Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
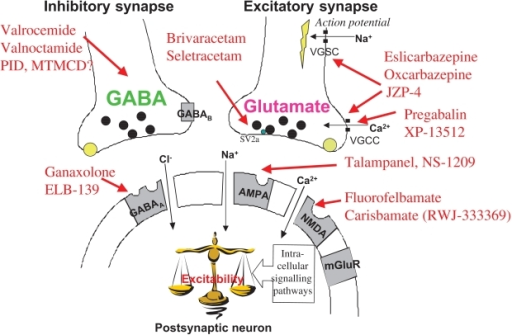
The huge mass of the brain’s synapses are created during development and the very early months and years after birth. Because gabapentin without difficulty crosses the placental barrier, it could potentially hinder with a fetus’ quickly developing brain just when global synapse arrangement is happening at prompt rapidity. Here we identify the neuronal thrombospondin receptor involved in CNS synapse formation as α2δ–1, the receptor for the anti-epileptic and analgesic drug gabapentin. The study shows that gabapentin halts the formation of new synapses, possibly explaining its therapeutic value in mitigating epileptic seizures and chronic pain. This insight, however, may lead physicians to reconsider the circumstances in which the drug should be prescribed to pregnant women. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to a novel binding site in brain tissues that is associated with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Recent electrophysiology results suggest that gabapentin may modulate certain types of Ca2+ current. Early intervention with gabapentin may prevent the development of injury-induced chronic pain, resulting from Ca v α 2 δ 1 /TSP4-initiated abnormal synapse formation. Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Recent Advances in Targeting Ion Channels to Treat Chronic Pain. A shocking new study shows that they block the formation of new brain synapses 1, drastically reducing the potential for rejuvenating brain plasticity – meaning that these drugs will cause brain decline faster than any substance known to mankind. The problem of these drugs is compounded by their flagrant illegal marketing. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major neurotransmitter for fast inhibitory synaptic transmission and tonic inhibitory control, is present in 25–50% of all synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000). L-glutamic acid (glutamate) is responsible for fast excitatory neurotransmission and is present at approximately 80% of brain synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000 However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. Consequently Gabapentin, also known by the brand name Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat seizures and manage neuropathic pain. It is a synthetic medication that works by regulating certain neurotransmitters in the brain. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Scientists have identified a key biochemical mechanism in the formation of new synapses in the brain that can be disrupted by the antiepileptic medication gabapentin, according to a recent study. The brain’s incredible plasticity is what lets us think, learn, create, and remember. Throughout our lives, brain cells called neurons constantly form new connections, or synapses, that pass electrochemical signals from cell to cell. This ability, called neuroplasticity, underlies every function of the human mind. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on The vast bulk of the brain's synapses are formed during gestation and the very early months and years after birth. Because gabapentin easily crosses the placental barrier, it could potentially interfere with a fetus' rapidly developing brain just when global synapse formation is proceeding at breakneck speed. AED may may prevent the formation of new brain synapses, reducing the so-called “brain plasticity.” Brain plasticity is a continuous mechanism that prevents all age-related cognitive decline, meaning that a drug that directly reduce this natural neural activity will cause a faster brain decline. In other words, these drugs cause brain damage. The study shows that gabapentin halts the formation of new synapses, possibly explaining its therapeutic value in mitigating epileptic seizures and chronic pain. Dopamine (DA) orchestrates essential brain functions including voluntary movement, action selection, and reward-related behaviors via volume transmission. 1, 2 Due to its spatiotemporal release properties, synaptic transmission through DA synapses has been considered slow and diffuse in space, possibly causing non-synapse-specific transfer of information to postsynaptic neurons. Synapses are asymmetric cellular adhesions that are critical for nervous system development and function, but the mechanisms that induce their formation are not well understood. We have previously identified thrombospondin as an astrocyte-secreted protein that promotes central nervous system (CNS) synaptogenesis. Here, we identify the neuronal thrombospondin receptor involved in CNS synapse Gabapentin receptor α 2 δ‐1 is a neuronal thrombospondin receptor responsible for excitatory CNS synaptogenesis. Cell 139: 380–392. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Field MJ, Holloman EF, McCleary S, Hughes J, Singh L (1997). Evaluation of gabapentin and S‐(+)‐3‐isobutylgaba in a rat model of postoperative pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |