Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
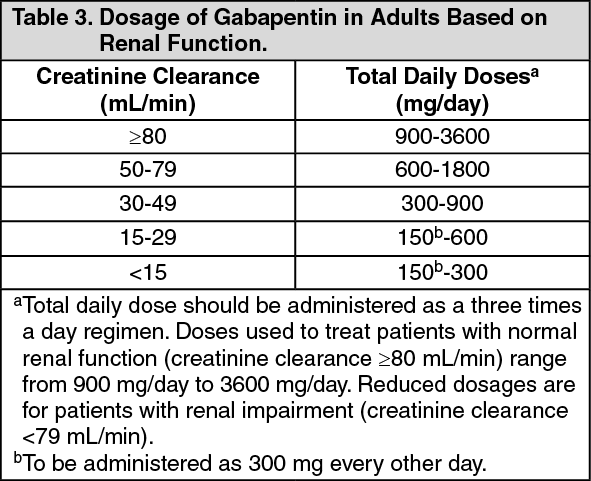
Given these risks, it is imperative for healthcare providers to adjust gabapentin dosage based on a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of kidney function. Generally, patients with mild to moderate CKD require lower doses or less frequent dosing of gabapentin compared to those with normal kidney function. Important: dosage adjustment advice in the BNF. Clinical laboratories routinely report renal function in adults based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) normalised to a body surface area of 1.73 m 2 —this is derived from either the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula or the Modification of Diet in Renal disease (MDRD) formula. The eGFR determines how well the kidneys are filtering waste from the blood and thus, dictates the appropriate gabapentin dosage. Monitoring for Toxicity. Beyond dose adjustment, regular monitoring is paramount. This may involve checking serum gabapentin levels, periodic eGFR tests, and closely observing patients for any signs of side effects. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Given the risk of accumulation, dosage adjustments are essential for patients with stage 3 kidney disease taking gabapentin. The precise dose reduction will depend on the individual’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) , which measures how well the kidneys are functioning. Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Pregabalin has six times higher binding affinity for the α2δ-1 receptor compared to gabapentin. 7 Gabapentin follows zero-order saturable absorption, where its bioavailability decreases as the dose increases. 1,7 Following oral administration, gabapentin’s bioavailability is 60%, 47%, 34%, and 33%, with 900, 1200, 2400, and 3600 mg/day in DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES ; CAPD :Probably dialysed. Dose as in GFR15 mL/min. HD :Dialysed. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each ; HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Kidney disease alters the pharmacokinetic disposition of many medications, requiring dosage adjustment to maintain therapeutic serum concentrations. The Cockcroft-Gault (CG) equation is used for pharmacokinetic studies and drug dosage adjustments, but the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study equation is more accurate and more often reported by clinical laboratories than the CG Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the best dose for you. Severe Kidney Problems (CrCl <30 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 200 - 700 mg/day QD. How Often to Take: Once a Day; Notes: Careful monitoring is needed. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) on Dialysis: Dose Recommendations: 100 Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression . rily be enhanced with higher doses. The optimal dose varies widely from 100mg at night up to 1200mg three times per day, depending on individual characteristics such as age. and concomitant medical conditions. Some people may manage a higher starting dose of 300mg three times daily, titrated up as per . Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Gabapentin and Pregabalin These anticonvulsants are effective in neuropathic pain (e.g. diabetic neuropathy). They are renally excreted and the dose should be adjusted accordingly. Information on dosage adjustment can be obtained from the renal drug handbook or renal pharmacist. Patients with severe renal failure taking Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally once Day 2: 300 mg orally 2 times day Day 3: 300 mg orally 3 times a day. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Pharmacologic treatment of mild to moderate CKD (eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2) Pharmacologic treatment of advanced CKD (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) - Principles for dosing and administration - Drug selection - Specific pain syndromes. Nociceptive pain - Acetaminophen - Opioids; Neuropathic pain - Gabapentin and pregabalin - Tricyclic antidepressants Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 shows the maximum recommended dose of pregabalin in renal impairment: In this scenario you are carrying out an audit of gabapentinoid prescribing in your work area, to ensure that the doses prescribed in renal impairment are safe and appropriate.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |