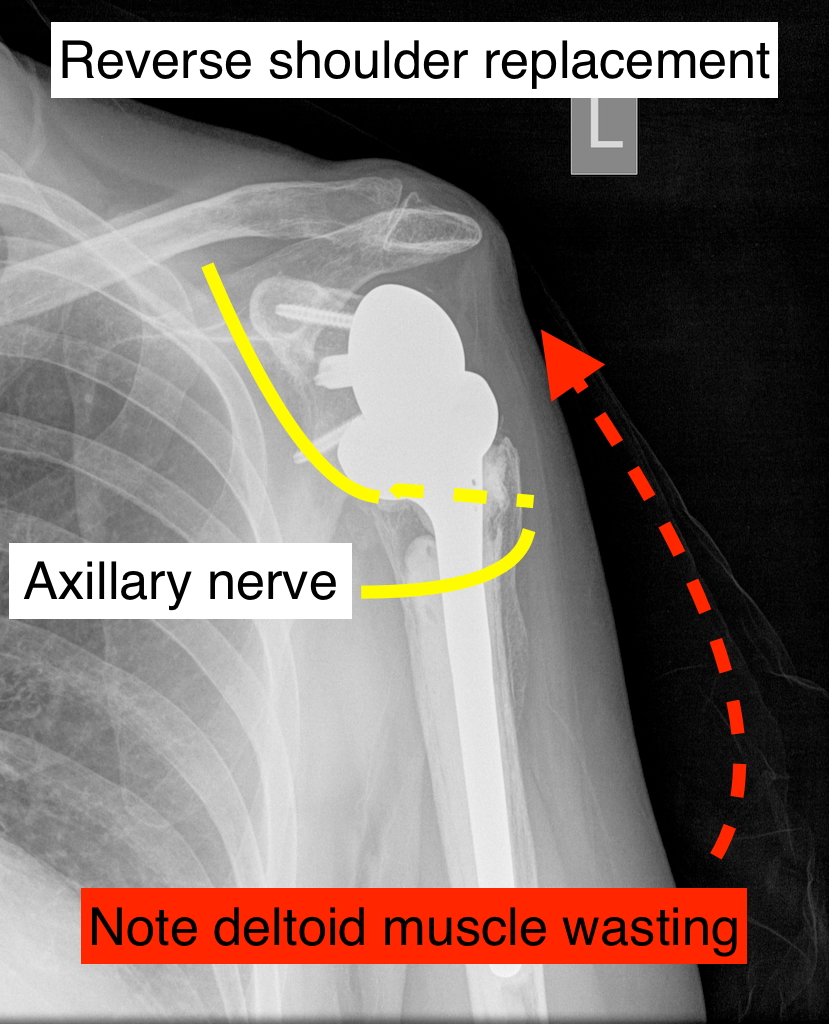
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
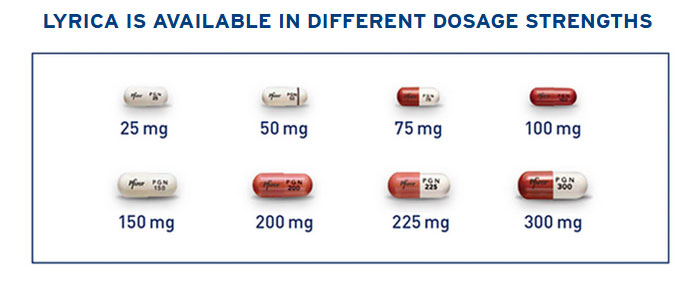
1. Gabapentin/Neurontin 300 mg (nerve pain control) Take 2 pills the night before your surgery (600 mg total) After your surgery, begin taking 1 pill (300 mg) 3 times a day for the next 5 days; Depending on what time your surgery ends, start taking the Gabapentin at lunch or dinner For treating nerve pain, one may recommend three doses of Gabapentin in a day divided into morning, afternoon, and evening doses. One may start with a low dose of 100 mg at night. One article described the effects of gabapentin on traumatic nerve injury or post-surgery nerve pain and found that gabapentin provided significantly better pain relief when compared to placebo, with more patients having at least a 30% pain reduction and less sleep interference due to pain. 28 Dolgun et. al. assessed the acute neuropathic pain Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. Perioperative gabapentin, 1200 mg, administered preoperatively plus 600 mg every 8 hours continued for 72 hours after surgery did not affect time to pain cessation, the rate of pain resolution, or the proportion of patients with chronic pain at 6 months or 1 year following surgery. Eleven studies (25,28–33,36,38–40) administered gabapentin as a single dose within 1 h to 2 h before surgery; the remainder involved initiating therapy on the day before surgery or continuing it for up to 10 days after surgery . Four unpublished studies met inclusion criteria; in three, participants had pain following dental surgery, and one followed major orthopaedic surgery; 177 participants were treated with a single dose of gabapentin 250 mg, 21 with gabapentin 500 mg, and 172 with placebo. This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Given the significant differences between the studies and the possibility of Gabapentin, an antiepileptic drug, is frequently used off-label to manage postoperative nerve pain due to its antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic properties. This article synthesizes research findings on the optimal dosage and efficacy of gabapentin for managing nerve pain after surgery. One article described the effects of gabapentin on traumatic nerve injury or post-surgery nerve pain and found that gabapentin provided significantly better pain relief when compared to placebo, with more patients having at least a 30% pain reduction and less sleep interference due to pain. 28 Dolgun et. al. assessed the acute neuropathic pain Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic Avoid pre-operative gabapentin doses >600 mg due to increased risk of side effects • Level 3 Scheduled gabapentin doses should be avoided in the post-operative period unless otherwise indicated for neuropathic pain Initial gabapentin doses for post-operative neuropathic pain should be limited to 300 mg per 24 hours Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. After taking a dose, IR gabapentin starts to work in the body within two to three hours. However, the full effects of gabapentin can take one to two weeks to become noticeable, and some people may need to wait longer to experience significant pain reduction. Post-operative gabapentin (600 mg) may be equally effective as a preoperative dose in decreasing PACU narcotic use. Concomitant administration of gabapentin as part of a multi-modal pain management strategy including narcotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), and muscle relaxants does not improve pain scores. They used a gabapentin dose of 1.2 g per day treatment 1 hour before surgery and for 2 days after surgery and investigated its effect on postoperative acute pain. Yu L, Ran B, Li M, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine 2013; 38:1947–1952. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ] Evaluation of the optimal preemptive dose of gabapentin for postoperative pain relief after lumbar diskectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005;17(2):65–68. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000151407.62650.51. Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |