Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
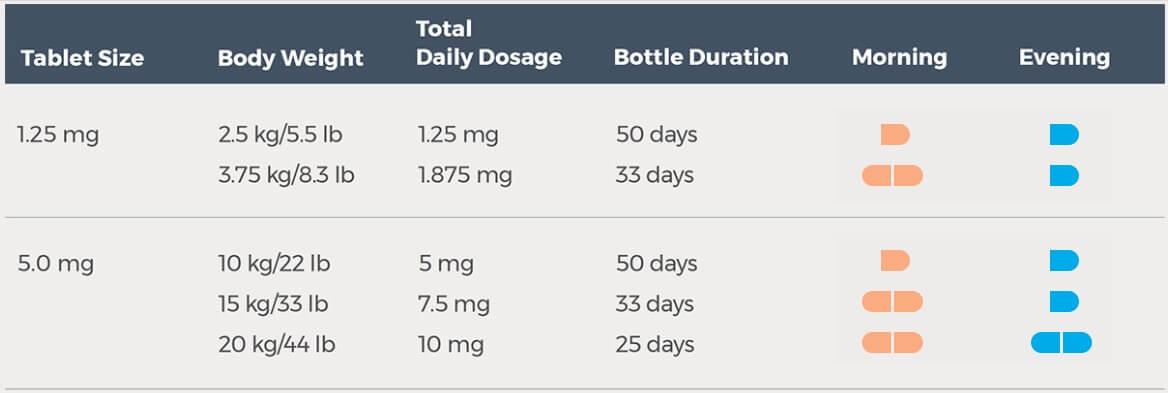
In veterinary medicine, Gabapentin is used “off-label” and in conjunction with other meds to prevent neuropathic pain and manage pets with seizures. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about Gabapentin for dogs. We will go through the medication’s benefits and considerations. Gabapentin . Gabapentin is a recent addition to the human anti-convulsant market, which has primarily been used as an adjunctive drug for humans with uncontrolled partial seizures with and without secondary generalization. Gabapentin is well absorbed from the duodenum in dogs with maximum blood levels reached in 1 hour after oral administration. Trazodone + gabapentin Trazodone + acepromazine Trazodone + clonidine + gabapentin Trazodone + acepromazine + gabapentin *Lorazepam can be added to any of the above combinations in non-fractious patients. All are safe premeds for injectable sedation in healthy dogs. Oral premed cocktails for cats: Lorazepam + acepromazine Acepromazine + gabapentin Gabapentin (Dog or Cat) This medication is particularly beneficial for neurologic/spinal pain as it alters how pain is transmitted in the spinal cord. It also has anti-anxiety effects. Sedation does not appear to be a common problem with gabapentin use in dogs, but occasionally occurs. There are two clinical reports of gabapentin use as an add-on drug for dogs with refractory epilepsy. Pregabalin has been used in human medication primarily for nerve pain and can be similarly used for pets. It came into veterinary use in 2024 when it was approved for cats needing help with transport anxiety. In a 2017 quick poll by the Veterinary Information Network, an online community for the profession, 81% of 2,064 respondents said they prescribed gabapentin in some way for acute pain management. When the same poll question was asked in 2024, the number had risen to 93% of 2,779 respondents. Gabapentin . Gabapentin is a recent addition to the human anti-convulsant market, which has primarily been used as an adjunctive drug for humans with uncontrolled partial seizures with and without secondary generalization. Gabapentin is well absorbed from the duodenum in dogs with maximum blood levels reached in 1 hour after oral administration. Trazodone + gabapentin Trazodone + acepromazine Trazodone + clonidine + gabapentin Trazodone + acepromazine + gabapentin *Lorazepam can be added to any of the above combinations in non-fractious patients. All are safe premeds for injectable sedation in healthy dogs. Oral premed cocktails for cats: Lorazepam + acepromazine Acepromazine + gabapentin Along with published data in animals, there seems to exist a strong rationale for using gabapentin in dogs and cats for the treatment of chronic pain. The drug is well tolerated in dogs and cats. Possible adverse-effects include sedation, nausea, and vomiting. Specific COX-2 inhibitor approved for use in dogs. No safer in renal compromise. Gabapentin 3–10 mg/kg PO q 24 hrs. The best effects are seen when used in combination with other analgesics such as NSAIDs or paracetamol (acetaminophen). Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate 13–15 mg/kg chondroitin sulfate PO q 24 hrs. Gabapentin is usually used to manage chronic pain, especially nerve-related pain. It is also used (primarily in cats) to relieve anxiety associated with veterinary procedures, travel, and other fear-generating situations. Gabapentin can also be used as an additional medication in seizure management. Gabapentin can treat and reduce the frequency of seizures and is commonly used as an anticonvulsant to treat or prevent seizures in dogs. Gabapentin may also be used to provide pain relief for dogs, particularly when other medications have proved ineffective or are not well tolerated. Separation anxiety is one of the most common and most devastating behavioral conditions diagnosed world-wide in pet dogs. In the absence of treatment, affected dogs are often relinquished or euthanized. Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Sedation is the main potential side effect of gabapentin, and the level of sleepiness varies from patient to patient. Overall, gabapentin is safe for dogs, but it’s important to follow certain precautions. Never give your dog liquid gabapentin made for humans. The reason isn’t the gabapentin, but the Gabapentin is well absorbed from the duodenum in dogs with maximum blood levels reached in 1 hour after oral administration. The elimination half-life of gabapentin in dogs is 3-4 hours in dogs, meaning that it may be difficult to attain steady state levels in dogs with tid dosing. Studies in humans and laboratory animals indicate that perioperative administration of gabapentin to animals with nerve injury may reduce the potential establishment of, or ongoing, neuropathic pain. Based on blood levels in dogs, dose at 10 mg/kg PO q 8 h (5 mg/kg PO in cats), increasing as needed to effect (dose range 10–15 mg/kg). For mild to moderate fear and anxiety in dogs, trazodone, clonidine, benzodiazepines (e.g. alprazolam, diazepam, lorazepam), gabapentin, imepitoin or dexmedetomidine oromucosal gel might be effective for car ride anxiety, veterinary visits and procedures. 3 In cats, gabapentin, trazodone and benzodiazepines (e.g. lorazepam, alprazolam) can be Gabapentin is usually used to manage chronic pain, especially nerve-related pain. It is also used (primarily in cats) to relieve anxiety associated with veterinary procedures, travel, and other fear-generating situations. Gabapentin can also be used as an additional medication in seizure management.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |