Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
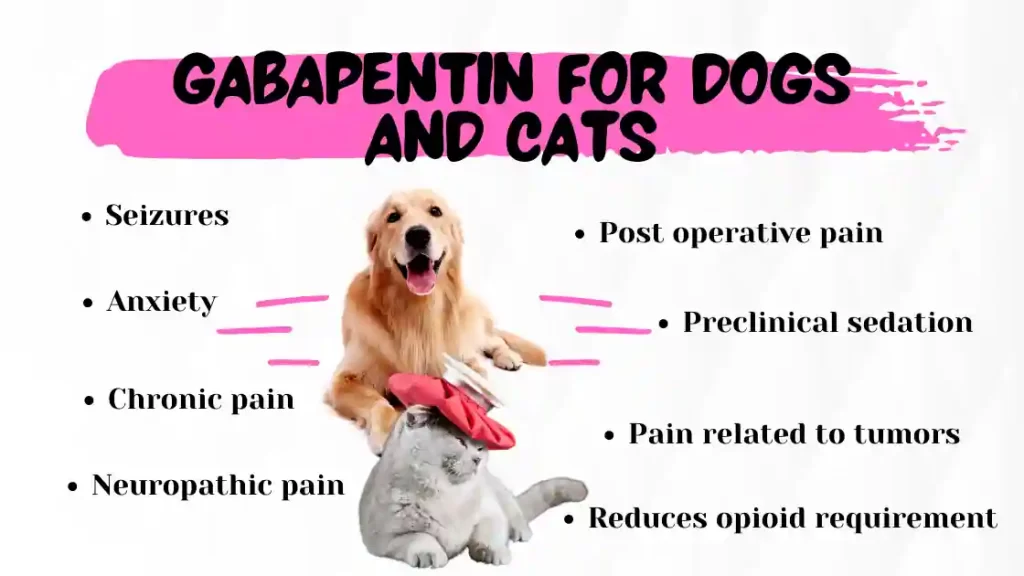
adequate relief, or if side effects become unacceptable. Note: Antacids can reduce the efficacy of gabapentin when taken at the same time.7 If antacids are needed, it is best to take them at least 2 hours before or after taking gabapentin.5 DOSE AS PER RENAL FUNCTION Dose adjustments are necessary for people with poor renal Concurrent drug therapy issues: Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information. Dosage form specific issues: In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Table 2. Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment in Adults Receiving Gabapentin Gastroretentive Tablets60; Cl cr (mL/minute). Adjusted Dosage Regimen. 30–60. 600 mg to 1.8 g once daily; initiate at 300 mg once daily and may titrate according to same schedule recommended for those with normal renal function based on individual patient response and tolerability Seizures may increase if you stop using gabapentin suddenly. Ask your doctor before stopping the medicine. Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how gabapentin will affect you. Dizziness or drowsiness can cause falls, accidents, or severe injuries. Do not stop using gabapentin suddenly, even if you feel fine. Hemodialysis (CrCl ; 15 mL/min): Administer supplemental dose (range 125-350 mg) posthemodialysis, after each 4 hr dialysis interval; further dose reduction should be in proportion to CrCl (eg, Gabapentin bioavailability is not dose proportional; i.e., as dose is increased, bioavailability decreases. Bioavailability of gabapentin is approximately 60%, 47%, 34%, 33%, and 27% following 900, 1200, 2400, 3600, and 4800 mg/day given in 3 divided doses, respectively. Dosage adjustment of GRALISE is necessary in patients with impaired renal function. GRALISE should not be administered in patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min or in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Reductions in GRALISE dose should be made in patients with age-related compromised renal function. There was a larger treatment effect in patients 75 years of age and older compared to younger patients who received the same dosage. Since gabapentin is almost exclusively eliminated by renal excretion, the larger treatment effect observed in patients ≥75 years may be a consequence of increased gabapentin exposure for a given dose that Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Standard pregabalin (Lyrica) capsules are available in 8 dosage increments of: 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg, 200 mg, 225 mg, and 300 mg. Standard gabapentin (Neurontin) capsules are available in 3 dosage increments of: 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg. Dosage and Administration. 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). Initial: 300 mg orally every 8 hours. Day 1: 300 mg orally once per day. Day 2: 300 mg orally every 12 hours. Day 3: 300 mg orally every 8 hours. Maintenance: Subsequently titrate as needed up to 600 mg orally every 8 hours; doses greater than 1800 mg/day have demonstrated no additional benefit. Gralise. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for adequate relief, or if side effects become unacceptable. Note: Antacids can reduce the efficacy of gabapentin when taken at the same time.7 If antacids are needed, it is best to take them at least 2 hours before or after taking gabapentin.5 DOSE AS PER RENAL FUNCTION Dose adjustments are necessary for people with poor renal Initially 300 mg once daily, then increased in steps of 300 mg, every 4–7 days, adjusted according to response; usual maximum 900 mg 3 times a day. Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally twice a day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three. Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg orally in 3 divided doses. If necessary, the dose may be increased using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules three times a day up to 1800 mg/day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin capsules in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic. But certain products are brand-only.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |