Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 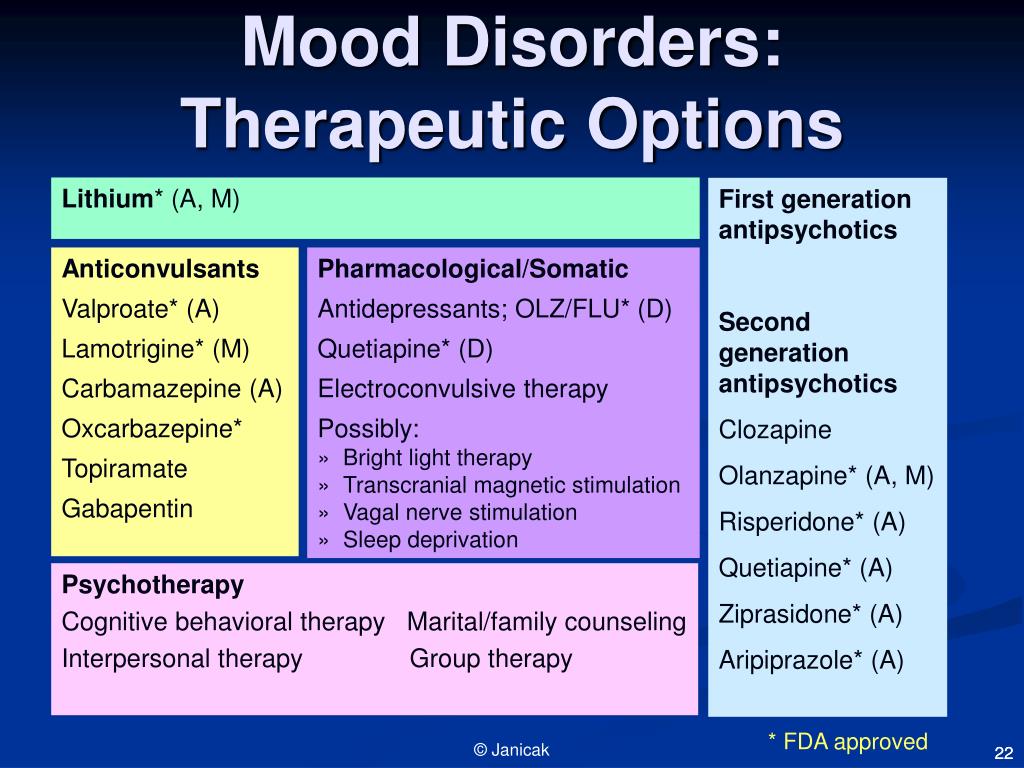 |
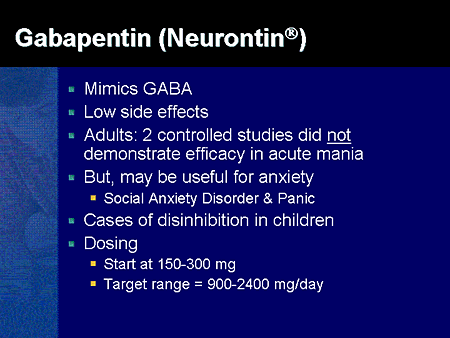
Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. Gabapentin shows promise as an adjunctive treatment for bipolar disorder, particularly in patients who have not responded adequately to other mood stabilizers. The effective dosages range widely, typically between 600 mg/day and 3,600 mg/day, with a mean dose around 1,300-1,700 mg/day being common in several studies. Gabapentin is not reliable on its own in bipolar disorder, but two placebo-controlled trials suggest it may have a role as adjunctive therapy. It augmented lithium in acute mania and had mild preventive effects over a year when added to various mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. For gabapentin, a dose-response pattern has been observed in GAD with remission/mild anxiety on total daily doses of gabapentin ≥900 mg/day and recurrence of severe anxiety, suggesting Can gabapentin make you feel good? 2. Is gabapentin as effective as Xanax for anxiety? 3. How long does it take for gabapentin to improve mood? 4. What mental health issues does gabapentin help with? 5. Does gabapentin make you calm? 6. What is the best mood stabilizer for anger? 7. What is the best mood stabilizer for anxiety? 8. What are the 1. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. The mean dose of gabapentin was 1,310 mg/day. Conclusion: Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. On the basis of the CGI-BP, 30% of patients showed significant improvement in mood. 36 In a similar report, Ghaemi and Goodwin 37 reviewed the charts of 21 patients with mood disorders treated with gabapentin (mean dose of 943 mg/d) either as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy for 2–52 weeks (mean of 17 weeks). On the basis of self-report mood This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Gabapentin misuse is increasing (oral, intranasal, and intravenous). Misuse can produce anxiolytic effects and a euphoria that is similar opioid misuse. Gabapentin can cause respiratory depression, physiologic dependence, and withdrawal symptoms on cessation (including diaphoresis, anxiety, confusion, and seizures). medications, mood stabilizer use and dosage, evidence regarding poor response to standard mood stabilizers be-fore gabapentin use, evidence regarding whether during gabapentin treatment mania or hypomania occurred, ad-verse events, maximum and maintenance gabapentin dose and duration of treatment, indications for treatment Adjunctive therapy of gabapentin to stable doses of mood stabilizers or atypical antipsychotics, initiated at 300 mg at bedtime and increased by 300 mg every four nights until symptom relief or adverse effects were noted. After 3 months of gabapentin treatment (mean dose of 1,615 mg/d), patients noted superior mood improvement compared to controls based on the Cornell Dysthymia Rating Scale. Groups were similar based on other mood scales, including the Hamilton Depression and Anxiety Rating Scales and the Beck Depression Inventory. 53 Gabapentin as an Adjunct to Standard Mood Stabilizers in Outpatients with Mixed Bipolar Symptomatology. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry: Official Journal of the American Academy of Clinical Psychiatrists, 11(4), 217–222. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Other medications have been studied more for anxiety, and they’re typically tried first. The recommended gabapentin dosage for anxiety and other conditions can range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg per day. Dosage of between 900 and 2,000 mg a day works as a mood stabilizer or antidepressant. Some people experience improvement within a week after treatment initiation, others need more time to feel significant symptom relief. American Psychological Association: Gabapentin has been “largely discredited as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.” Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance: Gabapentin “was used frequently for treatment of bipolar disorder, but controlled studies found it was no more effective than a placebo.” If used as a mood stabilizer or anti-depressant, the dose is usually between 900 and 2,000 mg a day. But, it may also be increased for better results. Gabapentin and lamotrigine low in side effects, may also help sleep, anxiety, and pain, and decrease alcohol abuse. It also may help perimenopausal symptoms. No lab tests needed. Gabapentin has very few, if any, significant interactions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |