Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
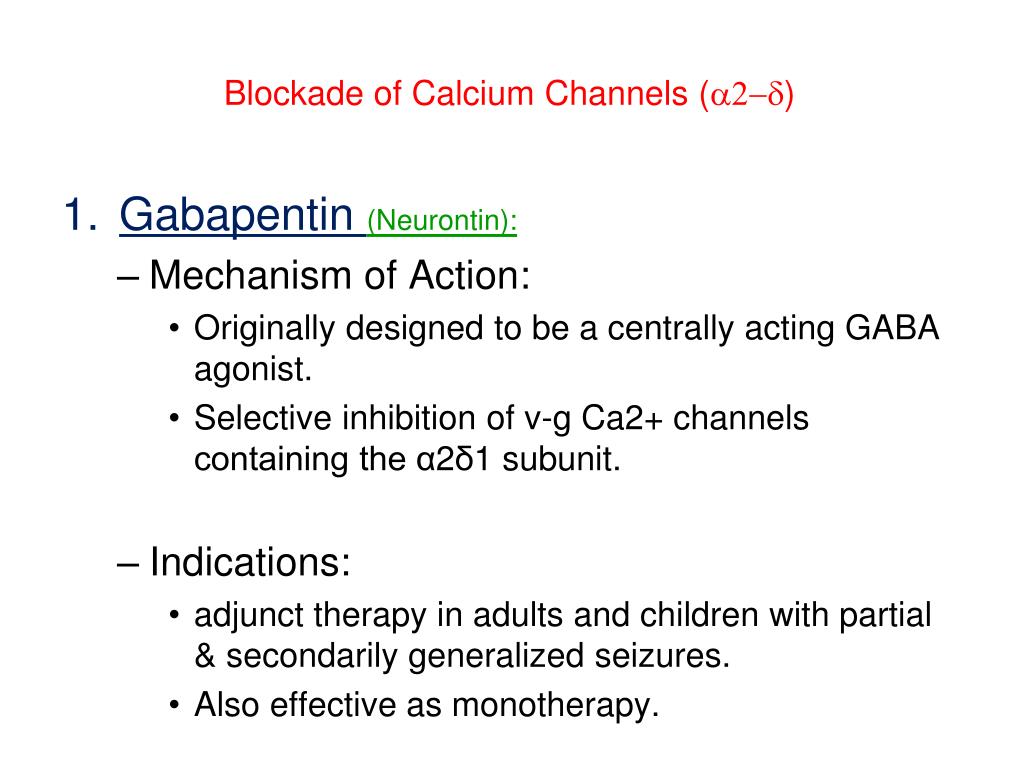
Gabapentin is approved for the former indication in the US. [7] In addition to these two neuropathies, European Federation of Neurological Societies guideline notes gabapentin effectiveness for central pain. [11] A combination of gabapentin with an opioid or nortriptyline may work better than either drug alone. [11] [33] Owing to the multiple actions of the GABA system, gabapentin has subsequently been used for a wide variety of conditions, with up to 95% of gabapentin today prescribed for off-label indications. 2,3 Prescribers are often unaware of gabapentin’s approved indications and their prescribing of gabapentin is largely guided by informal discussion 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE . NEURONTIN. is indicated for: • Management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults • Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary Neurontin was evaluated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) in 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter studies; N=563 patients in the intent-to-treat (ITT) Gabapentin was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of seizures in 1993 and was subsequently approved for one pain indication, postherpetic neuralgia. 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly FDA-Approved Indications. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. An increase in gabapentin AUC values have been reported when administered with morphine. (7.7) An antacid containing aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide reduced the bioavailability of gabapentin immediate release by about approximately 20%, but by only 5% when gabapentin was taken 2 hours after antacids. Table 1: FDA-Approved Indications for Pregabalin and Gabapentin: Indications. Pregabalin. Gabapentin. Neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. x. However, over the past 25 years, gabapentin has been prescribed for a variety of indications beyond those formally evaluated by the FDA. In this issue of JAMA, Moore et al 1 summarize an updated Cochrane review on the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain. Gabapentinoids are approved by the TGA for adjunctive therapy in patients with refractory focal epilepsy, and for treatment of neuropathic pain. Pregabalin is only approved for use in adults. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Medical Indications. In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization HORIZANT (gabapentin enacarbil) Extended-Release Tablets for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2011 -----RECENT MAJOR CHANGES-----Indications and Usage, Management of Postherpetic Neuralgia (1.2) 06/2012 Dosage and Administration, Postherpetic Neuralgia (2.2) 06/2012 Some of these individuals were taking higher than recommended doses of gabapentin for unapproved uses. When prescribing gabapentin, carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and observe them for signs and symptoms of gabapentin misuse or abuse (e.g., self-dose escalation and drug-seeking behavior). Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. Indications. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that was first discovered in the 1970s. The medication received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | .jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |