Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 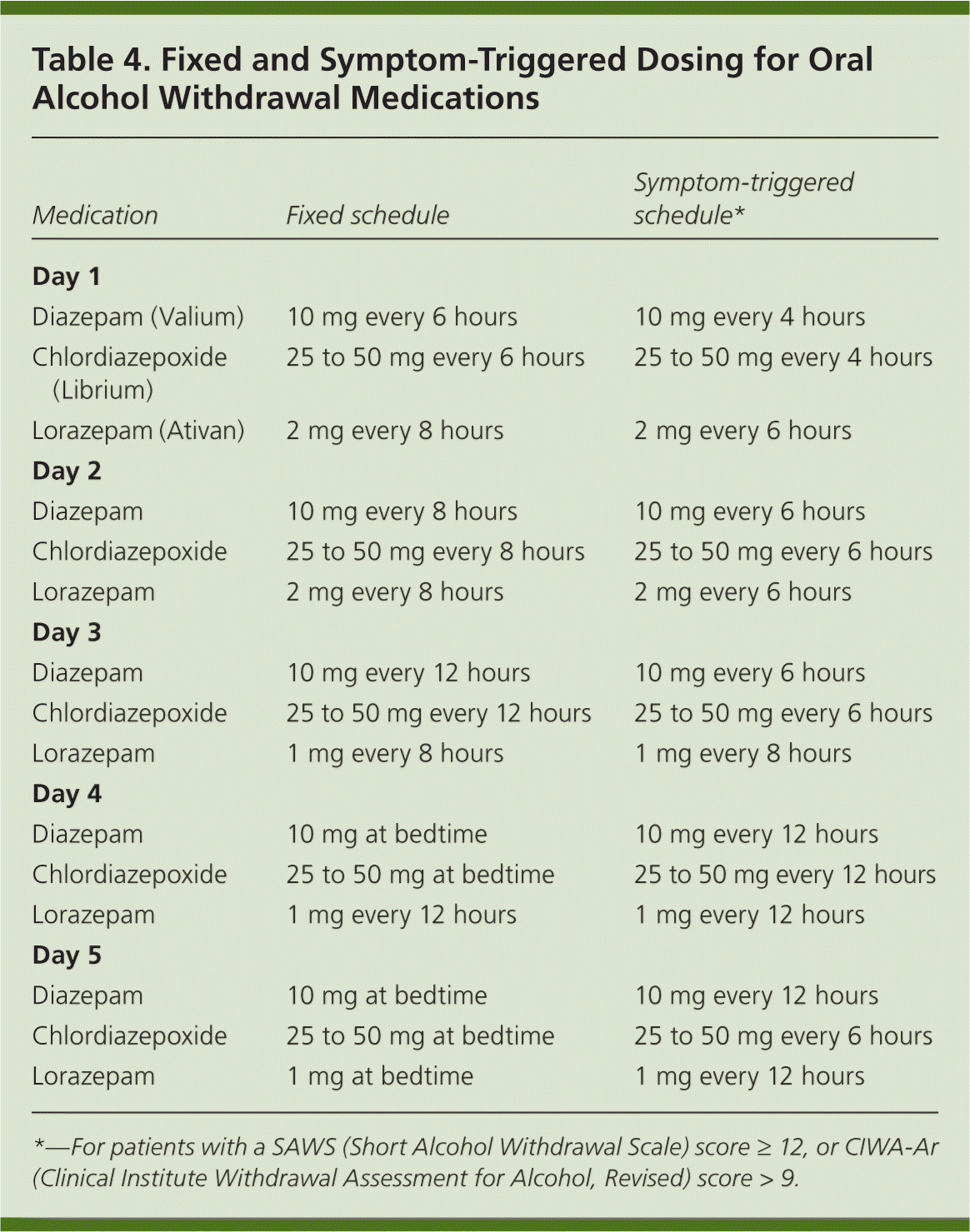 |
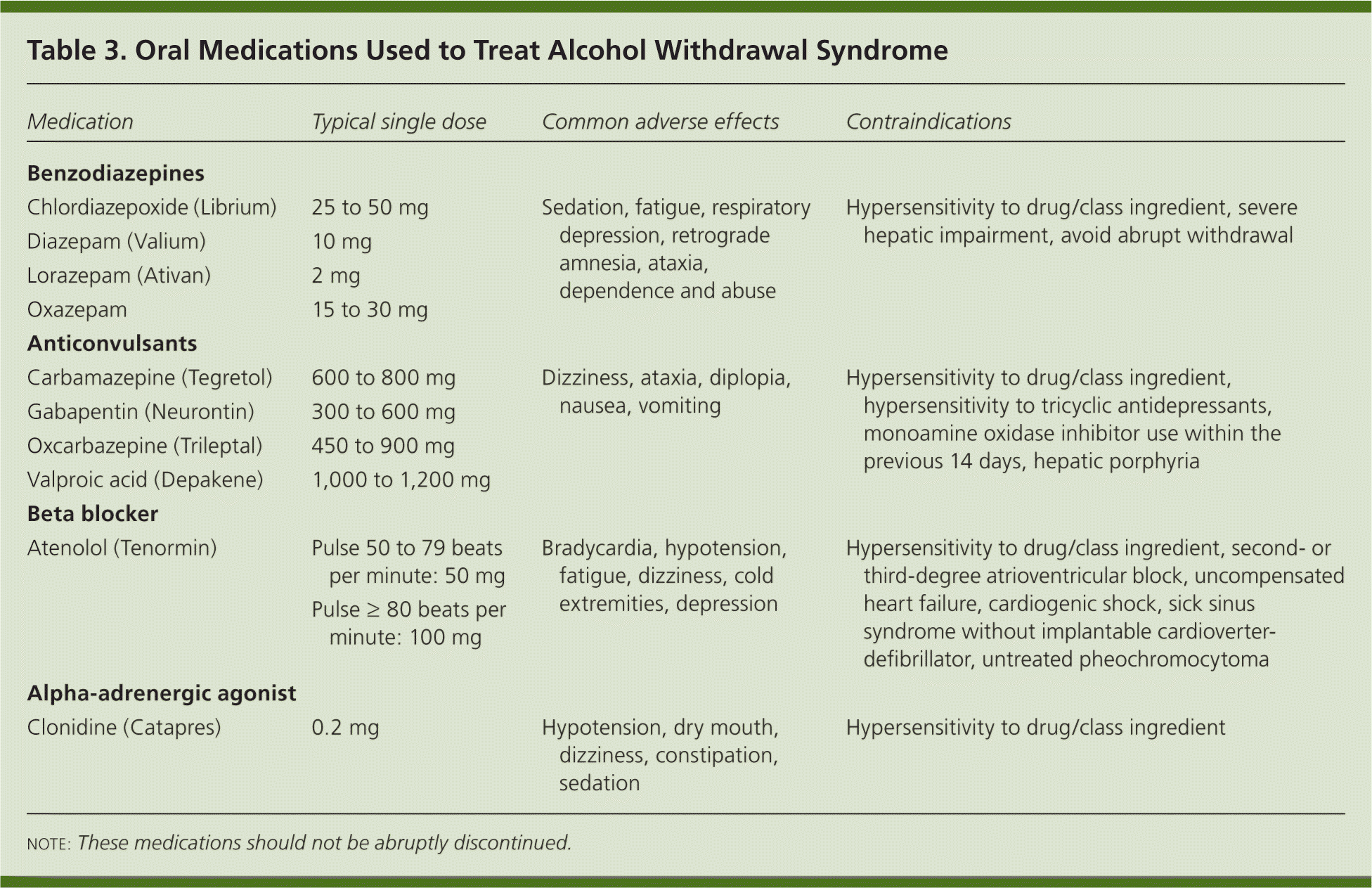
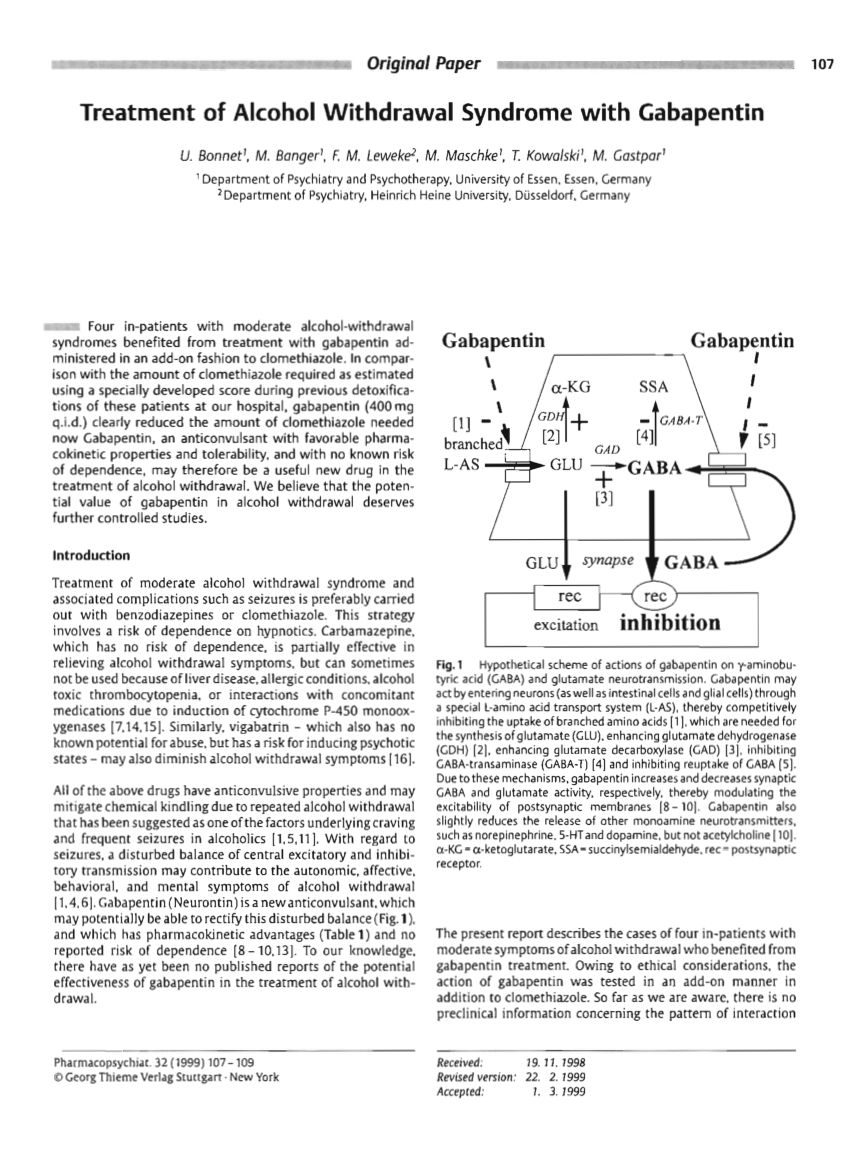
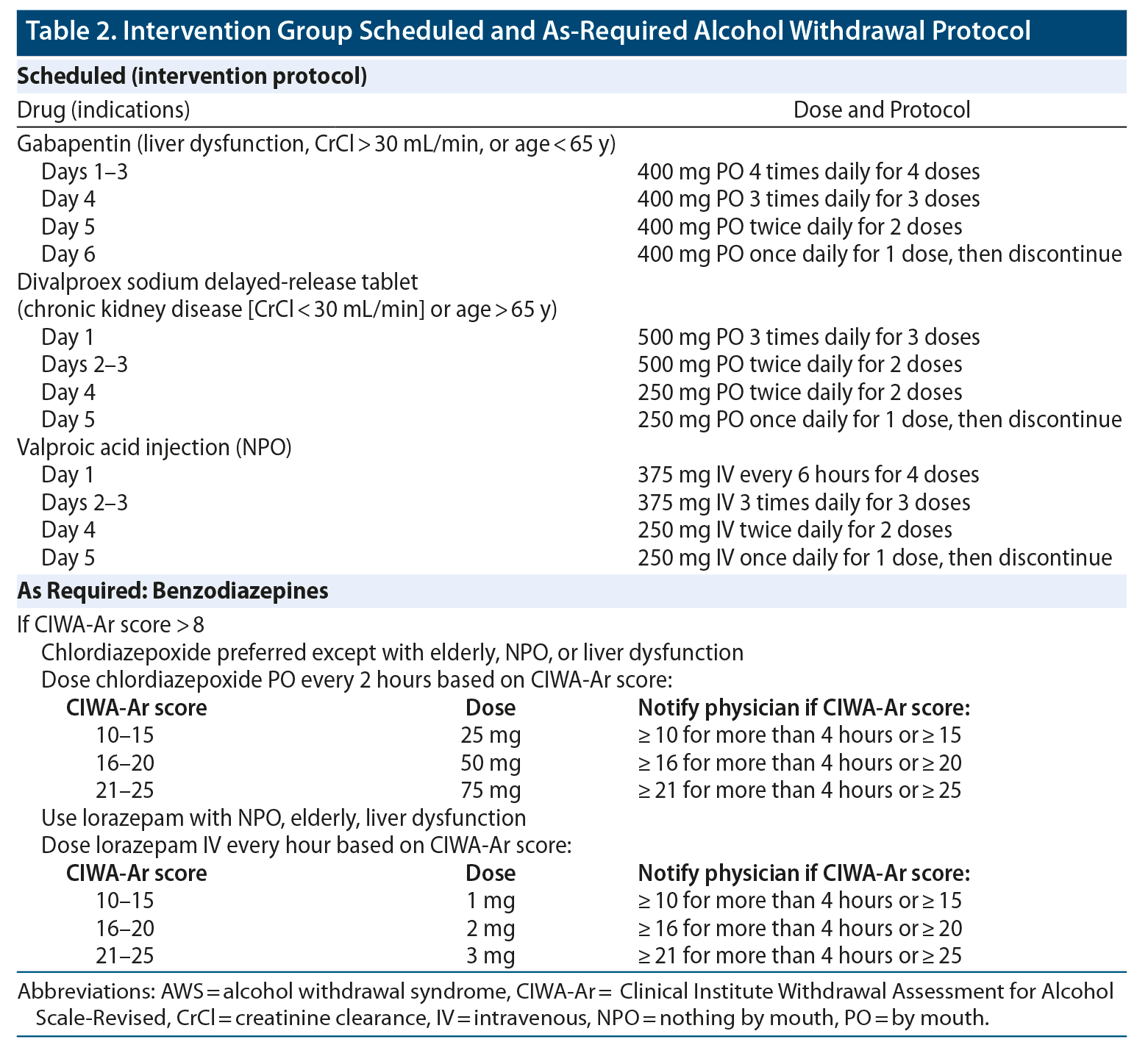
Alcohol is believed to potentiate the actions of GABA, a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, and suppress the actions of glutamate, a major excitatory neurotransmitter. Rapid cessation of alcohol use results in overall CNS hyperactivity and lower seizure threshold. The following dosage information may be useful if you are considering taking gabapentin for withdrawal: Since it is a generic drug, dosage amount may vary depending on the brand and different brand name tablets are not interchangeable. 600-1800 mg per day is typically effective to mitigate symptoms. Of note, Myrick and colleagues (2009) followed-up 100 subjects treated with double-blind gabapentin (2 dose conditions: ≤900mg/d and ≤1200mg/d) or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine, ≤6mg/d) in a 4-day alcohol withdrawal study, and found significantly decreased drinking, craving and sedation during the 6-day post-withdrawal follow-up period in measures included total average benzodiazepine and gabapentin dosage used during hospitalization and the development of severe complications of withdrawal including seizures or delirium. Finally, gabapentin can ease initial alcohol withdrawal symptoms and make it easier for people to transition to daily naltrexone. You should never combine naltrexone and gabapentin without consulting a medical professional first. But the combination is worth looking into if you’ve struggled with naltrexone alone. Side Effects of Gabapentin The authors concluded that gabapentin in a dose of 3,200 mg in the first 24 hours is useful only for milder forms of alcohol withdrawal. Hence, subsequent efforts on the use of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal have focused on outpatients. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that may help reduce symptoms and promote abstinence in alcohol withdrawal syndrome. However, it can cause serious side effects and should not be mixed with alcohol. Learn more about gabapentin, its uses, and its comparison with benzodiazepines. To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol Anton RF, Latham P, Voronin K, et al. Efficacy of Gabapentin for the Treatment of Alcohol Use Disorder in Patients With Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med 2020; 180:728. Kranzler HR, Feinn R, Morris P, Hartwell EE. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder. Objective: The current meta-analysis synthesizes previous findings on the effect of gabapentin on alcohol withdrawal and craving. Data Sources: Using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology, a search for relevant English-language literature published between January 1999 and February 2019 was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar with the Study objective: Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). The aim of We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). The gabapentin dosing schedule was 400 mg t.i.d. for 3 days, 400 mg b.i.d. for 1 day, and then 400 mg for 1 day. Scores on the alcohol withdrawal scale over four daily visits decreased from an average of 17 on day 1 to averages of 11, 2, and 0, respectively. benzodiazepines for alcohol withdrawal. The active group (n = 40) received gabapentin as well as a symptom-triggered alcohol withdrawal protocol of benzodiazepine. The control group (n = 43) received only the symptom-triggered alcohol withdrawal protocol without gabapentin. Alcohol use disorder affects about 14% of US adults Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. For instance, studies have highlighted the efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal symptoms (Mariani et al. 2006; Myrick et al. 2009). Additional trials found a benefit of combining gabapentin with naltrexone (Anton et al. 2011) and with flumazenil (Anton et al. 2009; Schacht et al. 2011). These studies consistently However, it can help with some alcohol withdrawal symptoms, making detoxification easier to handle. The exact mechanism of how gabapentin interacts with alcohol withdrawal is not fully understood, but medical professionals believe it influences neurotransmitter activity in the brain. Why You Shouldn’t Mix Alcohol With Gabapentin Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |