Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
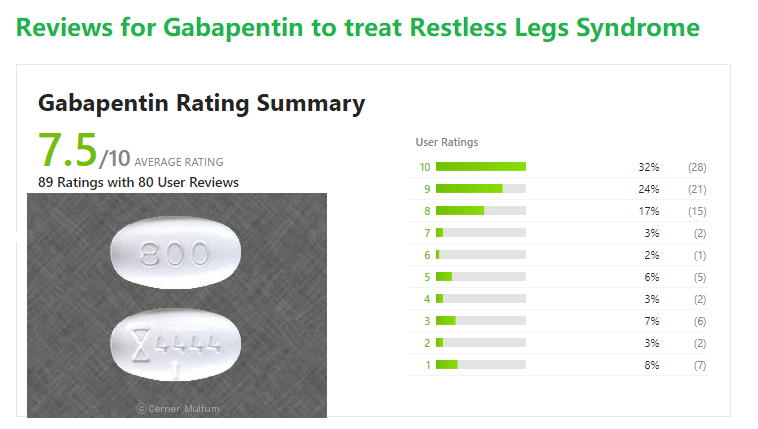
Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. I take 600 mg of gabapentin, 300 mg twice daily. No swelling in my feet. I still get some cramping and stabbing. I hope everything is going well with others. Sorry to say, but my swelling lead to weight gain.I was prescribed Gabapentin for nerve pain. I started at 200 mgs once daily at bedtime. I couldn't stay on it for longer than two weeks. Gabapentin is a common medication-related cause of peripheral edema. This is when you experience swollen tissues in the body, often in the arms and legs. Up to 8% of people report edema with gabapentin clinical studies. But it’s more likely to occur in older adults. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. We study how severe was Foot, leg, and ankle swelling, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin). This phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports submitted to eHealthMe, and is updated regularly. Although the mechanism behind peripheral edema from gabapentin is largely unknown, it has been theorized to be similar to the mechanism in which other calcium channel blockers (eg, amlodipine) cause peripheral edema. 6,7 This relationship has been hypothesized to be due to gabapentin's actions on presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels. 1,6 On hospital day 31, after 21 days at 1800 mg/d, gabapentin was identified by the resident pharmacist as a potential cause of the patient's edema, and the dose was decreased to 300 mg 3 times daily (900 mg/d). Leg edema might be occurred in systemic and local types. Systemic edema could be caused by congestive cardiac failure, renal failure, hypoalbuminemia, protein losing neuropathy. For localized edema we can note following reasons such as primary and secondary lymphedema, lipedema, deep vein thrombosis and chronic venous disease.[ 13 , 14 ] Elevate your legs: If you experience swelling in the legs or feet, elevating them while sitting or lying down can help alleviate edema. Prop them up on a cushion or pillow to encourage fluid drainage. Fluid retention, or edema, can occur when gabapentin affects vascular permeability or alters kidney function. Edema refers to swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation in tissues. It can occur in various parts of the body but is most commonly seen in the legs, ankles, and feet. Edema is a well-described side effect of gabapentinoid drugs (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin). In this study from Ontario, Canada, researchers used provincial databases to examine whether gabapentinoid use was followed by diuretic prescriptions — a so-called “prescribing cascade” in which a drug is prescribed to treat an adverse effect of another drug. NSAIDs commonly cause water retention, which can lead to swelling in the legs and ankles. This tends to be more likely in older adults and people with kidney problems. Typically, the swelling will go away once you stop taking the medication. But NSAIDs can also make heart failure worse. And worsening heart failure can cause leg and ankle Gabapentin, a medication primarily known for its use in treating seizures and nerve pain, has a complex relationship with the legs. While not specifically designed to target leg issues, gabapentin’s mechanisms of action and side effects can significantly impact this part of the body. It is important to recognize this adverse effect because gabapentin is used in conditions like diabetic neuropathy, which is associated with multiple co-morbidities that can give rise to bilateral leg swelling. Swelling in the feet and ankles. Patients taking Neurontin may experience swelling in the feet and ankles. The presence of lower leg swelling may cause discomfort and impair walking. My mother-in-law was unable to wear regular shoes because of swelling of her feet and ankles, so we found her socks and soft slippers that fit her feet comfortably. I have swelling in my legs caused by lymphedema and have to wear compression socks but mine was not caused by a medication. I also would be concerned if it's been over 5 months since stopping gabapentin and the swelling and pain is still in the hands and feet. What Causes Swelling from Gabapentin? Swelling from gabapentin can be attributed to several mechanisms: Fluid Retention. One common reason for swelling is fluid retention. Gabapentin can cause changes in kidney function or fluid balance in the body. When the body retains excess fluid, it can lead to noticeable swelling in areas like the legs Similarly, the incidence of peripheral edema caused by CCB is dose related and common in the elderly, comparable to reports of gabapentin induced edema. This case illustrates that gabapentin induced leg swelling can confound the clinical picture and it is thus important to recognize this side effect of gabapentin. A classical pharmacodynamic effect of CCBs is to induce diffuse and bilateral swelling of the feet, ankles and sometimes lower legs that worsens throughout the day and improves overnight. 3 The peripheral oedema observed with CCBs can differ in appearance from more traditional oedema states in that lower extremity redness, warmth and a
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |