Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
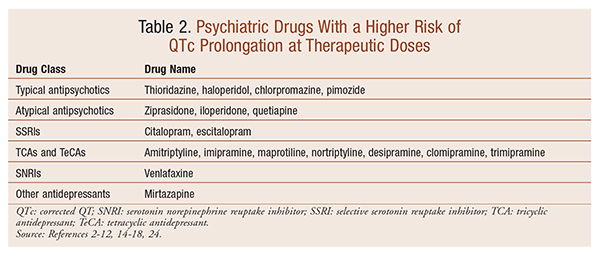
The QTc is considered prolonged if the values are greater than 450 milliseconds in males and greater than 470 milliseconds in females. 3 The risk of cardiac events correlates with the extent of QT prolongation. However, no QTc value has been established for cardiac arrhythmia. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided QT interval for heart rate is controversial and inexact. The reliability of the standard QTc decreases at higher heart rates. The major limitation of Bazett’s formula is that it overestimates QTc interval at any heart rate much higher than 60 beats per minute (bpm) and underestimates QTc interval at rates lower than 60 bpm. Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. 5. What was the patient’s heart rate and QTc (rate corrected QT-interval from 6. What is the patient’s latest heart rate and QTc measurement? 7. Biochemistry results (within last two weeks): sodium, potassium, urea, creatinine, eGFR [+ magnesium level if potassium (< 3.5mm/L]; FBC results 8. While the risk of TdP is well-defined for many of these agents, many are classified as QT-prolonging solely based on their drug class or presumed pharmacodynamic effects. We provide a direct PubMed search for each drug and we recommend the reader to use this link to assess the literature. Classified as QT prolonging drug in DrugBank. Summary: Electrocardiogram qt corrected interval prolonged is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 40-49 old, also take Mirtazapine, and have High blood pressure. Pregabalin use has been associated with QTc prolongation in patients taking other QTc–prolonging agents, although the relative contributions of pregabalin to QTc prolongation may be minimal. Pregabalin and gabapentin have been associated with a dose-related increased risk of atrial fibrillation. Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines Considering that not all agents that prolong the QT interval increase TDR, drugs can be distinguished into the following groups depending on their simultaneous effects on the QT corrected using the Bazzet’s formula (QTc) interval and on TDR: (1) drugs inducing both QTc prolongation and increased TDR, characterized by a high torsadogenic The effects of gabapentin enacarbil (GBPe), a prodrug of gabapentin (GBP), on cardiac repolarization were investigated in a single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, escalating-dose, crossover trial in 32 healthy volunteers who received single doses of either GBPe 2400 mg, 3600 mg, 4800 mg, 6000 mg, or placebo [34]. Gabapentin enacarbil, a prodrug of gabapentin, had no effect on cardiac repolarization in healthy volunteers [29,30]. In rabbits, therapeutic doses of pregabalin significantly prolonged the QT interval [ 31 ]. A QT-concentration relationship was reported with moxifloxacin. Gabapentin exposures were dose-proportional with gabapentin enacarbil doses of 1200 and 6000 mg. The most commonly reported adverse events with gabapentin enacarbil 6000 mg were dizziness and somnolence (60.0% and 54.0%, respectively). Normal QTc interval: <450 ms in males and <460 ms in females. What is considered to be a prolonged QT interval? The QTc interval is a surrogate marker of proarrhythmic risk and literature differs with regard to the QTc interval that would raise concern over development of arrhythmias. As a guide: Borderline QTc interval: The QTc interval is a surrogate marker of proarrhythmic risk and literature differs with regard to the QTc interval that would raise concern over development of arrhythmias. As a guide: Borderline QTc interval >440 ms but <500 ms . Although literature differs, a QTc interval within these values is considered borderline prolonged. Consideration Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Long qt syndrome is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Long qt syndrome when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co This may increase the risk of Torsades de Pointes (TdP), a potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. As the QT interval varies with a change in heart rate, various formulae can adjust for this, producing a 'corrected QT' (QTc) value. Normal QTc intervals are typically <450 ms for men and <460 ms for women. Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Anxiolytic drugs and sedatives Gabapentin ⁎ is FDA approved for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures. 8 Plasma exposure to gabapentin after oral dosing is variable and unpredictable due to saturation of its absorption pathway, a low-capacity transporter found only in a narrow region of the upper intestine.9, 10 The bioavailability of gabapentin decreases with increasing dose.11, 12 It is therefore
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |