Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
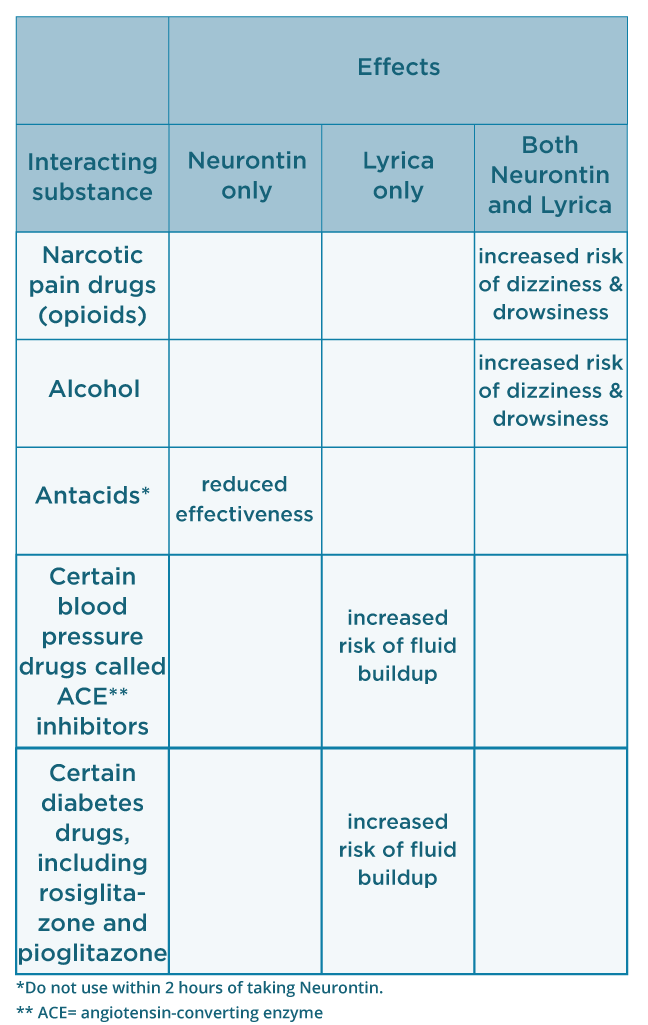
Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. However, this is routinely exceeded in clinical practice. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. If you are on gabapentin and are newly diagnosed with kidney disease, inform your healthcare provider immediately. They will need to evaluate your kidney function and determine if your gabapentin dose needs to be adjusted. This may also lead to a reassessment of your pain management approach. 15. While gabapentin levels were not measured, the rapid resolution of the delirium and recovery of renal function after only two sessions of low cut-off haemodialysis seem to indicate that gabapentin caused the symptoms. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. This football-sized powerhouse helps keep you alive and healthy. As you move throughout your day, it works hard to detoxify your blood, help with digestion, and restore your energy levels. You can’t live without it. Your liver also plays an important role in metabolizing medications. This means that your kidneys degrade and remove medications from the body. When your kidneys aren't working properly, medications can build up and cause you harm. It's important to get your kidneys checked and to work with your doctor to make any adjustments to your medication regimen, such as dosing changes or substitutions. gabapentin, kidney. Further information. Gabapentin uses and safety info; Gabapentin prescribing info & package insert (for Health Professionals) Side effects of Gabapentin (detailed) Similar questions Steven Coca, professor of medicine and a nephrologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, says you should know your estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the primary measurement of kidney function, and your urine albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR), a marker of kidney damage. Your eGFR will show up any time your Acetaminophen (Tylenol): For mild to moderate pain, acetaminophen remains a generally safe choice, although it should be used judiciously and at recommended doses. Opioids: Certain opioids like oxycodone, hydromorphone, fentanyl, methadone, and buprenorphine are generally considered safer to use in patients with kidney disease when used appropriately and under medical supervision. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. But they can sometimes dehydrate you, which can be bad for your kidneys. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Whether they're over-the-counter -- like aspirin,
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |