Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
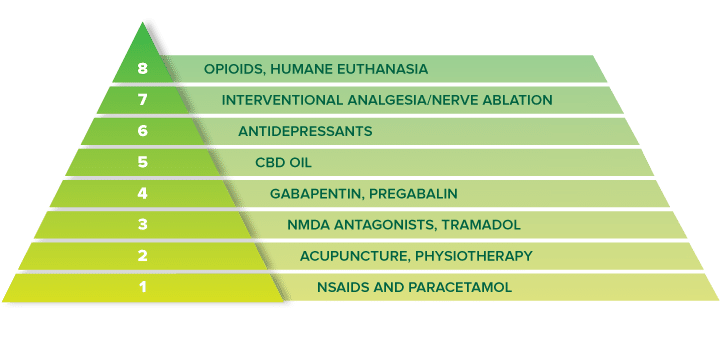
Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. For treating nerve pain, one may recommend three doses of Gabapentin in a day divided into morning, afternoon, and evening doses. One may start with a low dose of 100 mg at night. Treatment. Trigeminal neuralgia treatment usually starts with medications, and some people don't need any additional treatment. However, over time, some people with the condition may stop responding to medications, or they may experience unpleasant side effects. The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain trials is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. 3 This means the minimum effective dose is 600 mg 3 times a day. Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. Gabapentin has been shown to be beneficial in treating several types of neuropathic pain; however, the mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic effect is still unknown.¹ It is suggested that gabapentin may block the calcium channel alpha(2)delta (a2d)-1 receptor in the brain. Gabapentin has been associated with minor dose-related adverse effects but no serious events. 16, 19, 23 Clinical trials of gabapentin monotherapy for epilepsy have reported dizziness in 7% to 15% and somnolence in 3% to 7% of patients taking from 300 to 1,800 mg/day. 6 Higher doses of 900 to 3,600 mg/day in patients with neuropathic pain have Gabapentin for Neuropathic Pain Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. TN is a chronic pain disorder of the trigeminal nerve that causes sudden, intense facial pain. TN may be caused by vascular contact with the trigem-inal nerve (classic TN), an underlying pathology such as multiple sclerosis or tumor (secondary TN), or no known cause (idiopathic TN). in dose range is 900mg to 3600mg daily (dose reduced in renal impairment). Treatment can be initiated at a dose of 900mg/day given as three equally divided doses or at a sl. wer rate as described below: Step 1: Gabapenti. be increased in 300mg increments every two to three days until tolerated. The dose should be increased to either t. Horizant (gabapentin enacarbil) is an extended release tablet used to treat restless legs syndrome and for the pain from having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). Generic brands of gabapentin capsules, USP are used for postherpetic nerve pain and for add on therapy for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Warnings I am currently on 1800 mg/day of gabapentin, but am still having a fair amount of pain. On a scale of 1 to 10, the background level is about a 2 with occasional flares to a level of 5 or 6. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. If you have chronic pain in the face, we might prescribe you a medicine called gabapentin. Chronic pain (also called persistent pain) is long-term pain that lasts for more than 3 months. Gabapentin (Neurontin ® ) is used to treat epilepsy, or to treat nerve pain. In the CNS, gabapentin binds the N-type calcium channels, resulting in a decrease of calcium entry into the neurons. Gabapentin is started orally at a dose of 300 mg daily for TGN and can be increased by 300 mg every 2 to 3 days as tolerated. The maximum daily dose of gabapentin is 1,800 mg. Gabapentin therapy was initiated with a dosage of 200–600 mg/day. Pain intensity was assessed using a modified numerical rating scale (m-NRS) (0, no pain; 10, pain equal to that experienced on the day gabapentin therapy was initiated). In addition, the side effects were also recorded. The preferred treatment for trigeminal neuralgia consists of antiepileptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. Of the 92 who had trigeminal pain include: temporomandibular joints dysfunction, persistent idiopathic facial pain and rarely migraine with facial pain. In cases with paroxysmal short-lasting pain episodes, trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias such as short-lasting unilateral neuralgi-form headache attacks (SUNHA) should be considered Dosage for nerve pain. The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. Changes to your dose. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same. How to take it Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is one of the most common causes of facial pain seen in dental and neurologic practices. This classic neuropathic pain disorder has been known for centuries.1 The International Headache Society (IHS) defines TN as a “unilateral disorder characterized by brief electric shock-like pains, abrupt in onset and termination, and limited to the distribution of one or more In this review, based on a systematic search of relevant literature, we aim to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |