Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /klippel-feil-syndrome-5c895a9b46e0fb0001cbf608.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
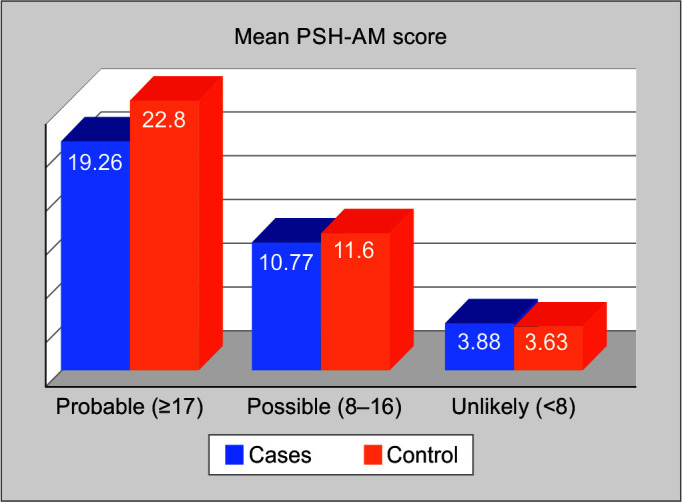
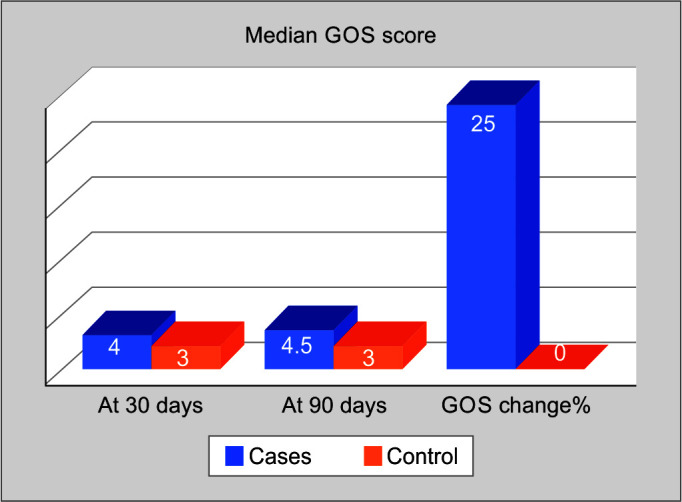
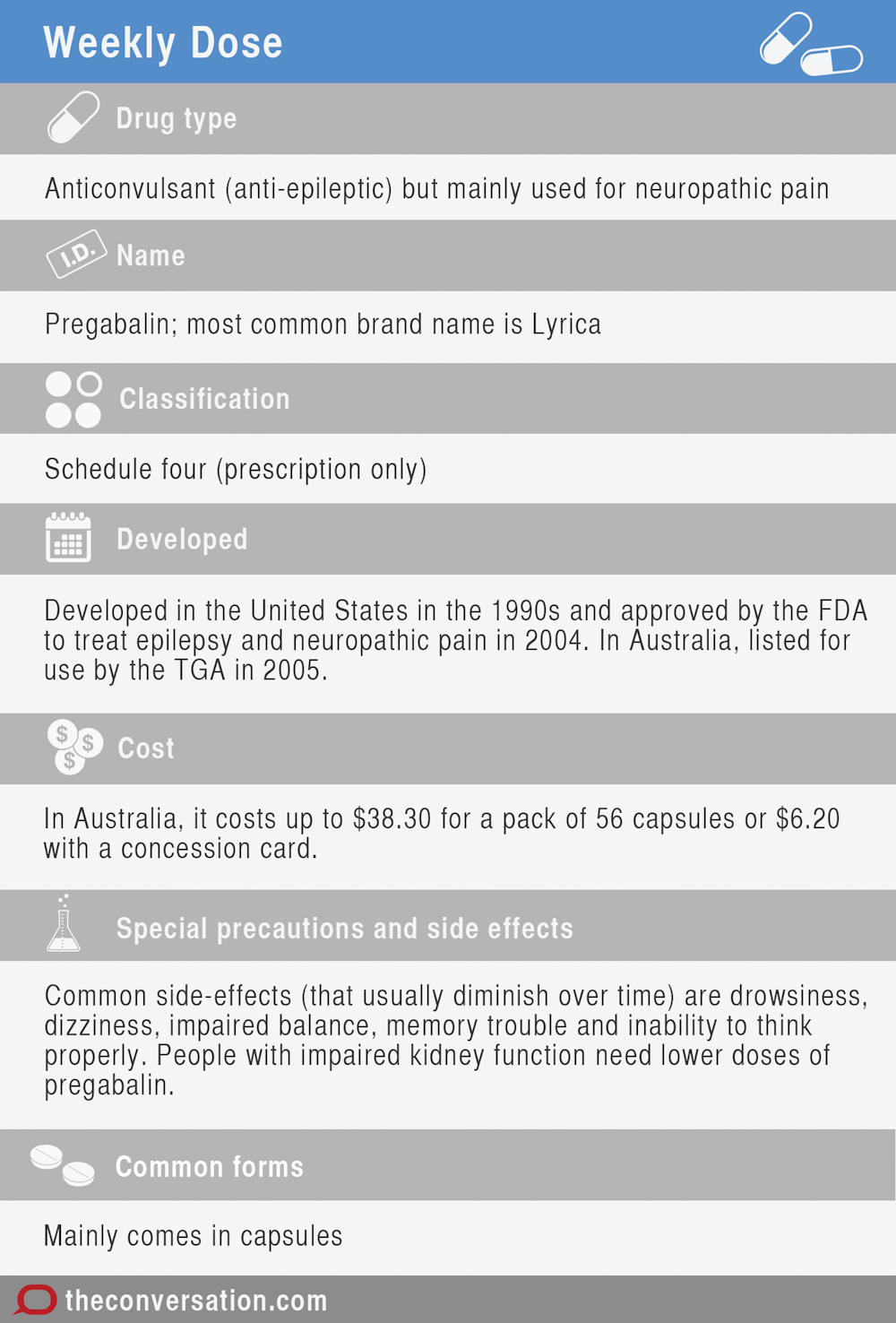
Gabapentin new users with normal cognition at the visit of gabapentin initiation (i.e., index visit) were included. New-users were matched on year of first enrollment and time of gabapentin initiation since enrollment to randomly select nonusers with replacement. Gabapentin works its magic by calming overactive nerves in the brain. It’s like a gentle hand soothing a frazzled mind, bringing relief to those who’ve long suffered. But here’s the rub: our brains are intricate machines, and tinkering with one part can have unexpected effects on others. Chronic administration of gabapentin and carbamazepine may cause increase in neurodegenerative changes in the adult brain. Keywords: Epilepsy, Antiepileptic drugs, Histology, Brain, Rats. Introduction. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by intermittent unprovoked seizures. It affects about 65 million people globally. Hence, by understanding the mechanism of action of gabapentin, we propose to use it to reduce sympathetic hyperactivity, and to reduce secondary brain damage by preventing the release of neurotransmitters. O bjectives. We conducted this prospective study to primarily investigate the impact of gabapentin on TBI. Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Taking the gabapentin away without proper care can lead to the development of distressing and potentially dangerous withdrawal systems, as the brain and body struggle to adapt to the sudden lack of gabapentin. For those with epilepsy, this is of special concern; without gabapentin, they are at risk for experiencing seizures, which can be very The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Not a doctor but yes lol. Every drug can damage your brain, but cns depressants are the worst. Go spend some time in r/benzorecovery. Benzos are worse than gabapentin obviously so that's more of a worst case scenario. But yeah taking any cns depressants for a long period of time will fuck your brain. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. Does Gabapentin cause brain damage? There's no conclusive evidence to suggest that Gabapentin causes permanent brain damage. However, some studies suggest that prolonged and high-dose use of Gabapentin may lead to cognitive impairments in some individuals. The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests.The experiments mimicked ischemic stroke in humans, which occurs when a clot blocks bloo Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. Neuropathic pain: Pain caused by nerve damage or irritation, such as diabetic neuropathy or post-herpetic neuralgia. Restless leg syndrome (RLS): A condition that causes an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. We conducted this prospective study to primarily investigate the impact of gabapentin on TBI. The study focuses on the role of gabapentin to avert secondary brain injury, mitigating brain edema, and improving the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that doctors often prescribe to manage seizures related to epilepsy. It is not a cure for epilepsy, but it can help people manage the condition. In this Background Gabapentin, a structural analog of γ-aminobutyric acid, although developed for epilepsy, is often used for pain, insomnia and anxiety. It is considered very safe, with neurotoxicity mostly limited to renally-impaired patients. Design/Methods: Case Report. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. The question of whether gabapentin is harmful to the brain is complex, with no simple yes or no answer. While gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication for various conditions, including epilepsy , nerve pain , and restless legs syndrome , mounting evidence suggests it can have significant effects on the brain, both in the short and long term. Gabapentin can cause brain damage to my understanding based on new studies that are coming out. It causes the calcium gateways to lose their conductivity. These calcium gateways allow brain synapses to communicate with each other via this calcium pathway.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /klippel-feil-syndrome-5c895a9b46e0fb0001cbf608.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |