Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
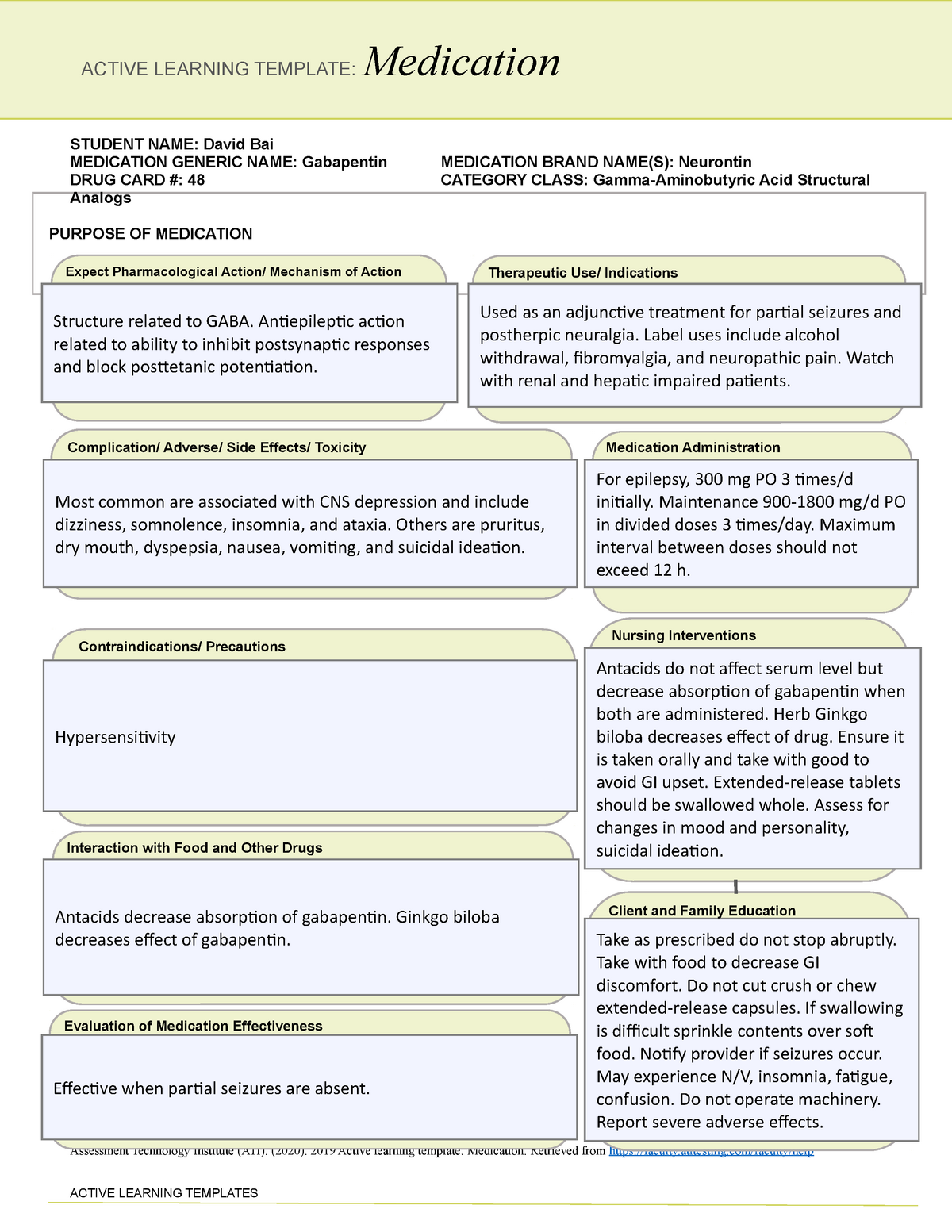
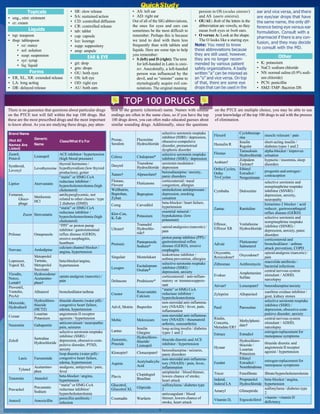
Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. This helps to alleviate seizures and reduce nerve pain. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin and pregabalin belong to the same drug class known as anticonvulsants. This drug class is also called antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) or simply seizure medications. These medications work by mimicking the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . NEURONTIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEURONTIN. NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) capsules, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) tablets, for oral use NEURONTIN ® (gabapentin) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1993 ----- Warnings and Pr ecautions, Respiratory Depression (5.7) 04/2020 Generic name: gabapentin Dosage form: tablet Drug class: The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) both belong to a class of drugs called gabapentinoids, which means they work in similar ways. They're both used to treat chronic pain in Gabapentin has been associated with a discontinuation syndrome when abruptly stopped. Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under a doctor's advice. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be reduced for kidney disease. Rarely do hypersensitivity reactions occur. Drug Class: Antiepileptic gabapentin is an amino acid & a structural analog of GABA, Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults. The Neuropathic pain: The recommended gabapentin dosage ranges from 300 to 1200 mg taken orally 3 times daily, with a maximum daily dosage of 3600 mg. Fibromyalgia: The recommended gabapentin dosage is between 400 and 800 mg taken orally 3 times daily, with a maximum daily dosage of 2400 mg. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults, treating the pain of post herpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs known as anti- seizure drugs. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin treats seizures by decreasing abnormal excitement in the brain. Gabapentin relieves the pain of PHN by changing the way the body senses pain. Generic name: gabapentin [ GA-ba-PEN-tin ] Drug class: Gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs. Medically reviewed by Philip Thornton, DipPharm. Last updated on Feb 21, 2025. Uses; Warnings; Before taking; Dosage; Side effects; Interactions; FAQ; What is Neurontin? Neurontin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals Neuropathic Pain Postherpetic Neuralgia Oral Gabapentin conventional (immediate-release) preparations: 300 mg on day 1, 300 mg twice daily on day 2, and 300 mg 3 times daily on day 3. Increase dosage as needed for relief of pain up to a total dosage of 1.8 g daily in 3 divided doses. No evidence of additional benefit with dosages >1.8 g daily. Following concerns about abuse, gabapentin has been reclassified as a Class C controlled substance and is now a Schedule 3 drug, but is exempt from safe custody requirements. Healthcare professionals should evaluate patients carefully for a history of drug abuse before prescribing gabapentin, and observe patients for signs of abuse and dependence.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |