Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585288169-5a938d4b6edd650036b6c9a8.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
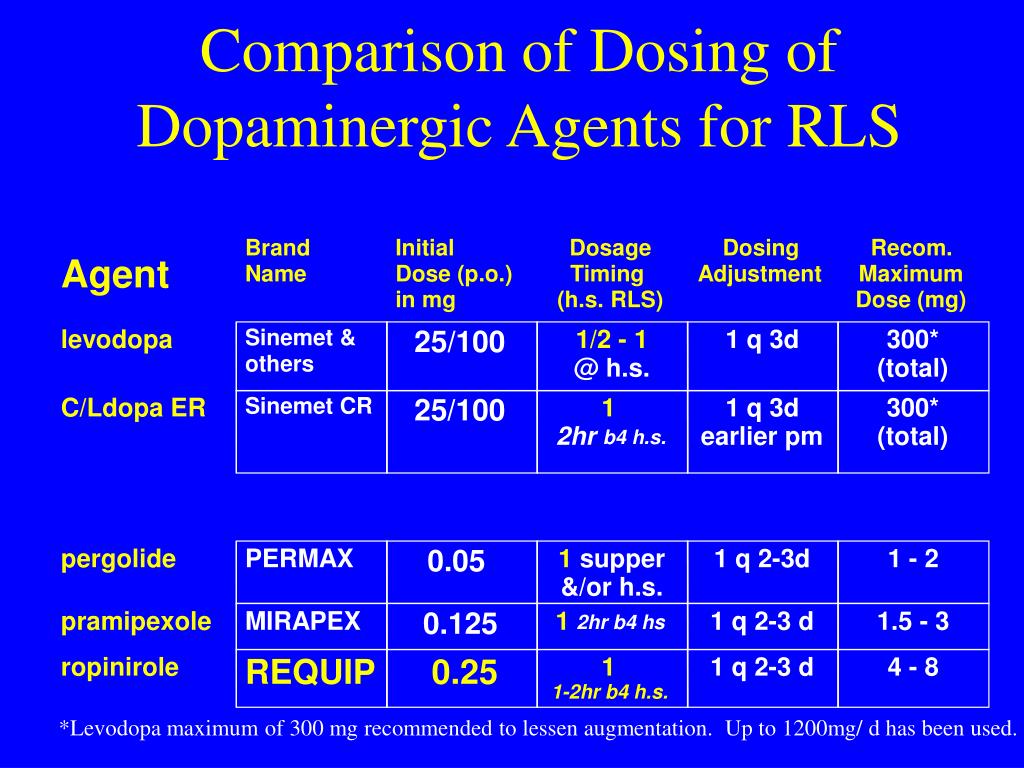
Introduction. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) or Willis-Ekbom disease is a sleep-related movement disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move, which usually involves the legs, although other parts of the body could also be involved. 1, 2 The four essential criteria used for the diagnosis of RLS are an urge to move the legs with or without abnormal sensations, worsening of symptoms at Recommended dose: 600 mg once daily, taken with food in the evening. Treatment is usually long-term. Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-2400 mg per day, divided into three doses. The duration of treatment depends on symptom control. Lee DO, Ziman RB, Perkins AT, et al; XP053 Study Group. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin enacarbil in subjects with restless legs syndrome. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011;7(3):282-292. Walters AS, LeBrocq C, Dhar A, et al; International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group. This article explains what gabapentin is, its approved and off-label uses, and how the drug works to treat restless legs syndrome and other medical conditions. It also describes the possible side effects and risks and lists other drugs and treatments that may help ease RLS symptoms. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, converted to gabapentin after absorption, and thus avoids the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of gabapentin. It is administered as a single daily dose of 600 mg (300 mg in patients older than 65 years) at 5 pm to target adequate therapeutic levels at bedtime. Keywords: restless legs syndrome, gabapentin, gabapentin enacarbil, treatment. Background. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) is a movement disorder that affects between 5% and 10% of adults [Hening et al. 2004; Phillips et al. 2000; Lavigne and Montplaisir, 1994]. Gabapentin is available in various forms, including oral capsules, tablets, and oral solutions. It is commonly prescribed for conditions such as epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless leg syndrome. Indications. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for the treatment of various conditions. The use of gabapentin for restless legs syndrome (RLS) is off-label. Initial dose of 300 mg if the person is under 65 years old and 100 mg if the person is over 65 years old. Maximum recommended dose for RLS is 2700 mg. CKS did not identify any specific guidance on dose titration for use in RLS. Gabapentin’s effectiveness for RLS may take weeks, with dosage ranging from 300 mg to 3,600 mg daily. It’s initiated at a low dose and increased gradually. Continuity in usage is crucial, as full effects may take up to four weeks. Gabapentin has common side effects and rare serious reactions. Restless legs syndrome (RLS) refers to an urge to move the legs, usually associated with unpleasant sensations. The urge to move the legs is worse at rest and at night and is relieved by movement. RLS is commonly associated with sleep disturbance and with involuntary, jerking movements of the legs during sleep, known as periodic limb movements First-line management options include iron-replacement therapy in those with evidence for reduced body-iron stores or, alternatively, with prescribed gabapentin or pregabalin, and dopamine agonists such as pramipexole, ropinirole, and rotigotine. Objective: To assess the effects of gabapentin on sensory and motor symptoms in patients with restless legs syndrome (RLS). Methods: Patients with RLS (22 idiopathic, 2 secondary to iron deficiency) were randomized and treated for 6 weeks with either Gabapentin The use of gabapentin for restless legs syndrome (RLS) is off-label. Initial dose: 300 mg if the person is under 65 years old and 100 mg if the person is over 65 years old. Titration: maximum recommended dose for RLS is 2700 mg. CKS did not identify any specific guidance on dose For oral dosage form (extended-release tablets): For restless legs syndrome: Adults—600 milligrams (mg) as a single dose at about 5 PM. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor. For postherpetic neuralgia: Tablets should be swallowed whole and should not be cut, crushed, or chewed. Tablets should be taken with food. HORIZANT is not interchangeable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles. The recommended dosage for HORIZANT is 600 mg once daily at about 5 PM. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin, converted to gabapentin after absorption, and thus avoids the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of gabapentin. It is administered as a single daily dose of 600 mg (300 mg in patients older than 65 years) at 5 pm to target adequate therapeutic levels at bedtime. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. In moderate to severe primary restless legs syndrome (RLS), clinicians should consider prescribing a pharmacologic agent to reduce RLS symptoms: Strong Evidence Pramipexole, rotigotine, cabergoline*, and gabapentin enacarbil (Level A).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-585288169-5a938d4b6edd650036b6c9a8.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |