Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 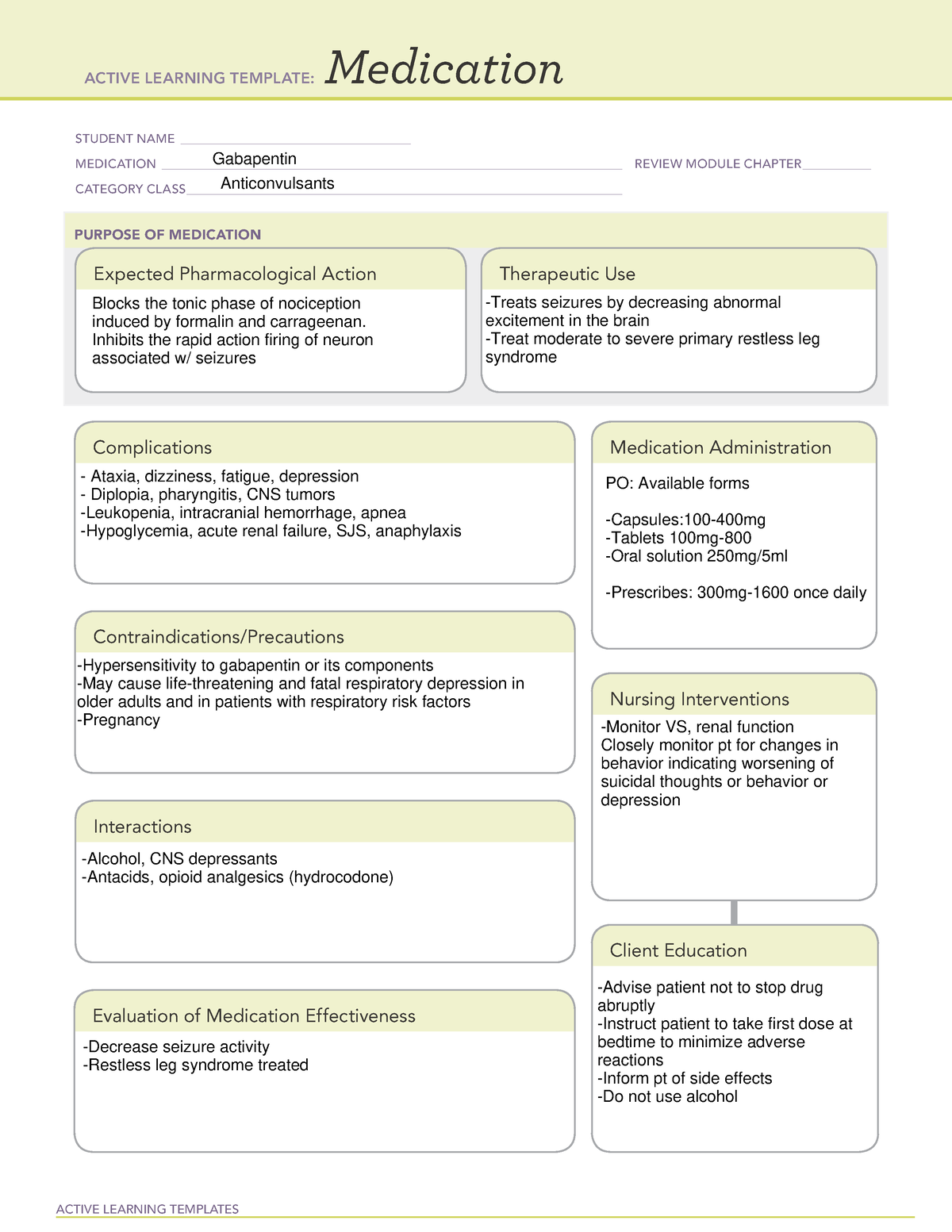 |
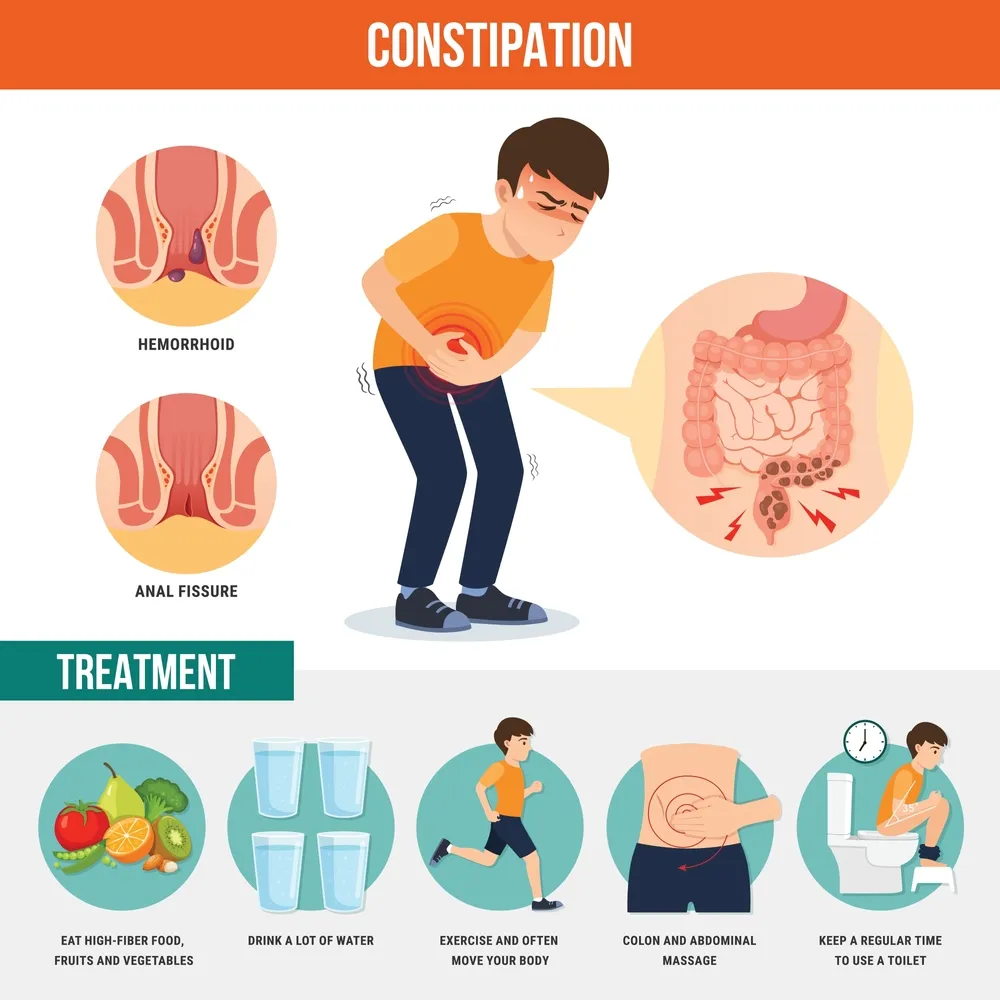
Taking gabapentin can result in constipation, but it is not a common side effect of taking the medication. In clinical trials of the drug, in adults taking gabapentin to treat nerve pain, only about 4% of people reported constipation, while in those taking gabapentin to control seizures, only 2% of people reported constipation as a side effect. Gabapentin is not typically associated with constipation, but some individuals may experience it. Dietary and lifestyle changes, such as increased fiber and fluids, can help manage it. Strategies for managing side effects include dietary adjustments, hydration, exercise, and consult a healthcare provider for persistent or severe symptoms. Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy. Fluid retention. Trouble balancing or controlling movement. Diarrhea or constipation. Nausea and vomiting. Brain fog. Headache. Weight gain. Dry mouth It's not entirely clear how gabapentin works to treat restless legs syndrome. Side effects of gabapentin. Common side effects of gabapentin include: drowsiness or dizziness; headache or blurred vision; nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation; dry mouth; weight gain; swelling of the hands, feet, or ankles; back or joint pain I have had problems with constipation from taking Gabapentin too. Along with many other side effects. I’ve been taking it for 8-9 years. I am drowsy and weak all the time and I can’t do much of anything. I take magnesium and probiotics and they are both helping me to be regular. I am tapering off Gabapentin slowly now at 10% every 12-14 days. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Gabapentin can interact with several medications commonly prescribed to older adults: • Opioid pain medications: Increased risk of respiratory depression • Antacids: Reduced gabapentin absorption if taken simultaneously • Diabetes medications: May require dose adjustments Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. In clinical trials of the drug, in adults taking gabapentin to treat nerve pain, only about 4% of people reported constipation, while in those taking gabapentin to control seizures, only 2% of people reported constipation as a side effect. On the other hand, the evaluation of mean GI symptom scores obtained from GSRS questionnaire, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, indigestion, and reflux, showed that the two groups were matched in terms of the severity of GI symptoms mentioned, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05) However, during treatment (after the treatment relative to Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin is Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. “Gabapentin can cause constipation, but it is not commonly reported in everyone taking the medication. Clinical trials indicate about 4% of the people taking the medication reported constipation as a side effect.” I have had problems with constipation from taking Gabapentin too. Along with many other side effects. I’ve been taking it for 8-9 years. I am drowsy and weak all the time and I can’t do much of anything. I take magnesium and probiotics and they are both helping me to be regular. I am tapering off Gabapentin slowly now at 10% every 12-14 days. Gabapentin can cause a variety of GI side effects including diarrhea, constipation, nausea, and abdominal pain. Studies have found that up to 15-25% of people taking gabapentin experience diarrhea while around 5-10% develop constipation. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Some of the off-label conditions where gabapentin is prescribed include anxiety disorders, headaches, pain, alcohol or drug withdrawal, phobia, etc. The reason why the drug is being prescribed for a variety of conditions is because there is a belief that it is a “safer alternative”. Significant increase in the pressure and corresponding wall tension inducing discomfort or pain were observed in the gabapentin group, but not in the placebo group. Rectal compliance significantly increased after gabapentin, but not after placebo. The postprandial increase of rectal tone was not affected by gabapentin. Gabapentin is safe for cats and is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat pain, anxiety, and feline hyperesthesia syndrome. It has a low risk of side effects when taken at the correct dosage. Gabapentin may cause constipation, but it is not a common side effect. In clinical trials of adults taking gabapentin for nerve pain, only about 4% of people reported constipation. Some people in these trials took an inactive medicine (placebo).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |