Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 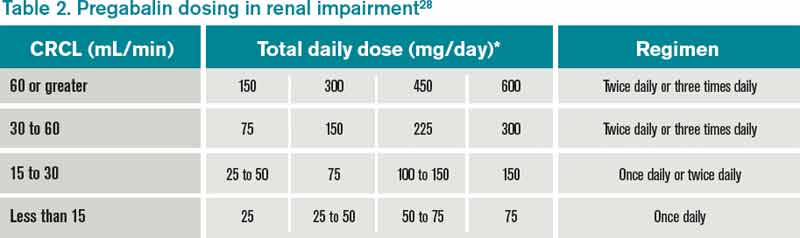 |
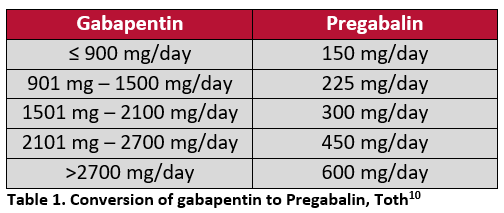
Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, NEURONTIN may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three Gabapentin has a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, because it is not protein-bound or metabolized and has no known drug–drug interactions. 10 Gabapentin has been widely used in elderly patients with multiple comorbidities, including chronic kidney disease. However, gabapentin is eliminated solely through the kidney, and kidney impairment Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. Gralise tablets swell in gastric fluid and gradually release gabapentin. Dosing Modifications. Renal impairment: Gabapentin dose reduction may be required, depending on renal function Dosing recommendations for individual drugs can be found in Drug Prescribing in Renal Failure: Dosing Guidelines for Adults. 4 The guidelines are divided into three broad GFR categories (less than Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older and adolescents with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. Gabapentin Capsules Dosage Based on Renal Function. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Detailed dosage guidelines and administration information for Neurontin (gabapentin). Includes dose adjustments, warnings and precautions. Adjust the dose for people with renal impairment (see Table 2). Consult the manufacturer's Summary of Product Characteristics if the person is undergoing haemodialysis. Table 2. Recommended dosage adjustment for gabapentin in people with renal impairment. 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT GFR (mL/MIN) 30–60 Start at low dose and increase dose according to response15–30 Start at low dose and increase dose according to response15 300 mg on alternate days or 100 mg at night initially, increase according to tolerability DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment. Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. GABAPENTIN Dosage Based on Renal Function Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |