Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
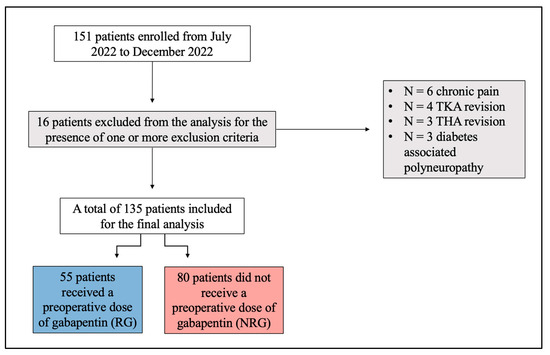
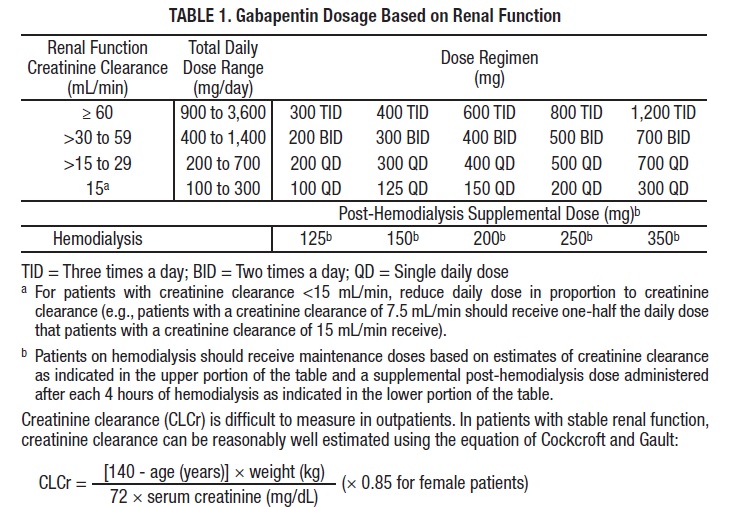
Preoperative gabapentin is associated with significantly decreased levels of consciousness in a dose-dependent manner and longer postanesthesia care unit stays. 36,37 Similarly, respiratory depression has been reported in patients receiving preoperative gabapentin, with greater risk noted in older patients and those receiving multimodal Pregabalin Dosing for preoperative orders for Ambulatory Orthopedic procedures 1) If patient is taking pregabalin already, just inform patient to take their regular dose on DOS and avoid ordering additional medication. We defined perioperative gabapentin use based on charge codes, which identify each service item (eg, medications and procedures) for billing and reimbursement purposes, on the day of surgery or postoperative day 1 or 2. We calculated total daily gabapentin dose (in milligrams) given during the exposure-defining period. A single low dose of 600 mg gabapentin administered 1 h prior to surgery produced effective and significant postoperative analgesia after total mastectomy and axillary dissection without significant side effects. Postoperative opioid consumption was reduced when using gabapentin within the initial 24 hours following surgery (standard mean difference −1.35, 95% confidence interval [CI]: −1.96 to −0.73; P <0.001). There was a significant reduction in morphine, fentanyl, and tramadol consumption (P <0.05). A single preoperative dose of gabapentin was administered in 11 studies [9–19], and 10 studies described gabapentin administration given preoperatively and as continued therapy postoperatively [20–29]. The gabapentin dosing regimen was not described in one of the included publications . The most common preoperative dose of gabapentin was 10 RESULTS: Pain relief was better in the gabapentin groups compared with the control groups. The opioid-sparing effect during the first 24 h after a single dose of gabapentin 300-1200 mg, administered 1-2 h preoperatively, ranged from 20% to 62%. Eleven studies (25,28–33,36,38–40) administered gabapentin as a single dose within 1 h to 2 h before surgery; the remainder involved initiating therapy on the day before surgery or continuing it for up to 10 days after surgery . from perioperative use of gabapentinoids is uncertain. The aim of this system-atic review was to assess the analgesic effect and adverse events with the perioperative use of gabapentinoids in adult patients. Methods: Randomized controlled trials studying the use of gabapentinoids in adult patients undergoing surgery were included. The early time course of perioperative gabapentinoid use was one of enthusiastic implementation. An early study used a single preoperative dose, evaluated patients for only 4 hr postoperatively, and reported substantially (50%) less pain during movement and morphine consumption. concluded 600 mg was the optimal dose for pre-operative gabapentin administration. In 2006, Ho et al. performed a review of 16 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the use of preoperative gabapentin in controlling postoperative pain (3). polypharmacy and the need for perioperative medication guidance .2. There are no well-designed trials to support evidence-based recommendations for perioperative medication management ; however , general principles and best practice approaches are available. General considerations for perioperative medication management include a thorough In the study of Pandey et al., increasing dosage of gabapentin from 600 mg to 1200 mg, did not show a reduction in pain scores after discectomy, then 600 mg gabapentin was determined as favorite dose for post discectomy pain reduction. In our study, regarding to type of surgery, which was a lower abdominal surgery, 400 mg of gabapentin Pre-operative gabapentin (600-1200 mg) reduces the amount of narcotics required in the post-anesthetic care unit (PACU). Pre-operative gabapentin does not decrease long-term narcotic use and is associated with increased side effects of respiratory depression, sedation, and falls. 1.1.2. Preoperative medications 1.1.2.1. Analgesic. (To beadministered in the preoperative holding area; dose adjustment may be required based on age and/or co-morbid con-dition; see Fig. 1) Acetaminophen 1000 mg PO/IV once Celecoxib 400 mg PO once Tramadol-ER 300 mg PO once Gabapentin 300–600 mg PO once or Pregabalin 75 mg PO once 1. Preoperative 1.1 A single 1000 mg dose of acetaminophen is recommended to be given preoperatively in open and laparoscopic colorectal surgical procedures (Level of evidence: Low) 1.2 A single 300 mg dose of gabapentin should be given be should be given preoperatively Different dosing regimens were tested to compare control versus either 1-Time preoperative 300 mg, 600 mg, 900 mg, or 1200 mg gabapentin on PONV [Citation 8], but according to our knowledge, no research was conducted to compare the different dosing regimens in the same setting to evaluate their effectiveness on PONV and the frequency of side Pandey CK, Navkar DV, Giri PJ, et al. Evaluation of the optimal preemptive dose of gabapentin for postoperative pain relief after lumbar diskectomy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005;17(2):65-68. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000151407.62650.51 [Google Scholar] 28. This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Given the significant differences between the studies and the possibility of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |