Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | 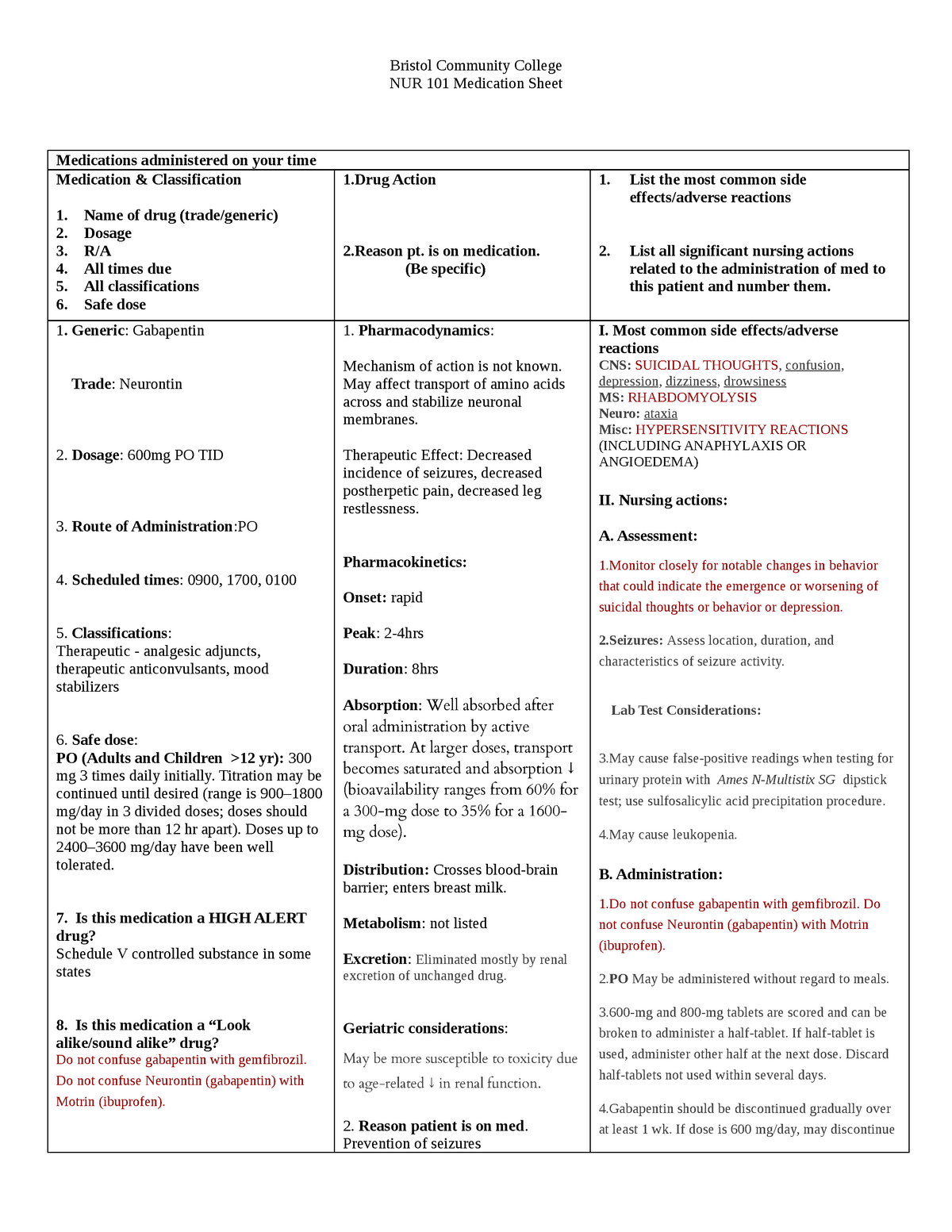 |
 |  |
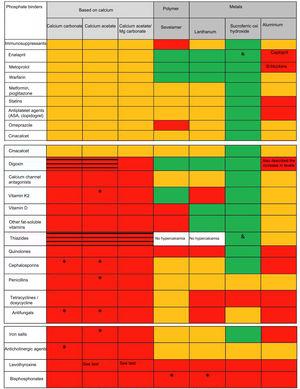 |  |
 |  |
 | 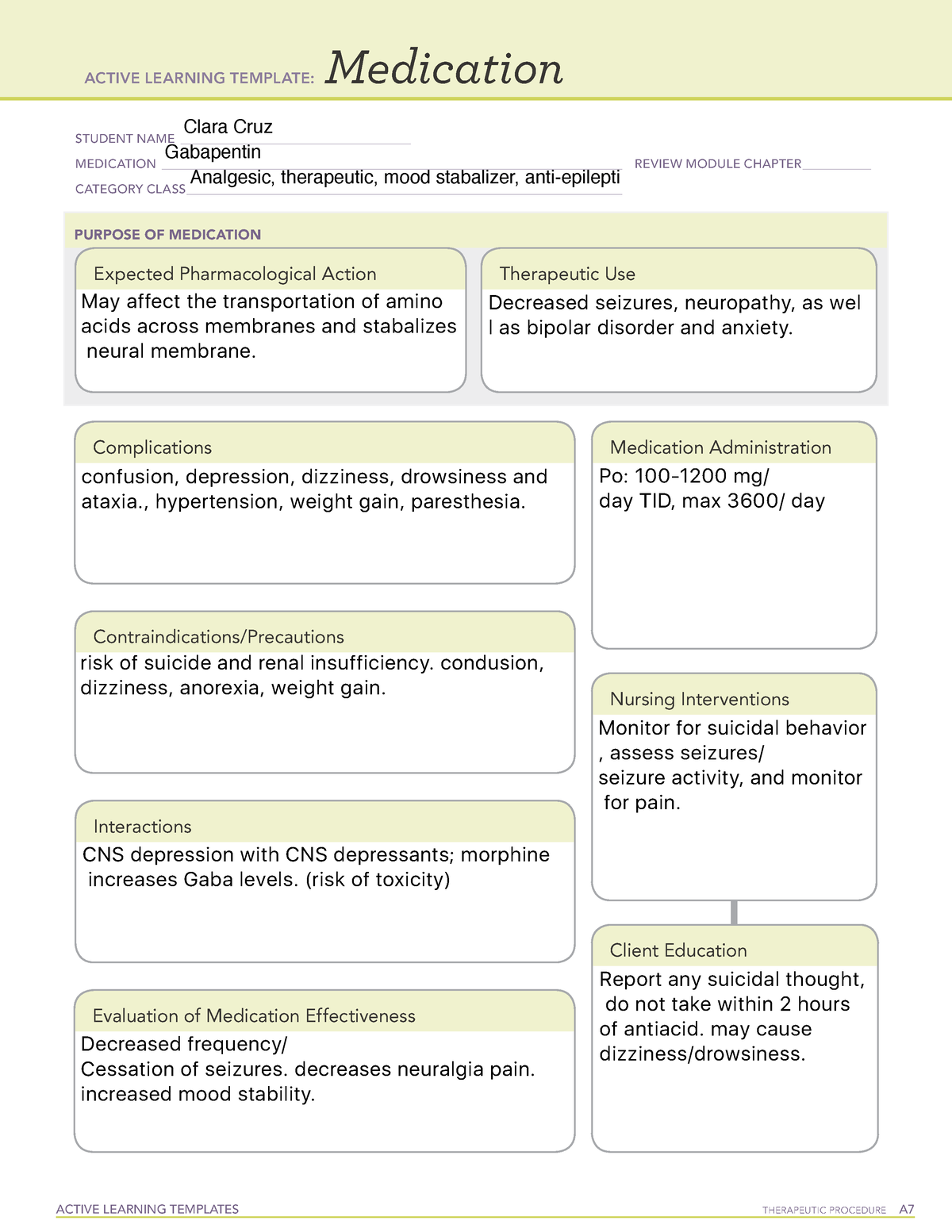 |
Gabapentin, under the brand name Neurontin, was first approved in May 1993 for the treatment of epilepsy in the United Kingdom, and was marketed in the United States in 1994. [43] [44] Subsequently, gabapentin was approved in the United States for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in May 2002. [45] Drug Class: Antiepileptic Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 13th Ed. (2014): Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. The Cochrane Gabapentin provides a well-tolerated and effective treatment of RLS. It improves sensory and motor symptoms in RLS and also improves sleep. In clinical study gabapentin was associated with reduced symptoms on RLS Rating Scale, Clinical Global Impression, pain analogue scale, and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Gabapentin | C9H17NO2 | CID 3446 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Gabapentin is available in two extended-release formulations in addition to the immediate release: a gastric retentive formulation (GBP-GR) and a gastro-retentive prodrug gabapentin enacarbil that are approved for the management of postherpetic neuralgia. The aims of this article are to review the pharmacology of gabapentin and its use in pain management. Chemistry Gabapentin, a structural analogue of GABA, is a water-soluble, bitter-tasting, white crystalline substance with a structure resembling GABA with a cyclohexane ring incorporated ( Fig. 1 ). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is especially effective at relieving allodynia and hyperalgesia in animal models. It has been shown to be efficacious in numerous small clinical studies and case reports in a wide variety of pain syndromes. Although it has been known for some time that gabapentin must bind to the α 2 δ-1 protein in order to act pharmacologically (see Pharmacodynamics), the three-dimensional structure of the α 2 δ-1 protein with gabapentin bound (or alternatively, the native amino acid, L-Isoleucine bound) has only recently been obtained by cryo-electron Gabapentin is chemically known as -[1-(aminomethyl) 2 cyclohexaneacetic acid]. Gabapentin closely resembles pregabalin, a schedule V drug under the Controlled Substances Act in its chemical structure and pharmacological activity. The chemical structure of gabapentin is derived from the addition of a lipophilic cyclohexyl group Gabapentin capsules are given orally with or without food. Gabapentin capsules should be swallowed whole with plenty of water. If gabapentin dose is reduced, discontinued, or substituted with an alternative medication, this should be done gradually over a minimum of 1 week (a longer period may be needed at the discretion of the prescriber). PLR regulations require that the following statement is included in the Highlights Indications and Usage heading if a drug is a member of an EPC [see 21 CFR 201.57(a)(6)]: Gabapentin is a medication commonly prescribed to treat various conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. This guide aims to educate patients about important considerations, including dosage instructions, potential side effects, and precautions, to ensure safe and effective use of gabapentin. While gabapentin's mechanism of action is generally understood, it appears to be a pharmacologic option for treating issues involving the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor system. Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology. Introduction. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The There were only some studies with class I evidence that assessed the effectiveness of gabapentin in patients with intractable partial seizures. 23 Doses experienced varied from 600 mg/day to 1,800 mg/day. 24 Rajna P and Szijarto E 25 acknowledged the efficiency and safety of gabapentin (GBP) in idiopathic or crypto/symptomatic partial epilepsy Following concerns about abuse, gabapentin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Healthcare professionals should evaluate patients carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing gabapentin, and observe patients for signs of abuse and dependence. Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |