Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
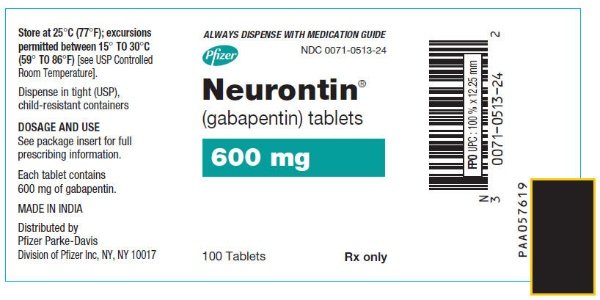 |  |
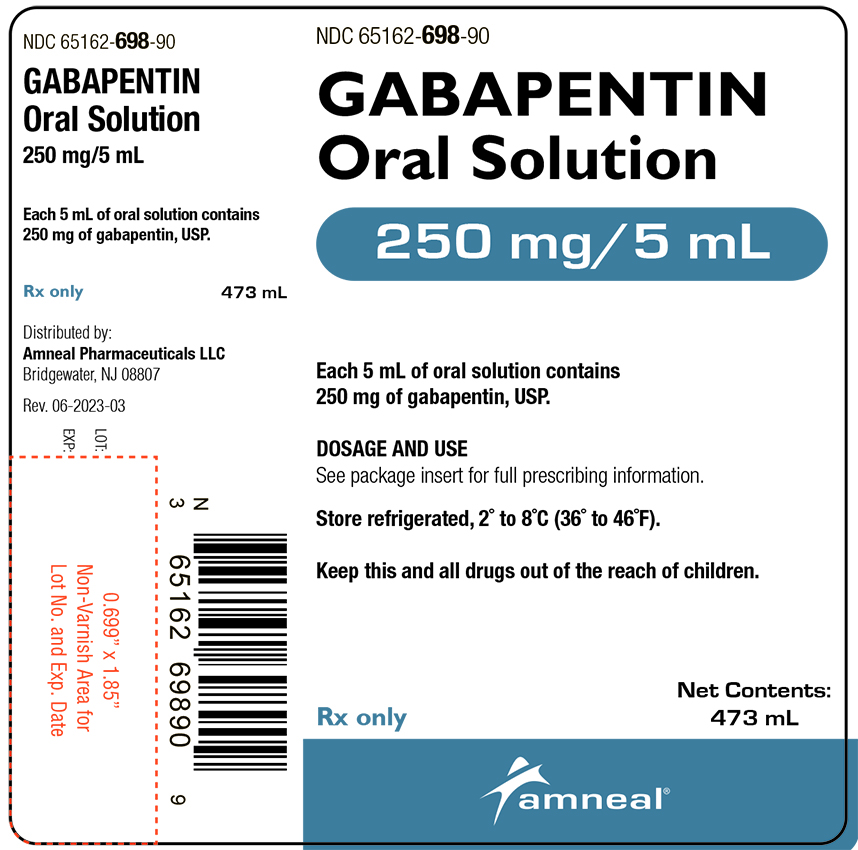
These are not all the possible side effects of gabapentin tablets. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. How should I store gabapentin tablets? Store gabapentin tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for Adults: Increase by 4-8 mg at 1W intervals to a maintenance dose of 32-56 mg/day divided BID-QID Children: Increase to 8 mg daily in 2 divided doses for 1W; then increase by 4-8 mg weekly to response Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Each tablet contains 600mg or 800mg of gabapentin. If you're taking gabapentin as a liquid, 2ml is usually the same as taking a 100mg tablet or capsule. Always check the label. The usual dose for: The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for thereafter titration according to clinical response up to a maximum dose of 2400 mg daily A slower increase in the daily dose may reduce the incidence of unwanted effects. The summary of product characteristics must be consulted before prescribing this drug. Administer gabapentin three times a day using 300 mg or 400 mg capsules. The maximum time between doses should not exceed 12 hours. The starting dose range is 10 mg/kg/day to 15 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses, and the recommended maintenance dose reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. Gabapentin comes as an immediate tablet or capsule and is typically doses 2-3 times a day. This translates to dosing of every 8 to 12 hours. Gabapentin also comes in an extended release formulation in the name of Gralise or Horizant. Both extended release formulations are dosed once daily. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. Gabapentin is available as a lower-cost generic. But certain products are brand-only. Starting Dose: ranges from 10 to 15 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses. Effective Dose: reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days. The effective dose of gabapentin in patients 5 years of age and older is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (three times a day). in a long-term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment . Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective Quick Answer. The recommended dosing interval for 300 mg of gabapentin is 8-12 hours. Gabapentin should be taken in divided doses throughout the day, with the maximum single dose being 600 mg. Spreading out doses helps maintain consistent levels of the medication in the bloodstream. 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum In patients with poor general health, i.e., low body weight, after organ transplantation etc., the dose should be titrated more slowly, either by using smaller dosage strengths or longer intervals between dosage increases. Elderly (over 65 years of age) During the controlled epilepsy trials in patients older than 12 years of age receiving doses of gabapentin up to 1,800 mg daily, somnolence, dizziness, and ataxia were reported at a greater rate in patients receiving gabapentin compared to placebo: i.e., 19% in drug versus 9% in placebo for somnolence, 17% in drug versus 7% in placebo for gabapentin 1200mg three times daily is included below. If the patient is taking a lower dose than 1200mg TDS then start the process further down the table and follow the suggested tapering guidance. An alternative regime is to take the same dose reduction across the day.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |