Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
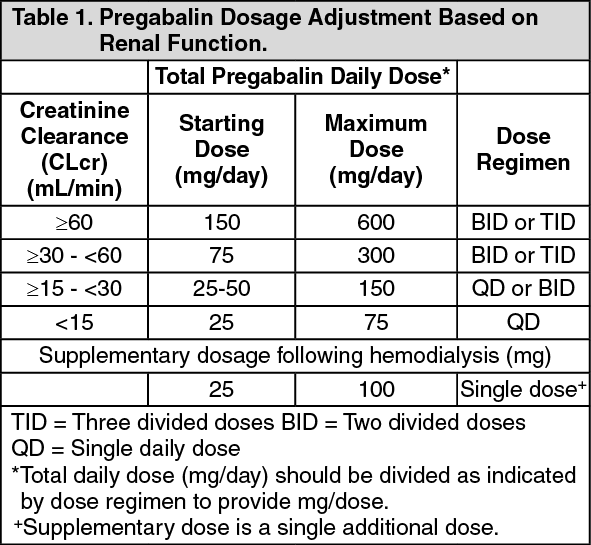
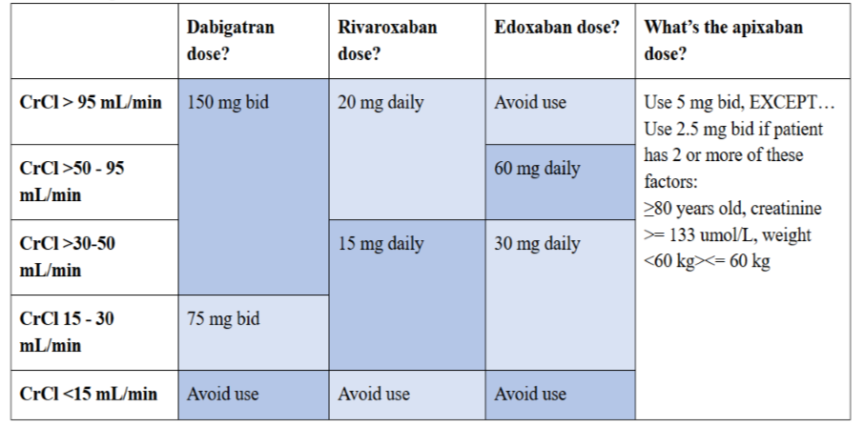
10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. For patients with creatinine clearance <15 mL/min, reduce daily dose in proportion to creatinine clearance (e.g., patients with a creatinine clearance of 7.5 mL/min should receive one-half the daily dose that patients with a creatinine clearance of 15 mL/min receive). Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/ min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption.1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 200–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally once Day 2: 300 mg orally 2 times day Day 3: 300 mg orally 3 times a day. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Important: dosage adjustment advice in the BNF. Clinical laboratories routinely report renal function in adults based on estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) normalised to a body surface area of 1.73 m 2 —this is derived from either the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula or the Modification of Diet in Renal disease (MDRD) formula. Because 40% to 50% of insulin is excreted by the kidney, dose decreases are made with loss of kidney function. 19 The American College of Physicians recommends decreasing doses by 25% for patients with creatinine clearances between 10 and 50 mL/minute and by 50% for patients with creatinine clearances less than 10 mL/minute. 30 However, the need for dose adjustments in patients with CKD is Drug dosing requirements for antihypertensives in patients with chronic kidney disease are listed in Table 4. 4, 5 Thiazide diuretics are first-line agents for treating uncomplicated hypertension Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. 41 Several cross-sectional studies have reported it being used in subtherapeutic doses among most patients. In a Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Mild Kidney Problems (CrCl 60-90 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Moderate Kidney Problems (CrCl 30-59 mL/min): Dose Adjustment: 400-1400 mg/day BID; How Often to Take: Twice a Day; Notes: Your doctor will decide the Sevelamer — absorption of gabapentin may be reduced if taken concurrently with sevelamer. Gabapentin should be taken at least 1 hour before, or 3 hours after, sevelamer if the reduction in gabapentin levels is clinically significant. Morphine — interaction of gabapentin with morphine sulphate increases risk of respiratory depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |