Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
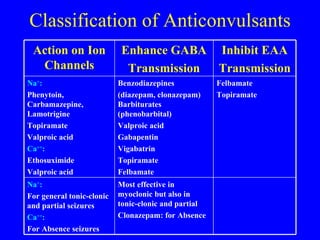
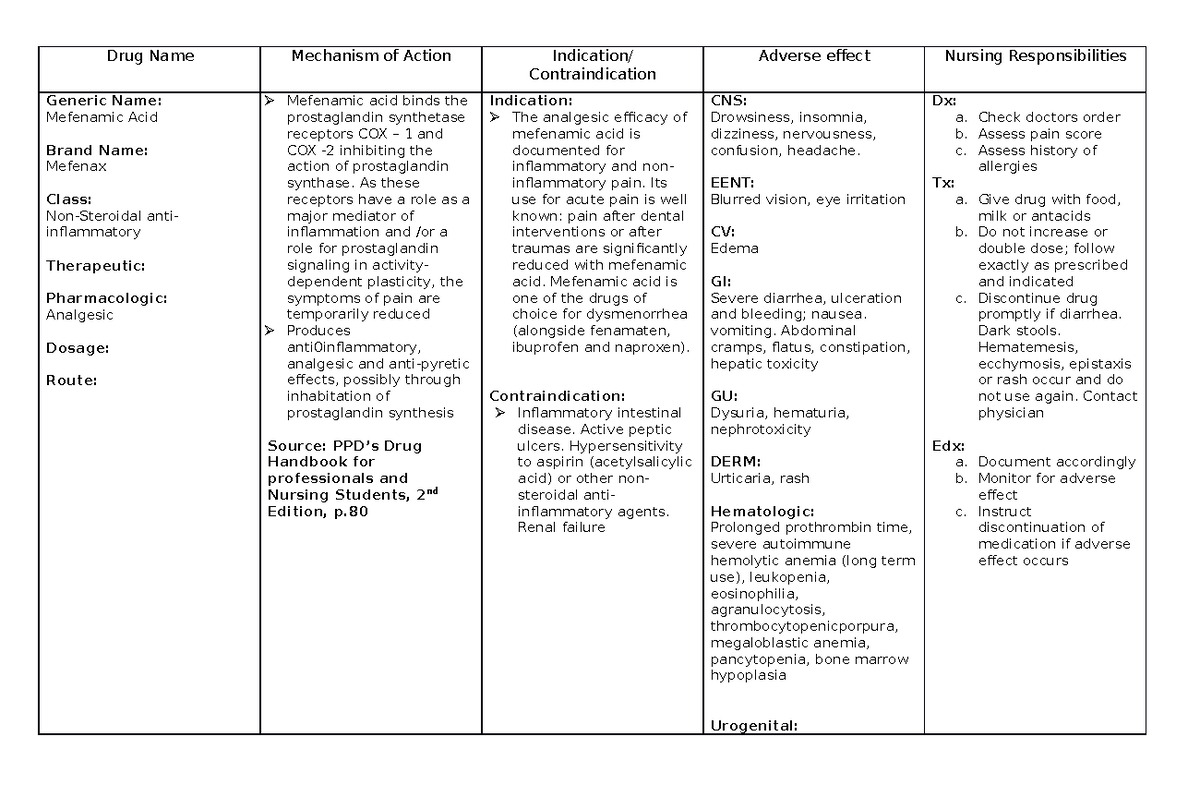
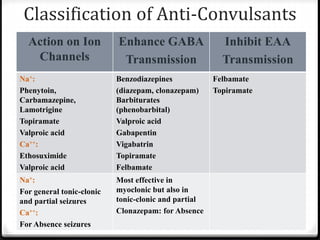
Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. One notable lawsuit emerged when the manufacturers of Neurontin reached a $325 million class action lawsuit settlement over allegations of fraudulent marketing practices. Additionally, there has been growing concern surrounding the link between Gabapentin and serious breathing problems , as well as a lack of substantial evidence supporting its Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Instruct patient to take medication exactly as directed. Patients on 3 times daily dosing should not exceed 12 hr between doses. Take missed doses as soon as possible; if less than 2 hr until next dose, take dose immediately and take next dose 1-2 hr later, then resume regular dosing schedule. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more. Mechanism of action: By inhibiting the voltage-gated calcium channels in the CNS, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (mostly noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin), and therefore decreases epileptogenesis. Clinical effects Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. It is used to treat partial seizures‚ postherpetic neuralgia following shingles and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Gabapentin works by calming overactive nerves in your body. Gabapentin Lawsuit – How to Join. The gabapentin class action lawsuit was filed in 2022 against three pharmaceutical companies – Teva, Pfizer, and Greenstone – accusing them of misrepresenting the drug’s risks and overstating its benefits. To join the gabapentin lawsuit, potential class members need to meet the following criteria: Gabapentin is an alternative therapy option for postherpetic neuralgia and partial seizures that can help individuals and children over the age of three, regardless of whether they have secondary generalization or not. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and characteristics of gabapentin toxicity. The Science Behind Gabapentin’s Mechanism of Action. Understanding what classification gabapentin falls into requires delving into how it works within the body. Although not fully understood, research suggests that gabapentin binds to specific subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin treats seizures by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin relieves the pain of PHN by changing the way the body senses pain. It is not known exactly how gabapentin works to treat restless legs syndrome.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |