Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
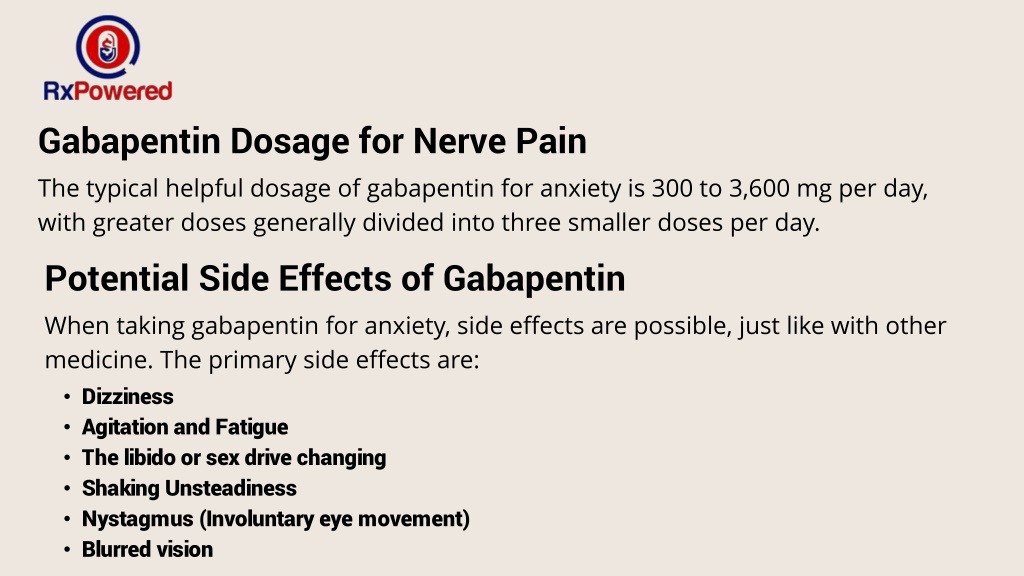 | 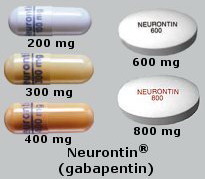 |
For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Dosage (adult) Adverse effects Notes Cost* Antivirals: Sweeney M. Real-world treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia with gabapentin or pregabalin. Clin Drug Investig. 2013;33(1):35-44. gabapentin systemic Drug class: gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs For consumers: dosage, interactions, side effects For professionals: AHFS DI Monograph, Prescribing Information Off-label: Yes Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Start with 100 mg at night, increasing by 100 mg a day until pain is significantly reduced, intolerable adverse effects occur, or a maximum daily dosage of 3600 mg (1200 mg three times a day) is reached [Dworkin, 2007]. This is a phase IV clinical study of how effective Gabapentin (gabapentin) is for Occipital neuralgia and for what kind of people. The study is created by eHealthMe from 17 Gabapentin users and is updated continuously. Occipital neuralgia is usually due to trauma to the occipital nerve (ON), often caused by an auto-accident where the head impacts the headrest. Other causes are spondylosis of the upper cervical spine (C1-C2), or rarely focal neuropathies due to diabetes or tumor (Ehni and Benner, 1984). The Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain recently sponsored the development of evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Tricyclic antidepressants, dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine, calcium channel α2-δ ligands (ie, gabapentin and pregabalin), and topical lidocaine were Occipital Neuralgia - Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Key Points: Occipital neuralgia may be a cause of head pain originating in the occipital region (back of the head). 1. Pain is episodic, brief, severe, and shock-like. It originates from the occipital region and radiates along the course of the occipital nerves. 2. Home; Conditions; Occipital Neuralgia; What You Need to Know about Occipital Neuralgia By Mark R. McLaughlin, MD, FACS, FAANS. Just imagine the discomfort and shock. One minute you are fine, the next, you are suffering from a headache unlike any you have ever experienced — pain described as throbbing, like an electrical shock, one that seems to pierce your upper neck, back of the head and In our own experience, it is the most effective treatment for occipital neuralgia with response rates exceeding 90%. Conservative complementary treatments that help manage the pain include: physical therapy. Our next treatment of choice is typically botulinum toxin injections. After seeing many doctors, I have most recently been diagnosed with occipital neuralgia and prescribed gabapentin. It has been the most helpful medication that has helped calm my occipital neuralgia. I take 600 mg 3x a day. Occipital neuralgia is a form of neuropathic head and/or neck pain characterized by a unilateral or bilateral paroxysmal shooting or stabbing pain in the posterior part of the scalp, involving the greater, lesser, and/or third occipital nerve distributions, sometimes accompanied by diminished sensation or dysesthesia in the affected area, and The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain trials is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. 3 This means the minimum effective dose is 600 mg 3 times a day. Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. Pain that lasts for more than 3 months after the onset of a herpes zoster infection is called ‘postherpetic neuralgia’; management options include prevention with vaccination, early antiviral treatment and gabapentinoids, tricyclic antidepressants, controlled release opioids, capsaicin cream and lignocaine patches. In the CNS, gabapentin binds the N-type calcium channels, resulting in a decrease of calcium entry into the neurons. Gabapentin is started orally at a dose of 300 mg daily for TGN and can be increased by 300 mg every 2 to 3 days as tolerated. The maximum daily dose of gabapentin is 1,800 mg. A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak . Occipital neuralgia symptoms can be triggered by certain movements, like turning your head or pressing on your scalp. The symptoms of occipital neuralgia are similar to migraine symptoms. There can be overlap between the two conditions; some people with migraines also have occipital neuralgia. The most common cause of occipital neuralgia is pinched nerves or muscle tightness. You may also develop occipital neuralgia after a head or neck injury. What are the symptoms of occipital neuralgia? Occipital neuralgia symptoms affect your head and neck. If you have occipital neuralgia, your symptoms may occur only briefly. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is one of the most common causes of facial pain seen in dental and neurologic practices. This classic neuropathic pain disorder has been known for centuries.1 The International Headache Society (IHS) defines TN as a “unilateral disorder characterized by brief electric shock-like pains, abrupt in onset and termination, and limited to the distribution of one or more
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |