Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 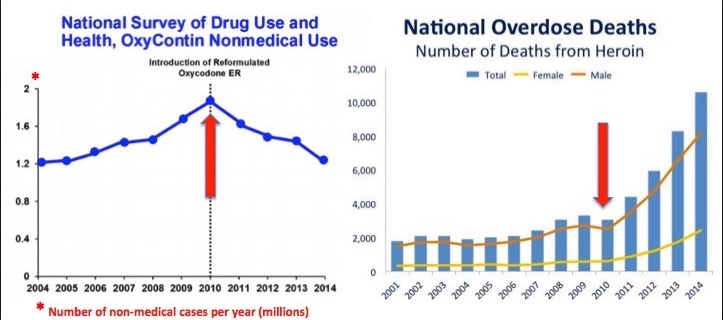 |
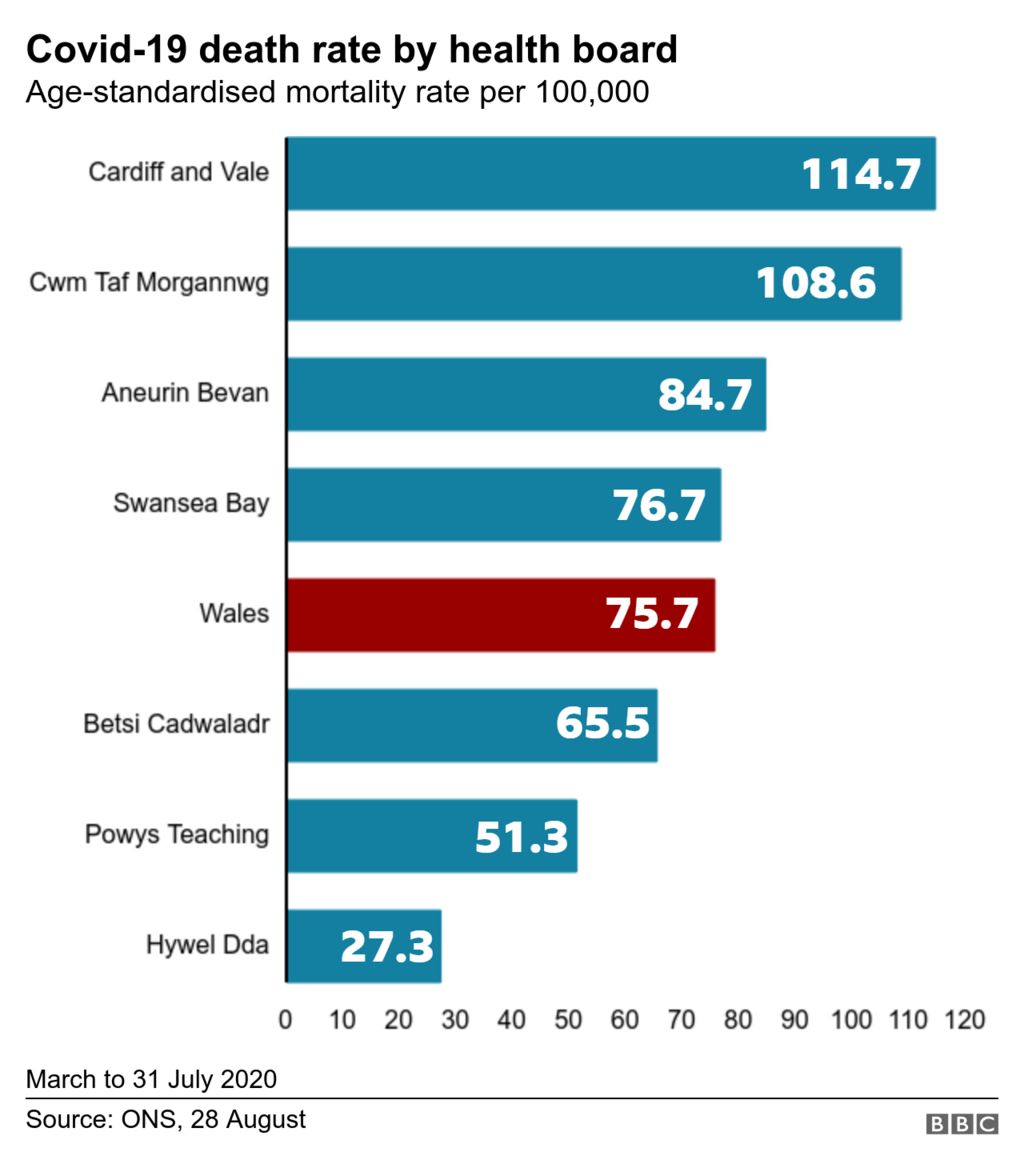
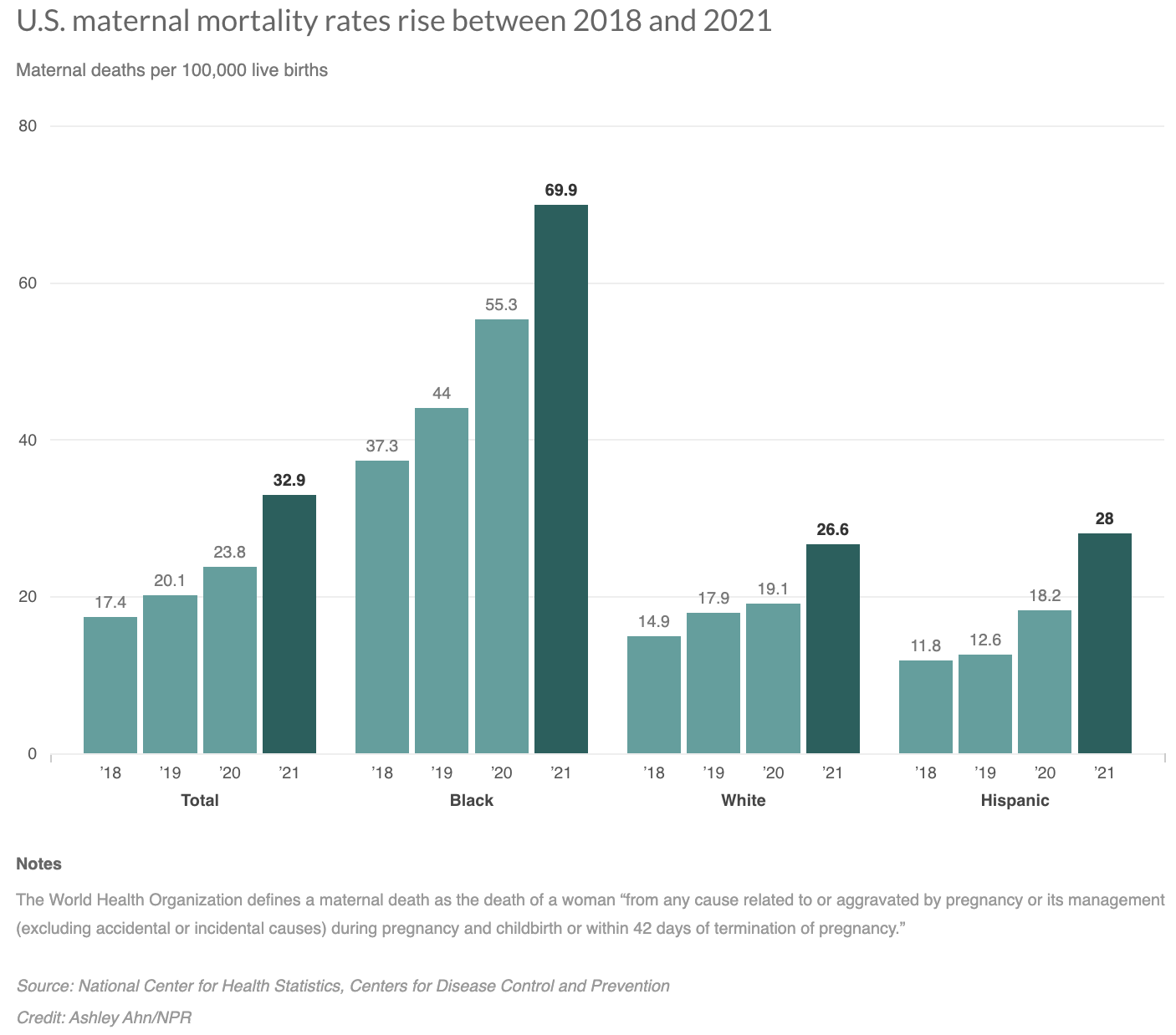
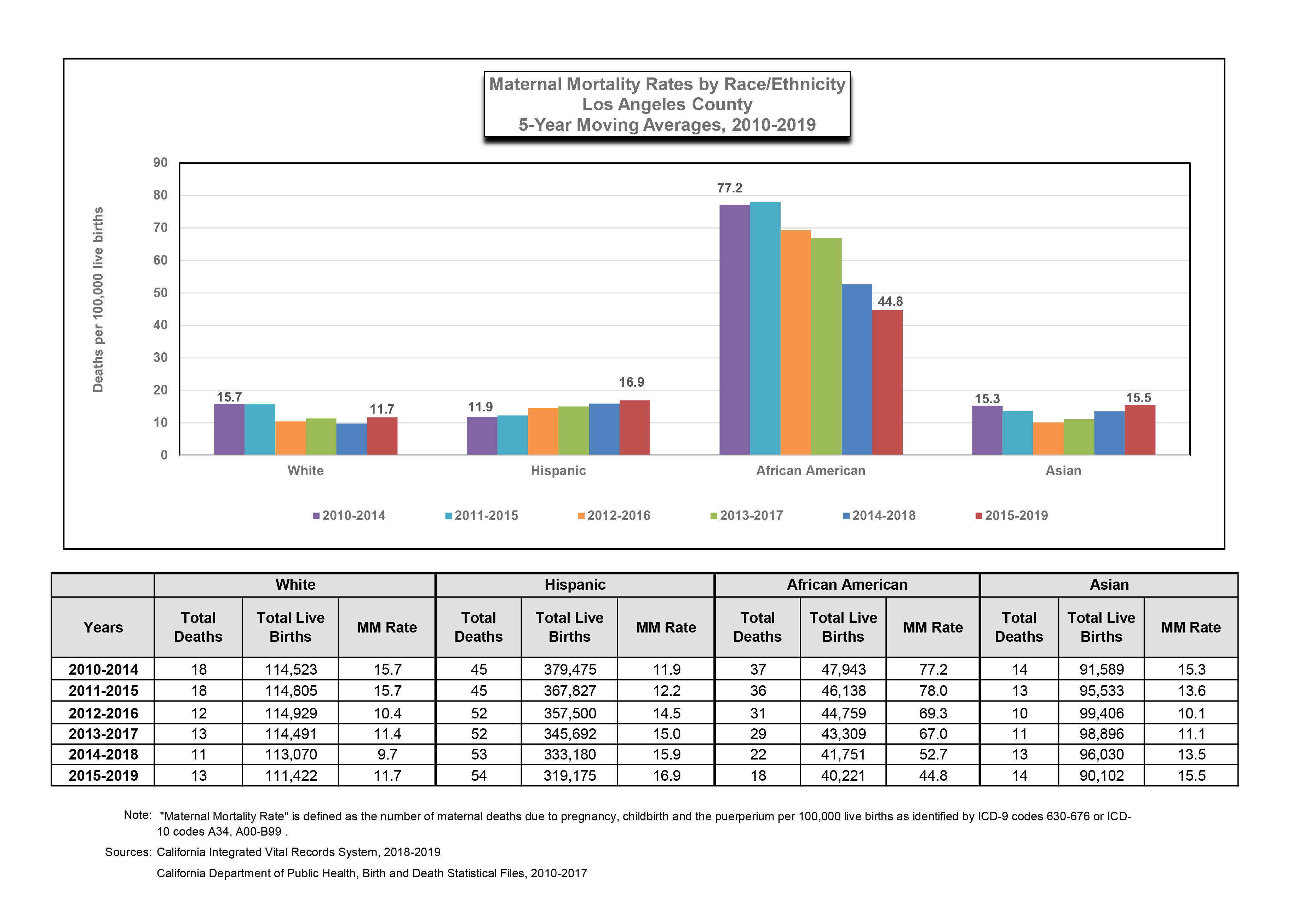
Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. Illicit opioid-involved deaths accounted for 56.8% of overdose deaths with gabapentin detected in the first quarter of 2019 and 69.2% in the last quarter of 2020; this increase was largely driven by illicitly manufactured fentanyl and fentanyl analogs. JAMA. 2022 Jun 28;327(24):2387. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.10100. Although this rate exceeds that expected in a healthy population matched for age and sex, it is within the range of estimates for the incidence of sudden unexplained deaths in patients with epilepsy not receiving gabapentin (ranging from 0.0005 for the general population of epileptics to 0.003 for a clinical trial population similar to that in Only 19 deaths involving gabapentin were identified as possible suicides during the five-year study period, but there were thousands of gabapentin-related calls each year coded as attempted suicides — including over 10,000 calls in 2017 alone. Gabapentin-involved deaths occurred in 2975 of 5687 decedents (52.3%) with a positive gabapentin test result. Most gabapentin-involved overdose deaths, 83.2%, occurred among non-Hispanic Age-adjusted overdose death rates increased from 2019 (21.6 per 100,000) to 2020 by 31%. (28.3 per 100,000) 5 . Between 2009 and 2016, the prescription rate for GBP doubled from roughly 13 to 27 per 1000 insurance beneficiaries due to an increase in its off-label use for treating nerve pain, epilepsy, and other illnesses. FDA is requiring new warnings about the risk of serious breathing difficulties that can lead to death in patients who use Gabapentinoid products include gabapentin, which is marketed under the Per capita overdose deaths involving gabapentinoids/Z-drugs increased almost continuously since 1999, averaging 15.8% annual growth. This rate increased to 32% in 2020, primarily due to overdoses involving synthetic opioids. The suicide attempt rates before and after gabapentin was prescribed were investigated in a cohort of 131,178 patients. The investigators found no significant differences in suicide attempt rates before (3.45/1000 patient years) versus after gabapentin prescription (3.45/1000 patient years). Data on 62,652 overdose deaths that occurred during 2019–2020 in the 24 jurisdictions were entered in SUDORS; among 58,362 deaths with documented toxicology results, a total of 5,687 (9.7%) had gabapentin detected on postmortem toxicology. Gabapentin-involved deaths occurred in 2975 of 5687 decedents (52.3%) with a positive gabapentin test result. Most gabapentin-involved overdose deaths, 83.2%, occurred among non-Hispanic White persons. More than half of gabapentin-involved deaths, 52.2%, occurred among persons aged 35 to 54 years. We determined concomitant gabapentin exposure among 1,256 individuals (cases) who died of an opioid-related cause and 4,619 matched controls. We found that concomitant gabapentin and opioid exposure was associated with a 49% higher risk of dying from an opioid overdose. What do these findings mean? With great interest we read the article of Tardelli et al. about the perceived increase of overdose-deaths “due to” non-benzodiazepine hypnotics including gabapentinoids (GPT) over the last two decades extrapolated from USA National Center for Health Statistics data.1 We have not seen comparable phenomena in Germany, despite the highest Western-European rate of non-medical GPT-use.2 German The 239 deaths in 2022 represent a 10% increase from the 217 deaths in 2021. The rate of death in 2021 was 33.6 per 100,000 Vermonters while the rate for 2022 is 37.0 fatal overdoses per 100,000 Vermonters. These rates are statistically similar. Of note, the percent increase from 2021 to 2022 was less than that from 2020 to 2021 (10% versus 37%). Gabapentin likely contributed to 5% of deaths from overdose with any substance in 2019 to 2020, according to a new study. The first death with gabapentin detected occurred in 2004, and with pregabalin in 2006. The number of deaths following gabapentinoid use has increased (Figure 1A): 8.9% of all NPSAD reports in 2014 detected a gabapentinoid, rising to 32.3% in 2020. In 47.1% of the fatality cases, gabapentin was directly involved in death. Most gabapentin fatalities had several other intoxicants present (opioids, over-the-counter medications, antianxiety, and antidepressant medications). A recent report from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that between 2019 and 2020, coroners and medical examiners detected gabapentin in 5687, or almost 10%, of the 58 362 overdose deaths in 23 states and the District of Columbia that had available toxicology results. Officials ruled that gabapentin was a cause of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |