Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
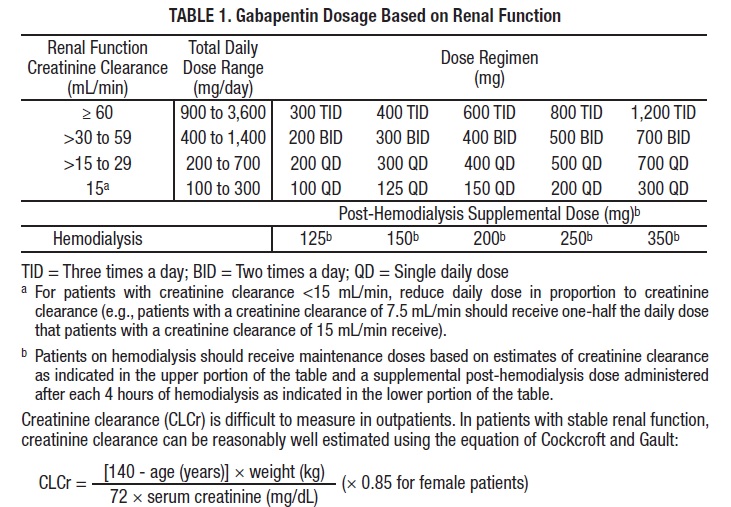
Gabapentin should be titrated until two months, every seven days, to achieve a maximum tolerated dose. The starting dosage is 100 mg three times a day. At the beginning of titration, a single increased bedtime dose should be considered to avoid daytime sedation. The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (3 times a day). Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral capsule. It may be reasonable to start older adults on a low dose of gabapentin, which can be effective to treat pain while exposing patients to a lower risk of adverse mental status side effects of gabapentin (dizziness, drowsiness and confusion) [7]. e.g. elderly, renal impairment, breast feeding which may affect the suitability for prescribing or the dosage. Gabapentin usually starts at 300mg once a day (at night) and titrates upwards, adjusted according to response to a maximum of 3600mg daily in divided doses. Evidence suggests that a minimum of 1200mg is usually needed and doses may need to The typical starting dosage of gabapentin for seizures is 300 mg by mouth three times a day, with or without food. Your prescriber may adjust your gabapentin dosage to up to 600 mg 3 times a day (1,800 mg per day). The maximum gabapentin dosage is 3,600 mg per day, but higher doses are more likely to cause side effects.Restless legs syndrome Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and dose should be adjusted based on creatinine clearance values in these Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided Elderly patients often require lower doses of gabapentin due to age-related changes in kidney function. A study by Ahmed et al. (2017) found that gabapentin clearance in elderly nursing home patients was significantly lower than in younger adults, necessitating dose adjustments. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin needs to be gradually increased over a period of time until a maximum daily dose of 600mgs three times a day is reached. Follow the table below taking from 1 tablet a day to a maximum of 2 tablets three times a day: Stay on three capsules a day for about a week and if your pain relief is adequate, keep on this dose. Gabapentin is used in 82.6% of people who need anticonvulsants. Dosing for gabapentin has a wide variety. The average dose is 975 mg/day, ranging from 100 to 4800 mg/day. Older adults should be started on a low dose of gabapentin, and then titrated to the optimum mg/day per each individual resident. The Study Appropriate studies performed to date have not demonstrated pediatric-specific problems that would limit the usefulness of gabapentin for treating partial seizures in children 3 years of age and older. However, safety and efficacy have not been established in children younger than 3 years of age. Optimizing Gabapentin Use In Elderly Patients. As we age, our bodies process medications differently, making it crucial to tailor treatment approaches for older adults. Optimizing gabapentin use in elderly patients involves careful consideration of dosing strategies, monitoring of kidney function, and exploring alternative or complementary Consider trialling gabapentin for 3–8 weeks, with at least 2 weeks at the maximum tolerated dose, before deciding it is not effective [Dworkin, 2007]. It may take several weeks to reach an effective dosage (usually 1200 mg to 3600 mg a day). The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain trials is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided dose s in patients with normal renal function. 3 This means the minimum effective dose is 600 mg 3 times a day. Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. Analysis of responder rate using combined data from all three studies and all doses (N=162, gabapentin; N=89, placebo) also showed a significant advantage for gabapentin over placebo in reducing the frequency of secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures. In two of the three controlled studies, more than one dose of gabapentin was used. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long-term clinical study. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Discover other significant concerns for elderly gabapentin users and the importance of personalized
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |