Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
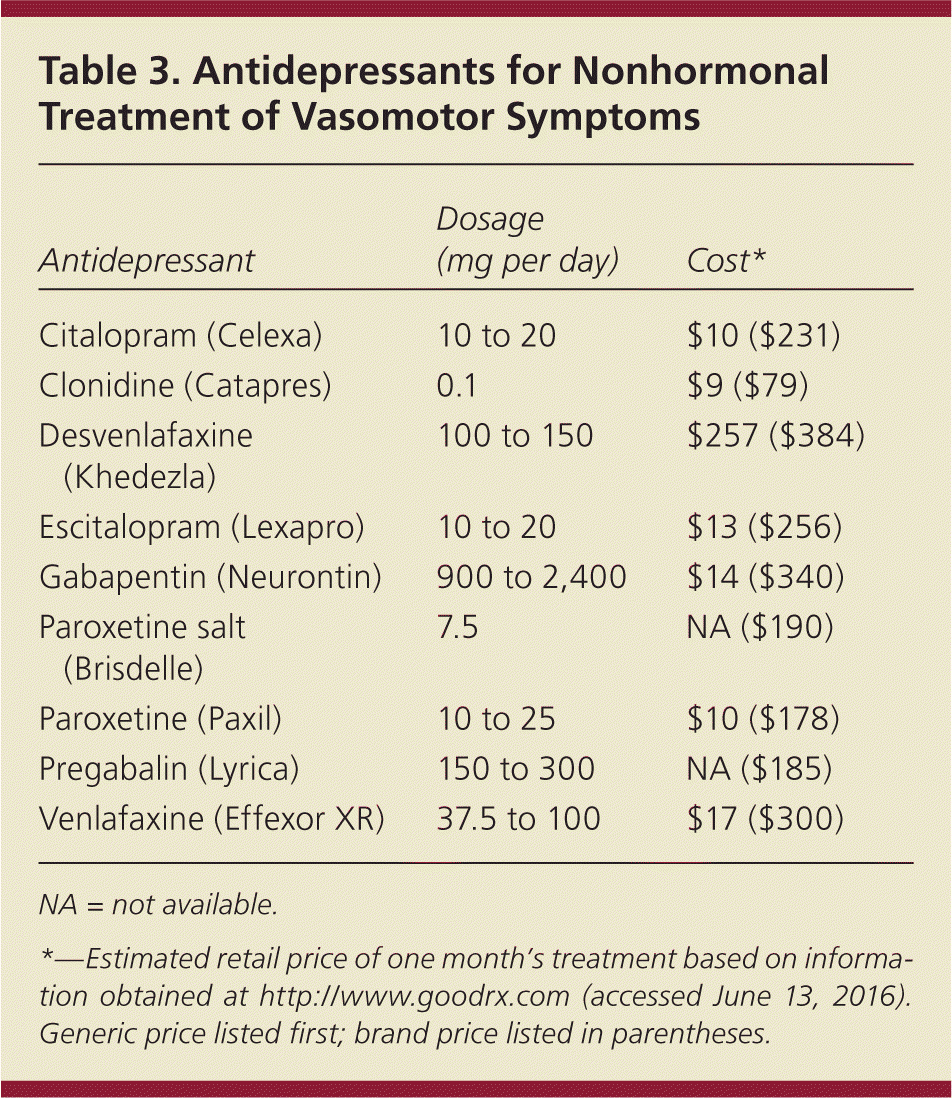
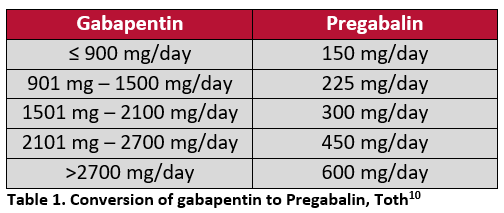
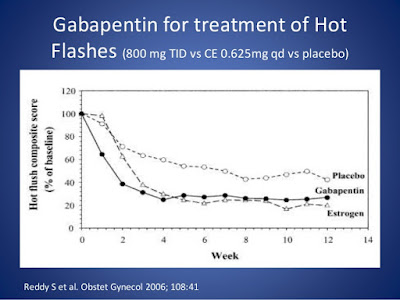
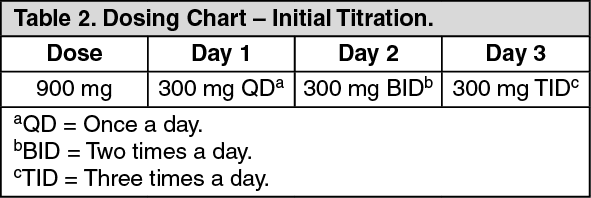
Vasomotor symptoms (VMS), more commonly known as hot flushes or flashes and night sweats, are the cardinal symptoms of menopause, occurring in up to 80% of postmenopausal women. 1,2 Apart from being disruptive and bothersome, VMS may independently have adverse health consequences associated with cardiovascular and metabolic changes, including increased carotid intima thickness, increased Gabapentin is a drug that doctors sometimes prescribe off-label to reduce hot flashes during menopause. Instead of affecting hormones, experts think it may act on the hypothalamus, the part of earched the PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases for English-language articles published until June, 2018. The following search terms were used: “menopause,” “hot flushes,” “vasomotor symptoms,” “gabapentin,” and “non-hormonal therapy.” Primary outcomes were frequency, duration, and composite score of hot flushes. Secondary outcomes were adverse effects and In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 RCTs and 2 randomized cross-over studies, gabapentin was found to reduce hot flash frequency after just 4 weeks of treatment in postmenopausal women, including breast cancer survivors, but there was no difference in hot flash duration. 113 The recommended total daily dose of gabapentin for The treatment is a low-dose form of paroxetine (Brisdelle). Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). This daily pill treats menopause hot flashes without Results of a study 33 involving 152 postmenopausal women receiving a high or a low dosage of black cohosh showed similar decreases in Kupperman index scores in the two groups (from a median score The Menopause-Specific Quality-of-Life vasomotor score decreased by 1.7 (95% CI: 1.3-2.1; P < 0.001) in the gabapentin group. These women reported greater dizziness (18%), unsteadiness (14%), and drowsiness (12%) at week 1 compared with those taking placebo; however, these symptoms improved by week 2 and returned to baseline levels by week 4. Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve pain. It also reduces menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin in higher doses has been shown to be as effective as estrogen in reducing the severity and frequency of hot flushes. The median age of menopause in North America is 51 years. There is an array of ultra low-dose estrogen may improve vaso- Adverse effects of gabapentin include dizziness, somnolence, and Gabapentin is usually used to control epilepsy or chronic nerve (neuropathic) pain. It is also a non-hormonal medicine that has been shown to be effective in reducing menopausal hot flushes. Gabapentin appears to be comparable with low dose oestrogen in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flushes.3 What is the usual dosage? Aguirre et al., compared gabapentin versus low-dose transdermal estradiol for treating post-menopausal women with moderate to very sever hot flashes. A total of 45 women were prospectively and single blinded randomized to receive oral gabapentin 600 mg/night or transdermal 25 μg/day estradiol/week. A randomized controlled trial of 12-weeks duration compared a higher dose of gabapentin (2400mg daily) and oestrogen (Premarin 0.625mg daily) against a placebo. There was a significant placebo effect (54% reduction in severity and frequency of hot flushes) and gabapentin appeared to be as effective as oestrogen (71% and 72% respectively) 14 . To evaluate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin for the treatment of hot flashes in women with menopause and/or breast cancer, we performed a search of the MEDLINE database (1966-March 2008) and International Pharmaceutical Abstracts, as well as manually searching reference articles for relevant articles and abstracts; 10 clinical studies Gabapentin may be a better choice for women with predominant nocturnal HFs for its added benefit on the maintenance of sleep cycle. It is as effective as venlafaxine, but patients often prefer venlafaxine due to better tolerance profile of later. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be individualized. side effects of gabapentin is to use the lowest effective dose or nightly dosing.11 Current recommendations from the Menopause Society no longer support pregabalin as a treatment for reducing VMS owing to limited evidence.11 Oxybutynin Evidence from several randomized controlled trials supports the effectiveness of oxybutynin in treating What is the gabapentin dosage for hot flashes? As the FDA hasn’t approved gabapentin for menopause, doctors must consider study results or their own clinical experience. The American Association of Family Physicians reports success with dosages between 900 and 2,400 mg daily.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |