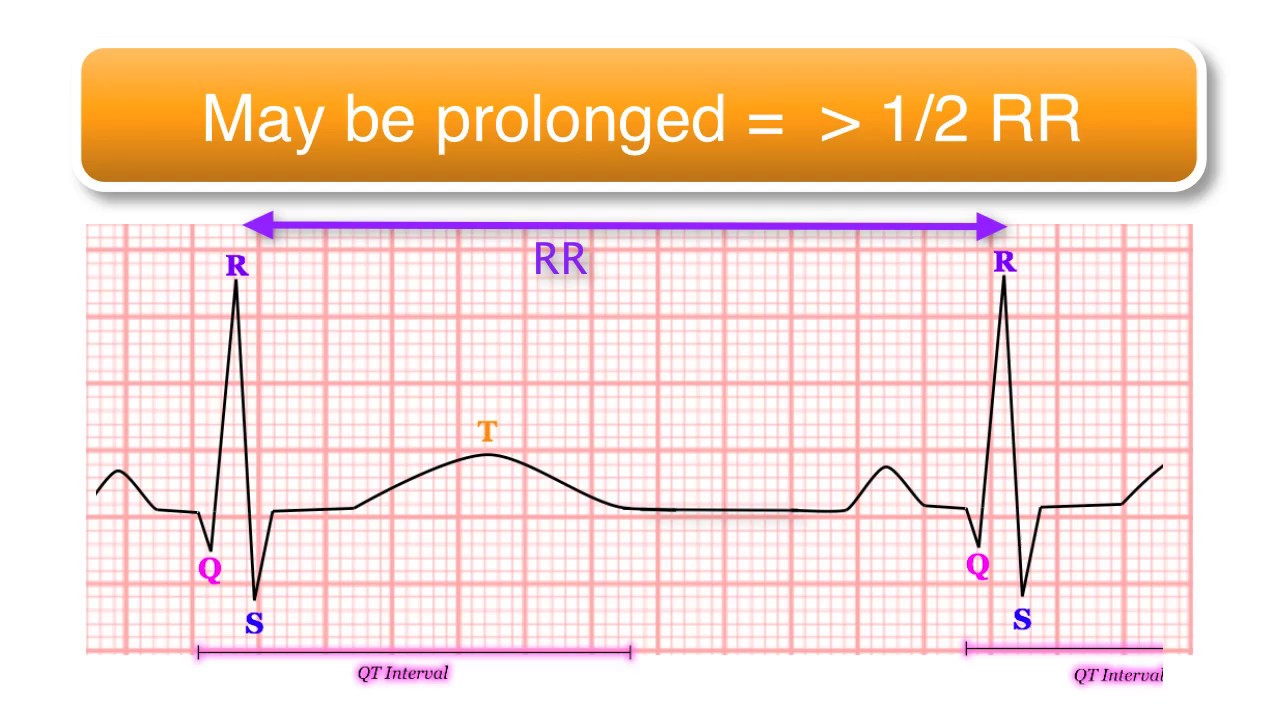
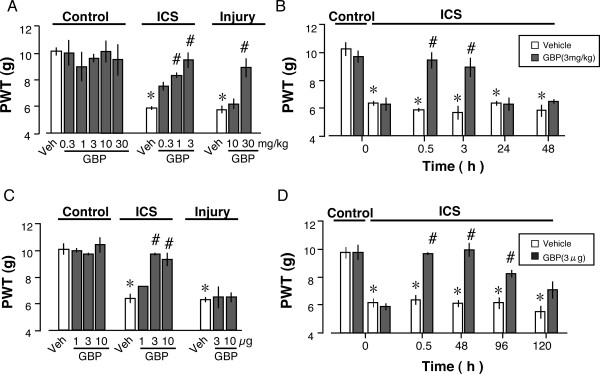
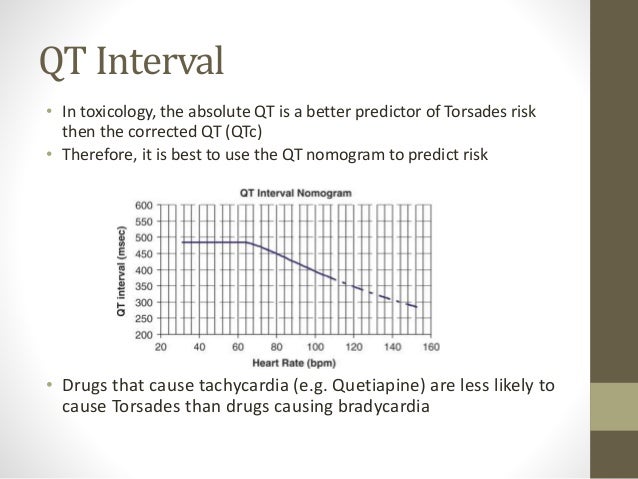
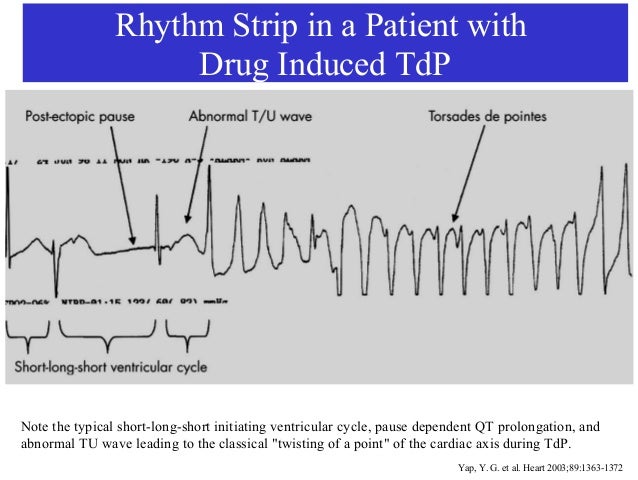
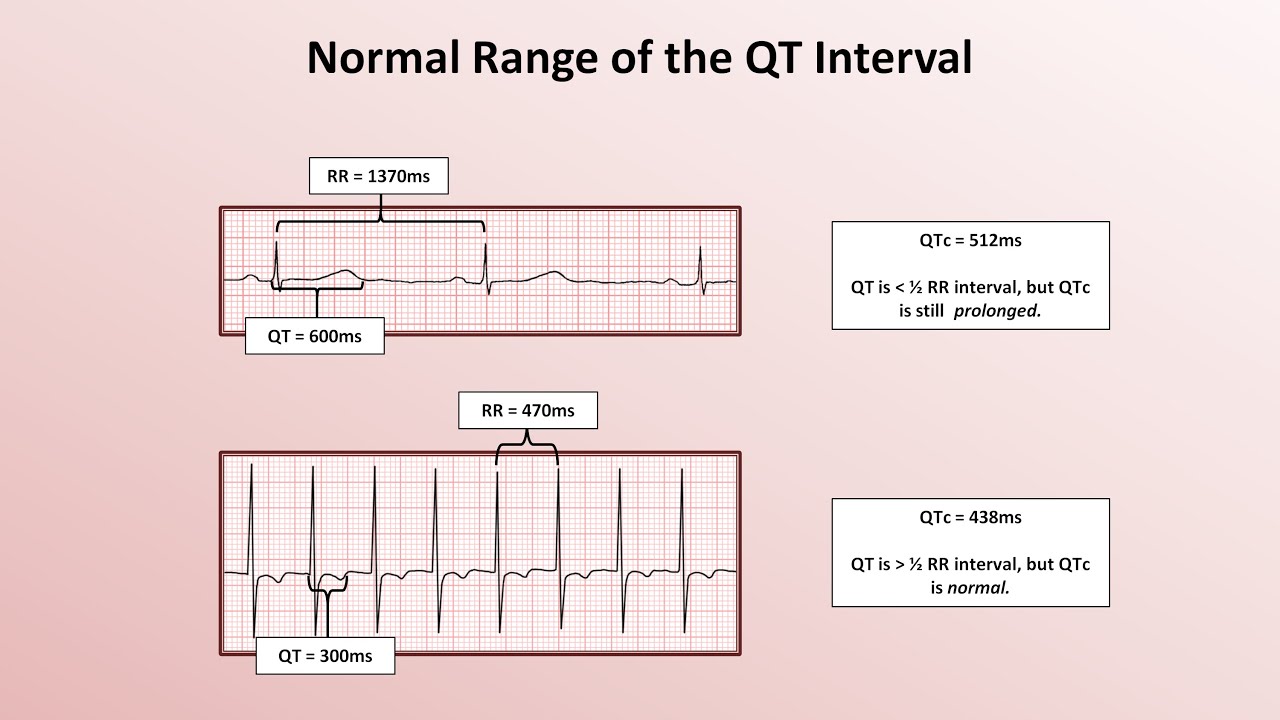
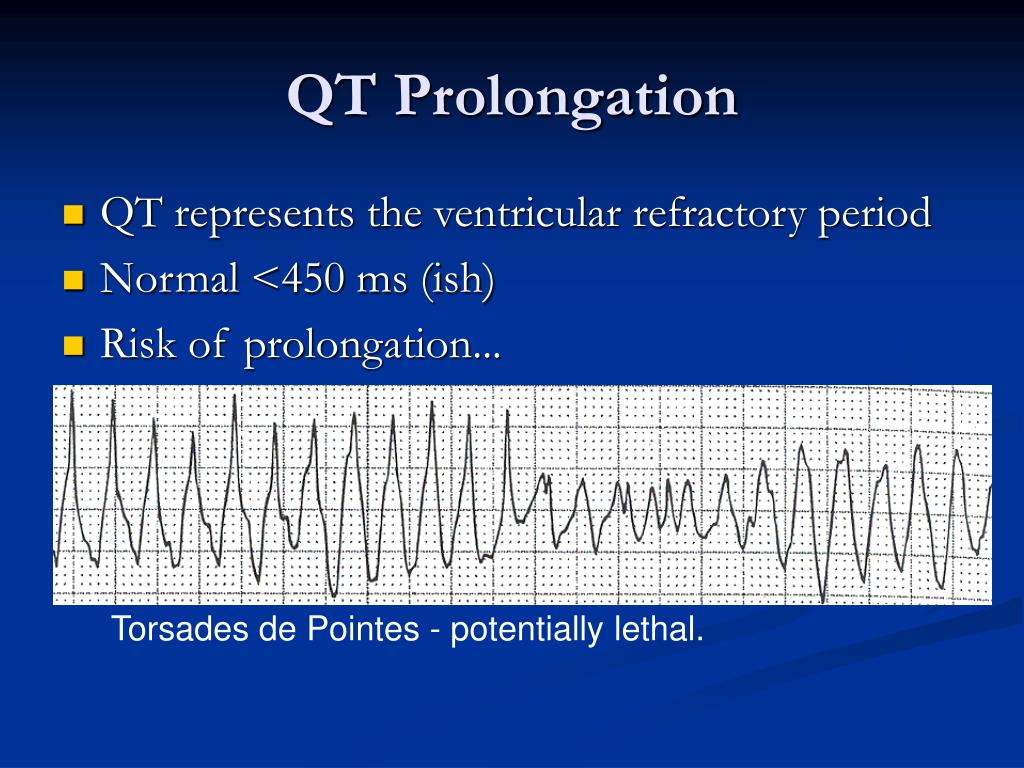
induced QT prolongation and drug . interactions Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. There are a number of widely used drugs which are known to cause QT prolongation. Recently there have been warnings relating to drug-induced The acquired form is most often attributable to administration of specific medications and/or electrolyte imbalance. This review provides insights into the risk for QT prolongation associated with drugs frequently used in the treatment of chronic pain. Electrocardiogram qt corrected interval prolonged is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 40-49 old, also take Mirtazapine, and have High blood pressure. Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. With regards to drugs, the risk of QT prolongation and TdP varies markedly across the list but tends to be rather similar within a drug class. While the risk of TdP is well-defined for many of these agents, many are classified as QT-prolonging solely based on their drug class or presumed pharmacodynamic effects. QTc = QT (RR−Intervall)2 Prolongation of the QT interval above 470 ms for men and 480 ms for women should be regarded as abnormal [4]. Several risk factors for QT prolongation have been identified, including female sex, advanced age, drug-drug interactions, genetic predisposition, hypokalemia, hypo-magnesemia, heart failure, and bradycardia The length of the QT interval represents the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Prolongation of ventricular repolarization can result in fatal ventricular arrhythmias [3]. Faster heart rates can shorten the QT interval [4], so it is often adjusted for rate and reported as the heart rate corrected (QTc) interval. ng the QTc interval should be offered an ECG regardless of other risk factors. Cardiology follow up should be sought w. pharmacological modifiable risk factors and repeat ECG in 1-2 weeks or sooner. If syncope/presyncope are also present, thi. A pilot study assessed the pharmacologic effects of gabapentin enacarbil on cardiac repolarization, as measured using the QT/corrected QT (QTc) interval, in conjunction with pharmacokinetic and tolerability evaluations. 19 In that double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, escalating-dose, crossover study, 32 healthy volunteers (8 subjects duloxetine, gabapentin, cymbalta, neurontin Good luck. I know how difficult and scary it is. Four years ago my doctor prescribed an anxiety medication (I don't remember the name anymore) that caused me to have a v-fib storm. Mary Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. The risk of torsades de pointes depends on patient factors and current medication. The QT interval duration is physiologically variable : the QTc is calculated using the Bazett’s formula [(QTc = QT/√RR), Table 2][70,71]. Genetic testing can help to recognize specific subtypes of c-LQTS. Pregabalin use has been associated with QTc prolongation in patients taking other QTc–prolonging agents, although the relative contributions of pregabalin to QTc prolongation may be minimal. Pregabalin and gabapentin have been associated with a dose-related increased risk of atrial fibrillation. Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Prolongation of the QT interval above 470 ms for men and 480 ms for women should be regarded as abnormal . Several risk factors for QT prolongation have been identified, including female sex, advanced age, drug-drug interactions, genetic predisposition, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart failure, and bradycardia [5, 6]. Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines The risk of QT interval prolongation was evaluated in a thorough QTc trial in 247 healthy individuals following treatment with LCM at 400 or 800 mg/day. Exposure to LCM did not appear to cause QT prolongation, nor does it seem to have important effects on QRS duration {UCB, Inc., data on file}. The drug interactions listed in Table 3 are likely to increase a patient's risk for QTc prolongation, further leading to TdP. For example, prior to terfenadine's withdrawal from the market, the QTc prolongation associated with this drug was estimated to be about 8 to 18 milliseconds. A QT-concentration relationship was reported with moxifloxacin. Gabapentin exposures were dose-proportional with gabapentin enacarbil doses of 1200 and 6000 mg. The most commonly reported adverse events with gabapentin enacarbil 6000 mg were dizziness and somnolence (60.0% and 54.0%, respectively). Long qt syndrome is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Long qt syndrome when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |