Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
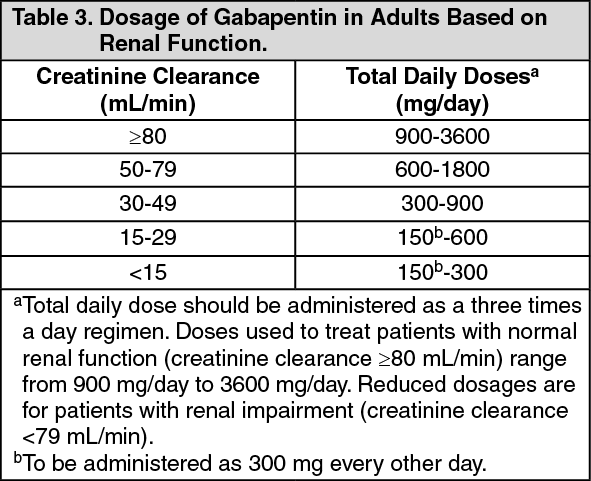
Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Dose as in GFR=15–30 mL/min Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAntacids: reduce absorption. Gabapentin dosing recommendations 1 Renal function (eGFR mL/min/1.73m2) Total daily dose (mg/day)* Greater than 80 900 - 3600 50-79 600 -1800 30-49 300 - 900 Gabapentin dosing guidelines for adult with renal impairment are summarized in Table 3. Dosing guidelines for gabapentin immediate-release are also applicable for adolescents 12 years of age and older with renal impairment. Patients received gabapentinoid prescriptions primarily from primary care physicians (79%). Gabapentinoid prescriptions were dispensed by 6,019 unique pharmacies and prescribed by 15,172 unique physicians. The median prescribed dose of gabapentin was 300 mg/d in each eGFR category . Given these risks, it is imperative for healthcare providers to adjust gabapentin dosage based on a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), a measure of kidney function. Generally, patients with mild to moderate CKD require lower doses or less frequent dosing of gabapentin compared to those with normal kidney function. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) Study equation is now widely recognized as providing more accurate estimates of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) than the CG equation and has been reexpressed for use with standardized serum creatinine values, enabling consistent performance across clinical laboratories after standardization of serum creatinine assays, anticipated to be Higher-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin >300 mg/d or pregabalin >75 mg/d) versus lower-dose gabapentinoids (gabapentin ≤300 mg/d or pregabalin ≤75 mg/d). Outcomes The primary composite outcome was the 30-day risk of a hospital visit with encephalopathy, a fall, or a fracture or a hospitalization with respiratory depression . Pharmacologic treatment of mild to moderate CKD (eGFR ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2) Pharmacologic treatment of advanced CKD (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) - Principles for dosing and administration - Drug selection - Specific pain syndromes. Nociceptive pain - Acetaminophen - Opioids; Neuropathic pain - Gabapentin and pregabalin - Tricyclic antidepressants In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors Gabapentin should be avoided in pregnancy unless the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding. Limited data indicate that gabapentin is excreted in low amounts in breastmilk. Maternal doses of gabapentin up to 2.1 grams daily produce relatively low levels in infant serum. Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the best dose for you. Severe Kidney Problems (CrCl <30 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 200 - 700 mg/day QD. How Often to Take: Once a Day; Notes: Careful monitoring is needed. End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) on Dialysis: Dose Recommendations: 100 Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications . 1, 2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Table 1. tolerated dose. Gabapentin can also be useful for post-operative analgesia.3 It appears to be less effective for migraine prophylaxis4 which is an unapproved indication.5 PROVIDE CLEAR DOSING AND TITRATION GUIDELINES Gabapentin has a short half-life and has to be dosed three to four times daily. To reduce troublesome adverse effects that can Dosages of drugs cleared renally should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance or glomerular filtration rate and should be calculated using online or electronic calculators. Recommended Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |