Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
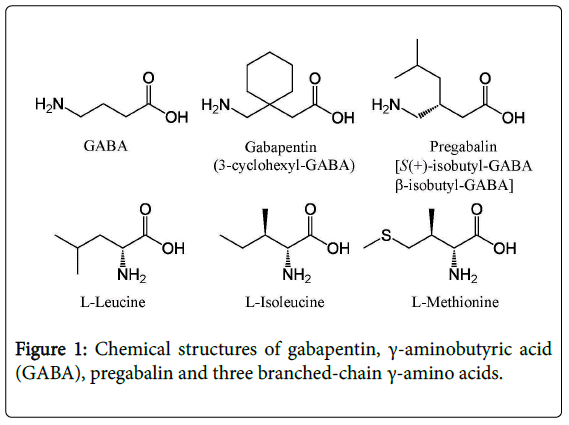
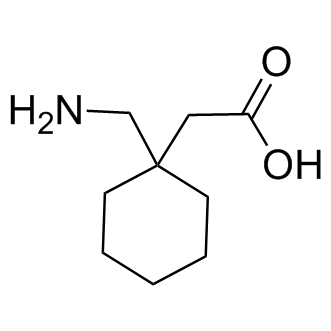
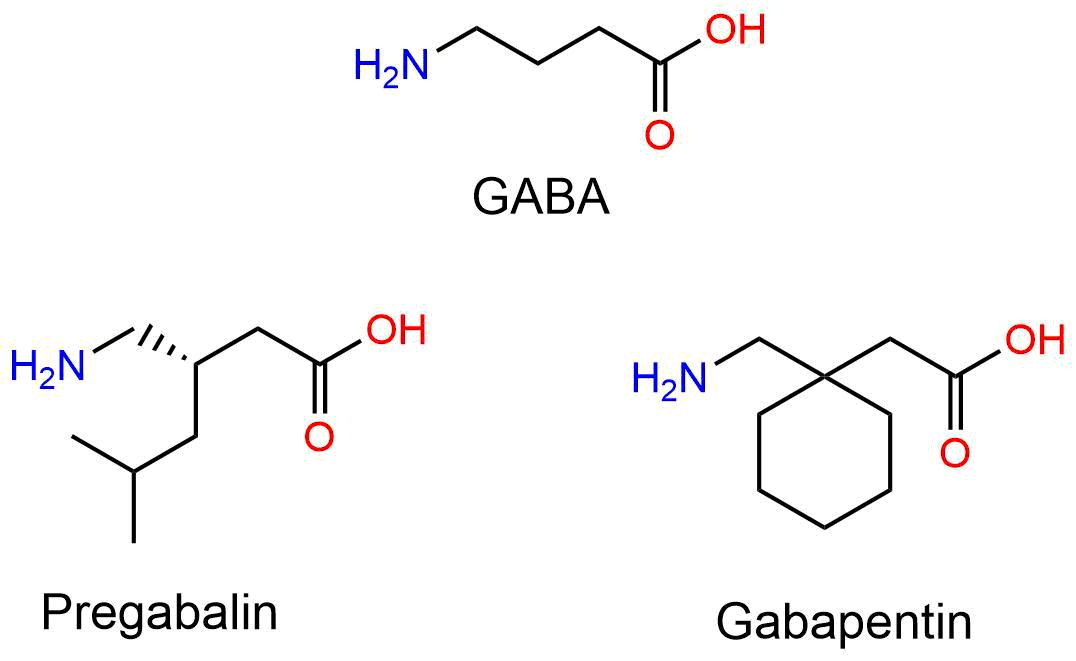
The chemical structure of gabapentin consists of a cyclohexane ring with a carboxylic acid group and an amino group attached. This unique chemical composition allows gabapentin to interact with the voltage-dependent calcium channels in the brain, which helps to control seizures and alleviate pain. The chemical structure of gabapentin is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABAA or GABAB receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. Gabapentin | C9H17NO2 | CID 3446 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. Chemical formula: C₉H₁₇NO₂ Molecular mass: 171.237 g/mol PubChem compound: 3446. Gabapentin readily enters the brain and prevents seizures in a number of animal models of epilepsy. The active ingredient in gabapentin tablets is gabapentin, USP which has the chemical name 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid. The molecular formula of gabapentin is C9H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 171.24. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is a nonprotein amino acid and a synthetic neurotransmitter that is related to γ-aminobutyric acid 1 (GABA). It was first described in 1976 West German patent DE2460891 on cyclic amino acids to Gerhard Satzinger and co-inventors at Goedecke AG (Freiburg). Its chemical formula is C 9 H 17 NO 2, and it is structurally related to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin works by affecting the chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain. Gabapentin caused a marked decrease in neuronal synapse formation in brains of intact mice and abnormal neuronal synapse formation in a mouse model of synaptic repair. Gabapentin has been shown in vitro to interfere with activity of the α2δ subunit of voltage-activated calcium channels, a receptor involved in neuronal synaptogenesis. Gabapentin (International) In the US, Gabapentin (gabapentin systemic) is a member of the drug class gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs and is used to treat Alcohol Use Disorder, Alcohol Withdrawal, Anxiety, Back Pain, Benign Essential Tremor, Bipolar Disorder, Burning Mouth Syndrome, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Pruritus, Chronic Pain, Cluster-Tic Syndrome, Cough Gabapentin (also known as Neurontin) is a depressant substance of the gabapentinoid class. It is a structural analog of the neurotransmitter GABA and acts by inhibiting certain calcium channels in the brain, namely α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VGCCs).[3] solutions. The chemical structures for gabapentin, GABA, and pregabalin are shown below: NH 2 OH O NH 2 OH O NH 2 OH O Gabapentin GABA Pregabalin. Pharmacology: The exact mechanisms through which gabapentin exerts its analgesic and antiepileptic actions are unknown however, according to ; information on the FDA-approved label for the gabapentin Chemical structures of GABA and gabapentin, with commonalities highlighted. Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. [102] [103] It is similar to several other compounds that collectively are called gabapentinoids. Gabapentin is described as 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid with a molecular formula of C9H17NO2 and a molecular weight of 171.24. The structural formula of gabapentin is: Gabapentin, USP is a white to off-white powder with a pKa1 of 3.7 and a pKa2 of 10.7. Gabapentin is a γ- aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue that acts as an anticonvulsant with proven analgesic effects in various neuropathic pain syndromes such as Complex Regional Pain Syndrome type one (CRPS 1). ChemSpider record containing structure, synonyms, properties, vendors and database links for Gabapentin, 60142-96-3, UGJMXCAKCUNAIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gabapentin hydrochloride | C9H18ClNO2 | CID 6453919 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. Gabapentin Enacarbil | C16H27NO6 | CID 9883933 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological Gabapentin is a new chemical compound designed as a structural analog of GABA that is effective in the treatment of partial seizures. In contrast to GABA, gabapentin readily penetrates the blood–brain barrier. In man, gabapentin has been demonstrated to increase GABA concentrations [126]. Most probably the mechanism of action is related to The active ingredient in GABARONE, USP is gabapentin, which has the chemical name 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid. The molecular formula of gabapentin is C 9 H 17 NO 2 and the molecular weight is 171.24.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |