Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
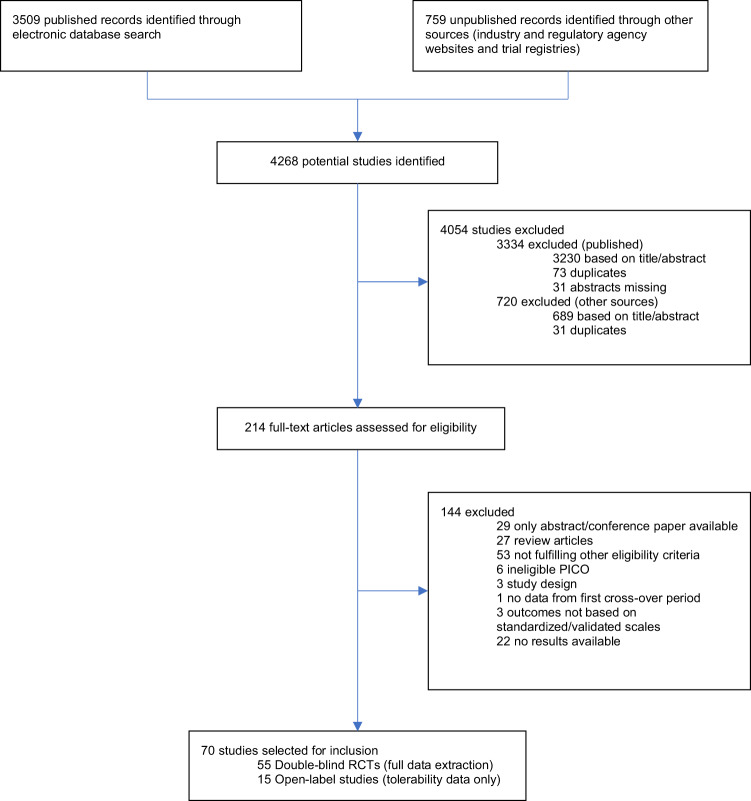
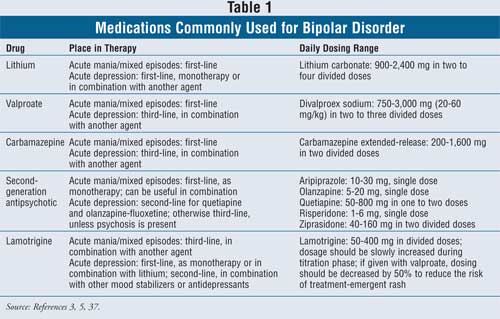
Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. Background: Gabapentin (GBP) may be useful in bipolar disorders, including as adjunctive therapy for bipolar depression, although controlled studies suggest inefficacy as primary treatment for mania or treatment-resistant rapid cycling. In another study of 16 bipolar I and II patients receiving adjunctive gabapentin (mean dose of 1,310 mg/d), 8 showed improved depression, anxiety, and irritability symptoms at 12-week follow-up. 34 Sokolski et al 35 noted in an open-label add-on trial (n = 10) that gabapentin was effective, with improvement in depressive symptoms, mania ratings A maximum dose of 3,600 milligrams in one day where this dosage is spread out over the course of the day (i.e., a 1,200 mg dose would be taken at three points during the day). Nerve pain: As with epilepsy, an initial dose of 300 milligrams is given on day one, 300 milligrams twice a day on day two, and 300 milligrams three times a day on day Multiple RCTs have shown gabapentin to be ineffective for bipolar disorder. There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of gabapentin for MDD, GAD, PTSD, or OCD. There is sufficient evidence to consider the use of gabapentin for social anxiety disorder and, potentially, severe panic disorder after other treatment options have failed. Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance. DSM-IV criteria for unipolar major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder type I, and bipolar disorder type II. The diagnosis of bipolar disorder, NOS, was made using DSM-IV criteria augmented by the recommended criteria of Akiskal,13 in order to assess possible effects of gaba-pentin on a broad definition of the bipolar spectrum. Indi- Gabapentin can also be prescribed off-label, for uses that are not approved by the FDA, including in the treatment of bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, treatment resistant depression, alcohol withdrawal, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and migraines . The mean dose of gabapentin was 1,310 mg/day. Conclusion: Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. Introduction Gabapentin has been extensively prescribed off-label for psychiatric indications, with little established evidence of efficacy. Gabapentin and pregabalin, a very similar drug with the same mechanism of action, bind to a subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels which are implicated in the aetiopathogenesis of bipolar disorder, anxiety and insomnia. This systematic review and Gabapentin in the acute treatment of refractory bipolar disorder. Lori L. Altshuler, Paul E. Keck, Susan L. McElroy, Results: Twenty-two patients (88%) com-pleted the 16 weeks of treatment with gabapentin; 19 (76%) had a positive response as measured by changes in CGI and BPRS scores. The mean dose was 1440 mg/day. The only side effect observed was oversedation, which decreased with continu-ing treatment. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). Flowchart of included and excluded studies. Bipolar disorder (BD) Four DB-RCTs investigating the efficacy of gabapentin in BD were identified. 101 patients were randomised to receive gabapentin, 81 to placebo, 30 to lamotrigine and 19 to carbamazepine. For bipolar disorder, four double-blind RCTs investigating gabapentin, and no double-blind RCTs investigating pregabalin, were identified. A quantitative synthesis could not be performed due to Results: Gabapentin was moderately to mark-edly effective in 30% (15/50) of patients, with statistically nonsignificant differences between patients with bipolar disorder type I, bipolar dis-order type II and NOS, and unipolar major de-pressive disorder. 70% reported side effects, mainly sedation, with 16% of the total sample discontinuing treat Right now, there is no good evidence that gabapentin can be used for treating people with bipolar disorder. High-quality, randomized controlled studies found that Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are needed to further delineate its acute efficacy when used as monotherapy and its prophylactic efficacy as monotherapy or in conjuction RESULTS. Bipolar Disorder. The randomized controlled trials 19 –21 investigating gabapentin for treating bipolar disorder indicate it is likely to be ineffective. Data interpretation is difficult: dosing varies by trial, gabapentin is used as both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, patients have heterogeneous diagnoses, and primary outcomes differ between studies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |