Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 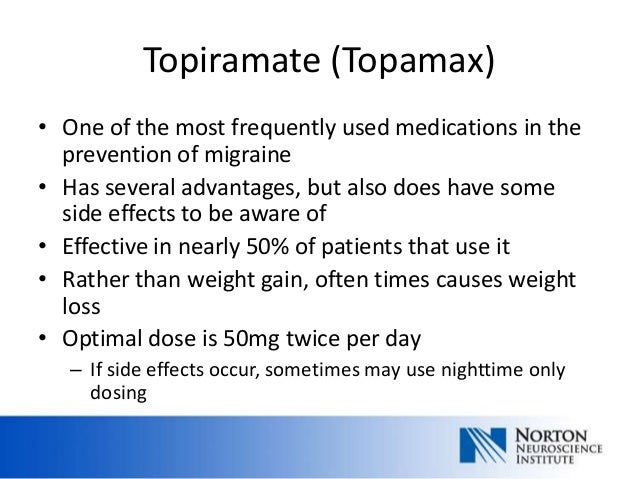 |
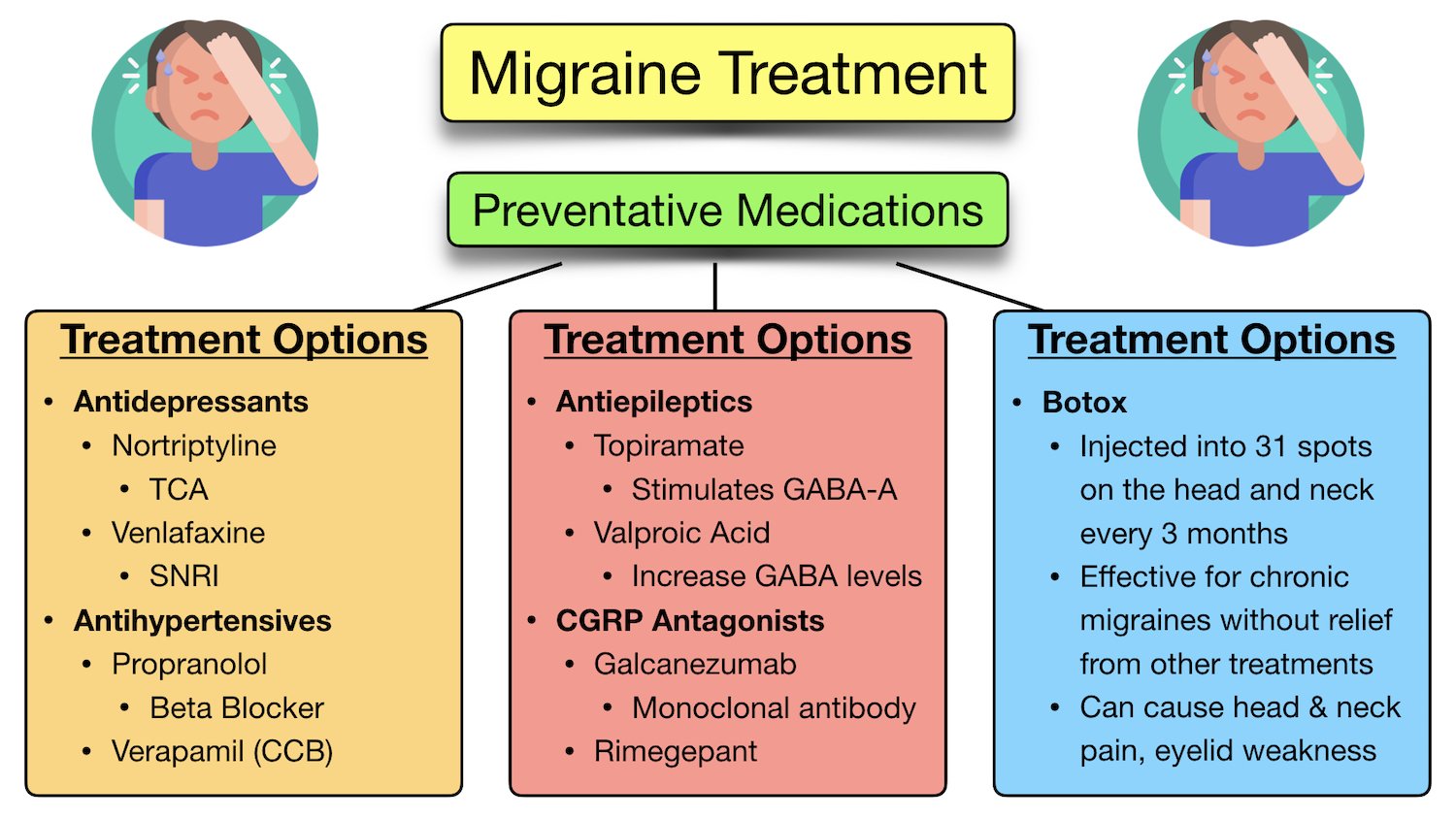
For the three trials of topiramate, NNHs for eight adverse events (100-mg dose) ranged from 2.4 to 32.9. Reviewers’ Conclusions. Anticonvulsants appear to be effective in reducing migraine Reduction in mean monthly migraine frequency (10.67 +/- 4.25 to 1.82 +/- 2.02) in the topiramate group was significantly greater compared with (11.97 +/- 4.452 to 2.73 +/- 2.59) that in the Topiramate (Topamax) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both antiepileptic medications, but they have different uses and dosing schedules. Topiramate is used to treat various types of seizures and to prevent migraines, while gabapentin is used for nerve pain from shingles and as an add-on treatment for partial seizures. Topiramate may be prescribed either alone or in combination with other medications for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy, or it may be given for the prevention of migraines. Drowsiness is a When it comes to managing epilepsy, nerve pain, and migraines, two popular medications often come to mind: Topiramate and Gabapentin. In this article, we'll delve into the comparison of Topiramate vs Gabapentin, exploring their similarities and differences to help you make an informed decision. Gabapentin Gabapentin’s mode of action in migraine is unclear (66). It interacts with the α 2δ-subunit of the calcium channel and increases the concentration and probably the syn-thesis of brain γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin binds to gabapentin-binding protein—a novel, membrane-associated protein in the outer layers of the Antiepileptic drugs, such as valproic acid (brand name: Depakote), gabapentin (brand name: Neurontin), and topiramate (brand name: Topamax) Beta blockers, such as propranolol (brand name: Inderal) The reasons for this are: (a) the definition of chronic migraine is still heavily debated, and a revision of the 2004 IHS criteria for this condition has been proposed (Olesen 2006); (b) transformed migraine and chronic daily headache, although commonly used terms, are insufficiently validated diagnoses; (c) the separation of these conditions Topiramate is also used with other medications to control seizures in people who have Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (a disorder that causes seizures and developmental delays). Topiramate is also used to prevent migraine headaches but not to relieve the pain of migraine headaches when they occur. Included studies were required to have at least one arm in which an antiepileptic drug other than gabapentin, pregabalin, topiramate, or valproate (without concomitant use of other migraine prophylactic treatment) was given regularly during headache‐free intervals with the aim of preventing the occurrence of migraine attacks, improving • Effective migraine preventive medications include candesartan, telmisartan, lisinopril, oral magnesium, topiramate, propranolol, erenumab, fremanezumab, and galcanezumab. • Galcanezumab reduces Prospective, controlled trials of antiepileptics taken regularly to prevent the occurrence of migraine attacks, to improve migraine-related quality of life, or both, were selected. Results: Mean headache frequency on topiramate and sodium valproate is significantly lower than placebo. Dr. Vargas also noted that topiramate (Topamax), which is an epilepsy drug approved for the prevention of migraines, is not a good choice for posttraumatic headaches. Topiramate often causes cognitive side effects which can worsen the concussion-related cognitive problems, including impaired memory and concentration. Compare Gabapentin vs Topamax head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Divalproex (Depakote), topiramate (Topamax), metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol are effective for migraine prevention and should be offered as first-line treatment. Petasites has been Four trials with a total of 351 patients compared gabapentin in a dosage of 900 to 2,400 mg per day with placebo. The meta-analysis found no significant reduction in the frequency of migraine Gabapentin appeared well tolerated in 30 (75%) patients compared to topiramate in 23 (57.5%) patients. Both drugs were equally effective in migraine prophylaxis. We found high certainty evidence that, compared to placebo, fremanezumab, erenumab, galcanezumab, eptinezumab, gepants, topiramate, and beta-blockers reduce monthly migraine days, and that oxcarbazepine and gabapentin are not different from placebo. Taking topiramate at the FDA recommended dose of 100mg per day has no reported effect on birth control effectiveness. However, taking topiramate at over 200mg per day decreased the estrogen part of OCPs by 18%. Anticonvulsants gabapentin (Neurontin®) and valproate (Depakote®) don’t interact with OCPs.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |