Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
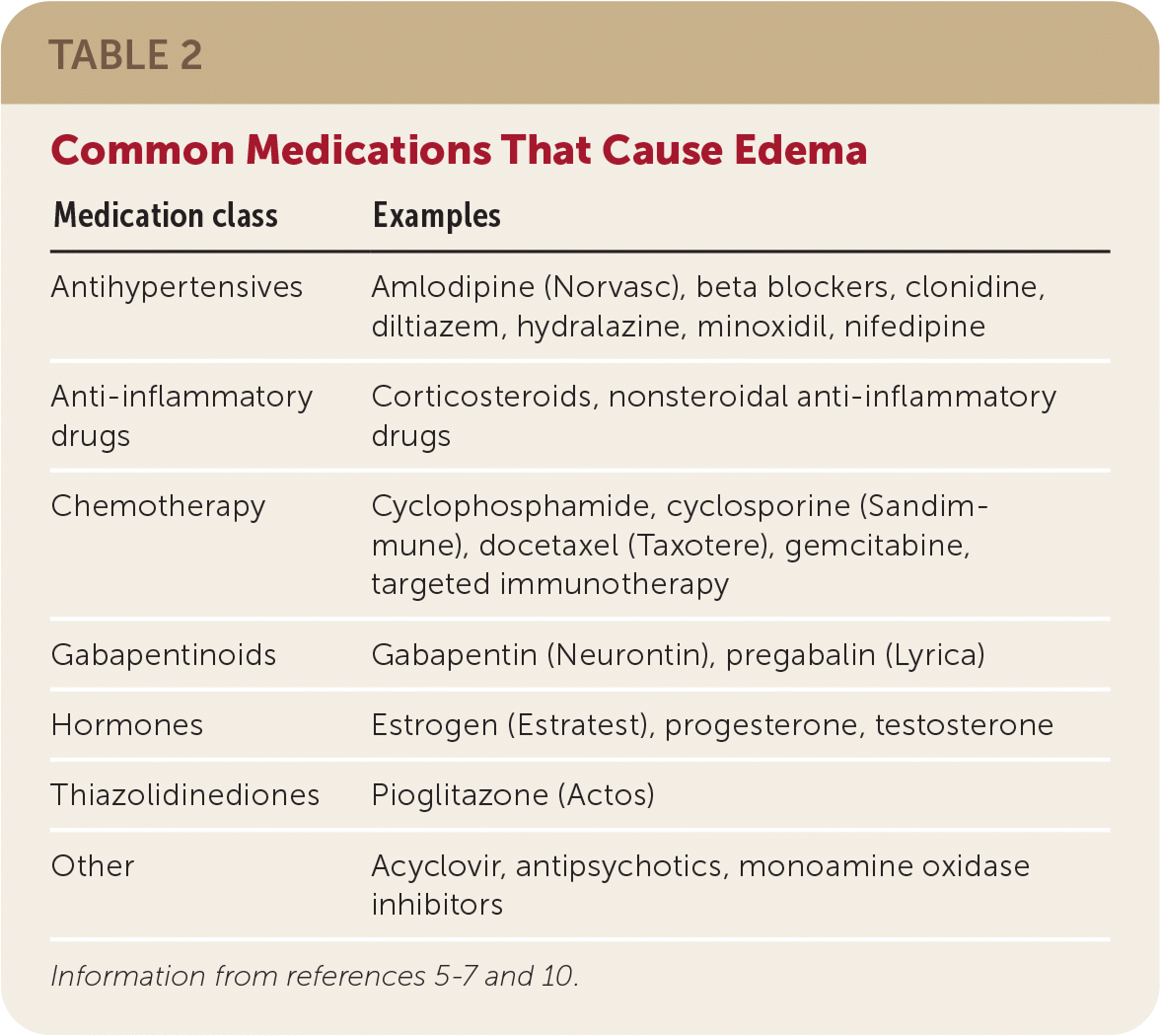
No.: Exceedingly rare individual side-effects or drug reactions/allergies aside, no it does not effect BP. Summary: Hypotension is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. However, in the vast majority of people taking gabapentin, it does not lower blood pressure to a worrisome extent. A blood pressure of 113/64 is below average, but it is not at a worrisome level unless it is associated with any lightheadedness or dizziness. There is no need to do anything in response to a blood pressure of 113/64 without Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. This medication may cause accidental overdose and death if taken by other adults, children, or pets. To get rid of medications that are no longer needed or have expired: Take the medication to a medication take-back program. I have extremely low blood pressure (hypotension) which Gabapentin lowered. I fainted in the morning after taking it and my doctor immediately took me off of it. If you have ANY blood pressure condition, make sure your prescribing doctor is aware of that before prescribing this medication. Prozasin had the same effect on me. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that helps manage seizures due to epilepsy. It can also treat nerve pain and restless leg syndrome (RLS). Gabapentin appears to work by When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Some medications can cause a low platelet count, which can lead to excessive bleeding. Heparin is the most frequent cause, but common drugs like acetaminophen and some antibiotics can also cause Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin is Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Results: Unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS produced prominent dose-related depressor and bradycardic effects in SHR rats. The cardiovascular Low blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The low frequency domain power (LF; A, B, and C) and the ratio of LF to high frequency powers (LF/HF ratio; D, E, and F) calculated by power spectral analysis of systolic blood pressure variability; in partially restrained spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats pretreated with gabapentin (GBP), nifedipine (NIF), or ω Common side effects of gabapentin include: flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. More serious (but rare) side effects include suicidal thoughts or behavior, and mood changes in children. Hypertension (high blood pressure). Sweating. Confusion. Incoherent speech. Impaired ability to pay attention. Nausea. Pain. Insomnia. Restlessness. Anxiety. Agitation. Tremors. Seizures. Someone using gabapentin to control seizure activity should not stop using gabapentin suddenly without talking to their physician. Several medications can cause low blood pressure (hypotension). Examples include phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, nitrates, and blood pressure medications. Opioids, antipsychotics, and certain antidepressants can also cause low blood pressure. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |