Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
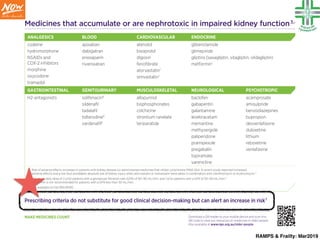 | 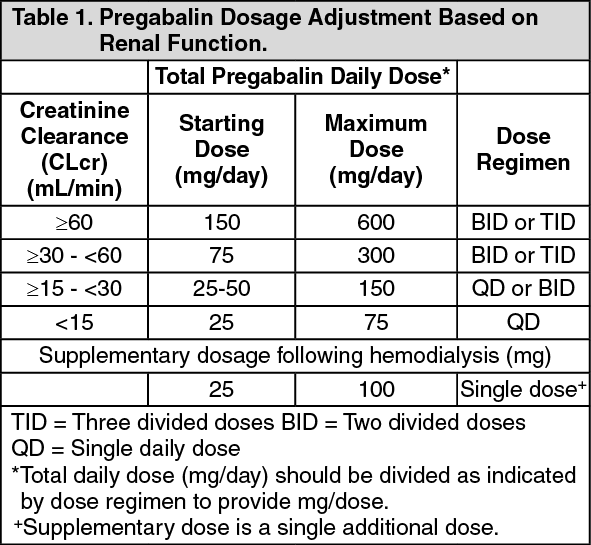 |
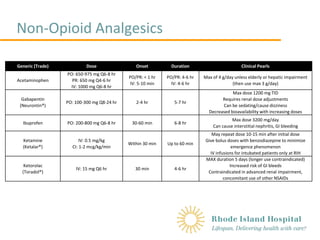
Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). However, patients with renal impairment were often excluded from these studies. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease normal renal function on maximum recommended dosing yielded concentrations of 5–8 mg/L for gabapentin and ~ 2.8–8.2 mg/L for pregabalin. 22–25 The elimination half-lives of gabapentin and pregabalin are prolonged with renal impairment leading up to accumulation with In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Renal impairment: Gabapentin dose reduction may be required, depending on renal function. Next: Interactions. Interaction Checker. Enter a drug name to check for any INTRODUCTION. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [].The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms []. The Renal Dosage is an educational tool designed by an experienced physician, Dr. Safwan Sayyal in consultation with nephrologists to ascertain the appropriate medication dosage based on a patient's kidney function. This will help to eliminate dosing errors in individuals with renal impairment. The risk of respiratory depression should be assessed when initiating gabapentin in patients with respiratory comorbidities, neurological disease, renal impairment and in combination with other respiratory depressants such as opioids. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Drug dosing errors are common in patients with renal impairment and can cause adverse effects and poor outcomes. Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment . Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): Reference ID: 4584064 . This label may not be the latest approved by FDA. Gabapentin has also been linked to causing behavioral changes such as confusion and CNS depression including somnolence and dizziness, which is more prominent in patients with renal impairment. (Lexicomp 2016). Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): Subjects (N=60) with renal impairment (mean creatinine clearance ranging from 13 to 114 mL/min) were administered single 400 mg oral doses of gabapentin. The mean gabapentin half-life ranged from about 6.5 hours (patients with creatinine clearance >60 mL/min) to 52 hours (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) and gabapentin renal clearance from Adjust the dose for people with renal impairment (see Table 2). Consult the manufacturer's Summary of Product Characteristics if the person is undergoing haemodialysis. Table 2. Recommended dosage adjustment for gabapentin in people with renal impairment. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |