Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
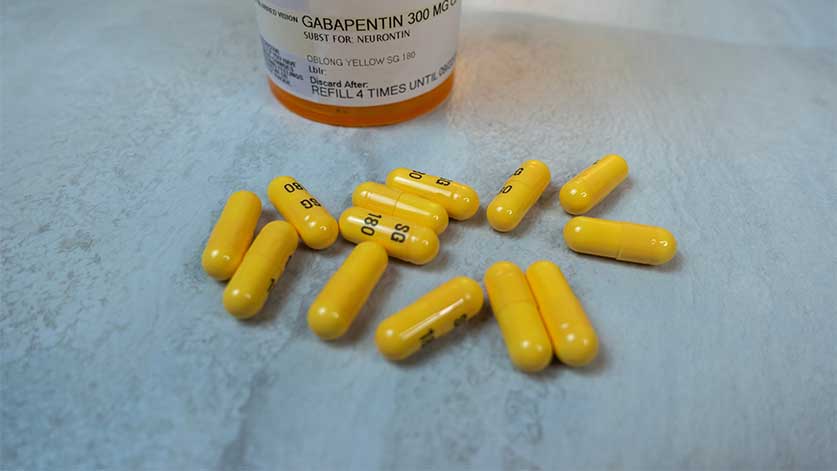
Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures. Gabapentin, a medication that sounds like it could be the name of a quirky robot sidekick in a sci-fi flick, is actually a serious player in the world of pain management and neurological disorders. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Use only the brand and form of gabapentin your doctor has prescribed. Check your medicine each time you get a refill to make sure you receive the correct form. Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Sleepiness and dizziness are quite common complications of both drugs. Your doctor should have warned you about the dangers of driving while taking either medicine. Gabapenin & Pregabalin Brain Side Effects Include: Memory Loss; Amnesia; Memory Impairment; Confusion (fuzzy thinking) Somnolence (sleepiness) Dizziness; Disorientation (brain fog The vast bulk of the brain's synapses are formed during gestation and the very early months and years after birth. Because gabapentin easily crosses the placental barrier, it could potentially interfere with a fetus' rapidly developing brain just when global synapse formation is proceeding at breakneck speed. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. Gabapentin works its magic by calming overactive nerves in the brain. It’s like a gentle hand soothing a frazzled mind, bringing relief to those who’ve long suffered. But here’s the rub: our brains are intricate machines, and tinkering with one part can have unexpected effects on others. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain, has been the subject of intense scientific scrutiny in recent years. On the other hand, dopamine, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, plays a crucial role in various brain functions, including motivation, pleasure, and movement. The Impact of Gabapentin Administration on Brain GABA and Glutamate Concentrations: A 7T 1 H-MRS Study Kejia Cai 1,5 , Ravi PR Nanga 1,5 , Lisa Lamprou 2,3 , Claudia Schinstine 2,3 , Mark Elliott Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been sh Why the drugs affect your mind. Both anticholinergics and benzodiazepines affect the activity of neurotransmitters—chemical messengers that work in the central nervous system—but the drugs work in slightly different ways. Anticholinergic drugs block the action of acetylcholine. In the brain, acetylcholine is involved in learning and memory. Yes, gabapentin may cause brain zaps as the medication tends to alter the amount of neurotransmitters in your brain. However, it is not considered a common side effect and it mostly occurs in people who don’t seem to tolerate gabapentin well. Gabapentin works by “slowing the brain down.” If you take gabapentin with other medications or substances that slow down the brain, dangerous effects can occur. This includes slowed breathing, confusion, and extreme sleepiness. And the risk is higher for people with existing breathing problems. If you’re looking to improve your focus and concentration, try to quit smoking cigarettes. It won’t be easy, but it’s worth it for your health and your brain. If you’re taking gabapentin, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and take the medication as prescribed. Gabapentin reduces the number of neurons that are firing in your brain. By doing so, this medication can help improve mood and cognition while also reducing anxiety or depression-related symptoms. The neurotransmitter GABA is responsible for slowing down neuronal activity when it binds to its receptors found on nerve cells. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |