Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
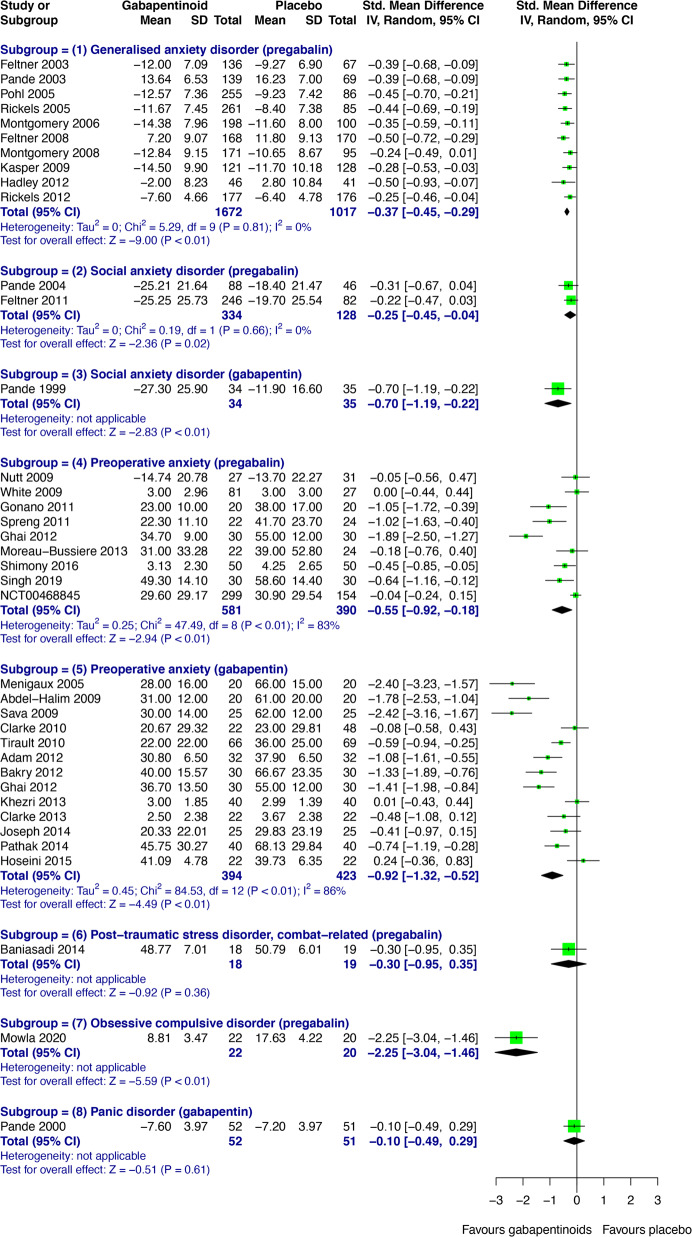
In recent years, gabapentin has gained attention for its potential role in managing anxiety disorders, particularly for individuals who do not respond well to traditional anxiety medications like SSRIs or benzodiazepines. 2002: In one study analyzing the efficacy of Gabapentin as an adjunct treatment for bipolar disorder, it was discovered that improvements were most notable on anxiety-somatization measures of the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D). Results of the study suggest that those with bipolar disorder who attained the most benefit from A systematic search strategy employing different combinations of the keywords (bipolar, mania, hypomania, gabapentin, neurontin, gralise, gabarone, fanatrex, pregabalin, lyrica) was developed and performed in five databases namely OVID Medline, PubMed, ProQuest, PsychInfo and ScienceDirect from database inception to 7 June 2021. While it's true that GABA plays a role in anxiety, anxiety is complex, and researchers are still trying to figure out how and if gabapentin might work to ease symptoms of moderate or severe anxiety. We conclude that there is moderate evidence of the efficacy of gabapentinoids in anxiety states, but minimal evidence in bipolar disorder and insomnia and they should be used for these disorders only with strong justification. For gabapentin, a dose-response pattern has been observed in GAD with remission/mild anxiety on total daily doses of gabapentin ≥900 mg/day and recurrence of severe anxiety, suggesting Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of gabapentin for MDD, GAD, PTSD, or OCD. There is sufficient evidence to consider the use of gabapentin for social anxiety disorder and, potentially, severe panic disorder after other treatment options have failed. gabapentin (SMD -0.92, 95% CI -1.32 to -0.52) were more effective than placebo in reducing preoperative anxiety. In insomnia, results were inconclusive. The lifetime prevalence of anxiety disorders is 45% when BD is present; patients with BD are 3 to 7 times more likely to meet criteria for diagnosis of an anxiety disorder than the general population.1,2 Panic, posttraumatic stress (PTSD), and generalized anxiety disorders (GAD) are the most common (13% to 60%), followed by obsessive compulsive Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication If you have bipolar disorder and you also have anxiety or a substance use disorder, your healthcare provider might suggest adding on gabapentin. The bottom line There are many good medications for bipolar disorder, but gabapentin isn’t one of them. Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Gabapentin and pregabalin in bipolar disorder, anxiety states, and insomnia: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and rationale November 2021 Molecular Psychiatry 27(3):1-11 Numerous other off-label and investigational uses for gabapentin have been described, including alcohol dependence, 1, 2 bipolar disorder, 3 posttraumatic stress disorder, 4 essential tremor, 5 and perioperative anxiety. 6, 7 Pregabalin, approved for clinical use in the United States in 2004, is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and partial A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% with anxiety disorders, and 12.7% with insomnia disorder; for pregabalin, the figures were 2.9%, 2.6%, 3.0% respectively (PJH, unpublished observations). Gabapentin appears to have some benefit for anxiety disorders but failed to show benefit in bipolar disorder trials. In the individual patient with a mixed psychiatric disorder, benefits are most likely due to anxiolytic effects. "I have bipolar disorder, chronic depression, and anxiety, and gabapentin has helped tremendously without the use of other narcotic medicines. Yeah, it makes you feel a little loopy for the first few weeks, but after that, it does a wonderful job calming the nerves. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). Evidence also suggests gabapentin is more effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and certain types of anxiety than conditions like bipolar disorder, panic disorder, or panic
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |