Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
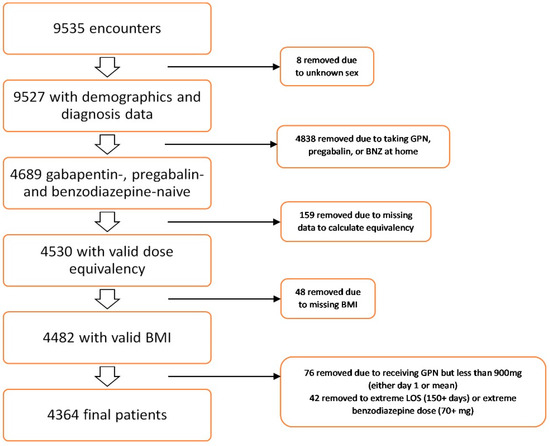
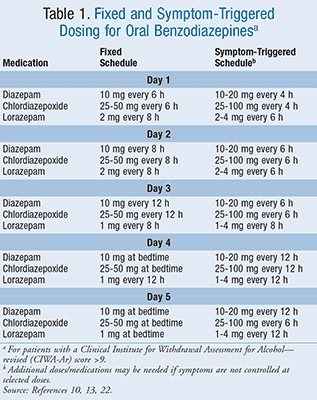
Keywords: gabapentin, benzodiazepine, treatment, alcohol withdrawal, inpatient. Introduction. Benzodiazepines have the largest and best evidence in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal and as a result are considered the gold standard for treatment. 1, 2 However, there are several limitations It does mean they will likely be open to following a taper you design. They normally will not be able to help with any protracted issues post cessation. Most doctors are undereducated about benzodiazepines in general. Temper expectations. Patients frequently find that they have to do most of the work to successfully get off their benzodiazepine. Depending on the patient and the benzodiazepines involved, substitution can add 1-4 weeks to a taper. Some patients may find substitution intolerable, whether due to the differing phramacokinetics or the equivalency ambiguities of the two benzodiazepines. Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers. There are three basic approaches to a benzo-diazepine taper: (1) use the same medication for tapering; (2) switch to a longer-acting equivalent; and (3) use adjunctive medications to help The combination of gabapentin and benzodiazepine can be safe in the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to data presented at American Psychiatric Association annual meeting, i did a 21 day K taper and was on about 2400mg per day (I think) of Gabapentin while I tapered off. I then took Gabapentin for about 2 weeks post jump from the benzos. I personally felt Gabapentin saved my life and allowed me to get off Benzos. Developed through a partnership of ten medical and professional societies, this guideline focuses on evidence-informed and consensus-based strategies to help clinicians determine whether tapering benzodiazepine medications may be appropriate for a given patient, and if so, how to taper them. Consider de-prescribing (tapering and stopping) for any patient taking benzodiazepines daily for longer than one month, especially persons: Assess the patient’s underlying condition for which the BZRA was originally prescribed; consider alternative treatments as needed. Defoster et al. recently conducted a randomized controlled trial in the inpatient setting, using fixed-dose gabapentin taper and CIWA-directed benzodiazepines to treat mild/moderate AWS . Their study found no significant differences between the groups; however, the results were constrained by under-enrollment and prior benzodiazepine use in Patients experiencing difficulty with taper may benefit from: Gabapentin 300 mg HS the day before stopping the final 10-20% of benzodiazepine dose. Titrate to gabapentin 300 mg TID - QID Continue gabapentin for 3 months or longer depending on benzodiazepine dose and duration Prior to beginning taper: 1. Initiate an SSRI 2. Over 3 weeks Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other medical conditions was associated with better outcomes of benzodiazepine withdrawal (N=57 gabapentin, N=115 no gabapentin). You may consider discussing with your doctor using non-benzodiazepine bridge medications like trazodone or gabapentin to help with the benzodiazepine tapering process. There will be more on this topic below in the section that covers the topic of bridge medications. Tapering to help clinicians determine whether and how to taper benzodiazepine (BZD) medications. Who should taper? Regularly reassess the risks and benefits of ongoing BZD After physiological dependence is established, withdrawal symptoms may occur following any reduction in dosage, during a taper, or after a drug switch, as well as discontinuation of the drug. 78 The rate of drug tapering seems to influence the development of withdrawal symptoms throughout the taper and afterward, slower tapers probably allowing Three steps to tapering benzodiazepines 1. Establish patient expectations based on duration of benzodiazepine use (see Talking to Patients About Benzodiazepines). 2. Create alternative plan to address anxieties. 3. Taper benzodiazepine using this document as guidance. When the decision is made to deprescribe a benzodiazepine, patients with al is necessary. Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other BENZODIAZEPINE TAPER Basic principle: Expect anxiety, insomnia, and resistance. Patient education and support will be critical. Risk of selzures with abrupt withdrawal increases with higher doses. The slower the taper, the better tolerated. SLOW TAPER RAPID TAPER 3 2 4 Pre-medicate two weeks prior to taper with va proate Introduction. Benzodiazepines, a class of medication known as anxiolytics, are listed as Schedule IV controlled substances.They are often prescribed for conditions such as anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and alcohol withdrawal, but are also given for a vast array of off-label uses such as restless leg syndrome, muscle spasms, tinnitus, dementia, mania, and akathisia.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |