Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
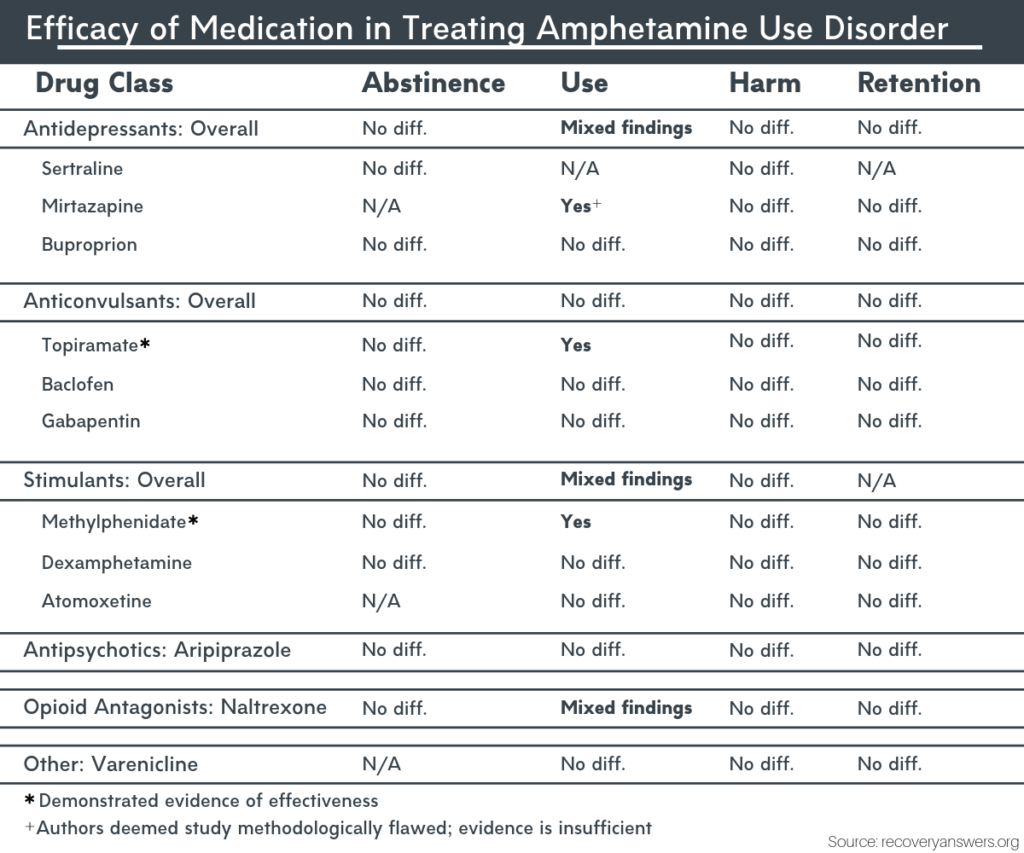
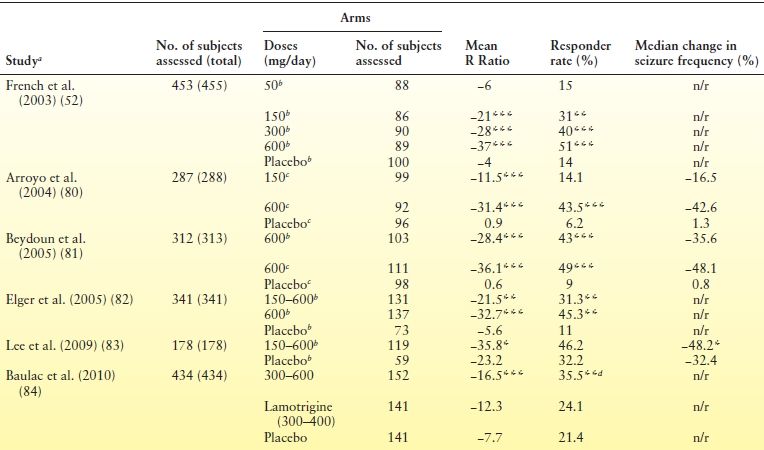
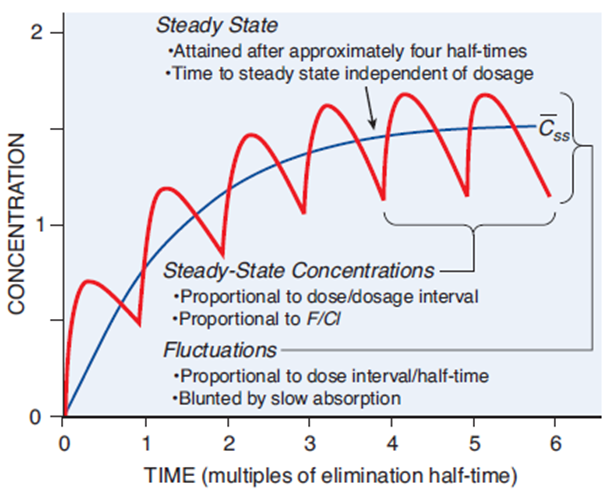
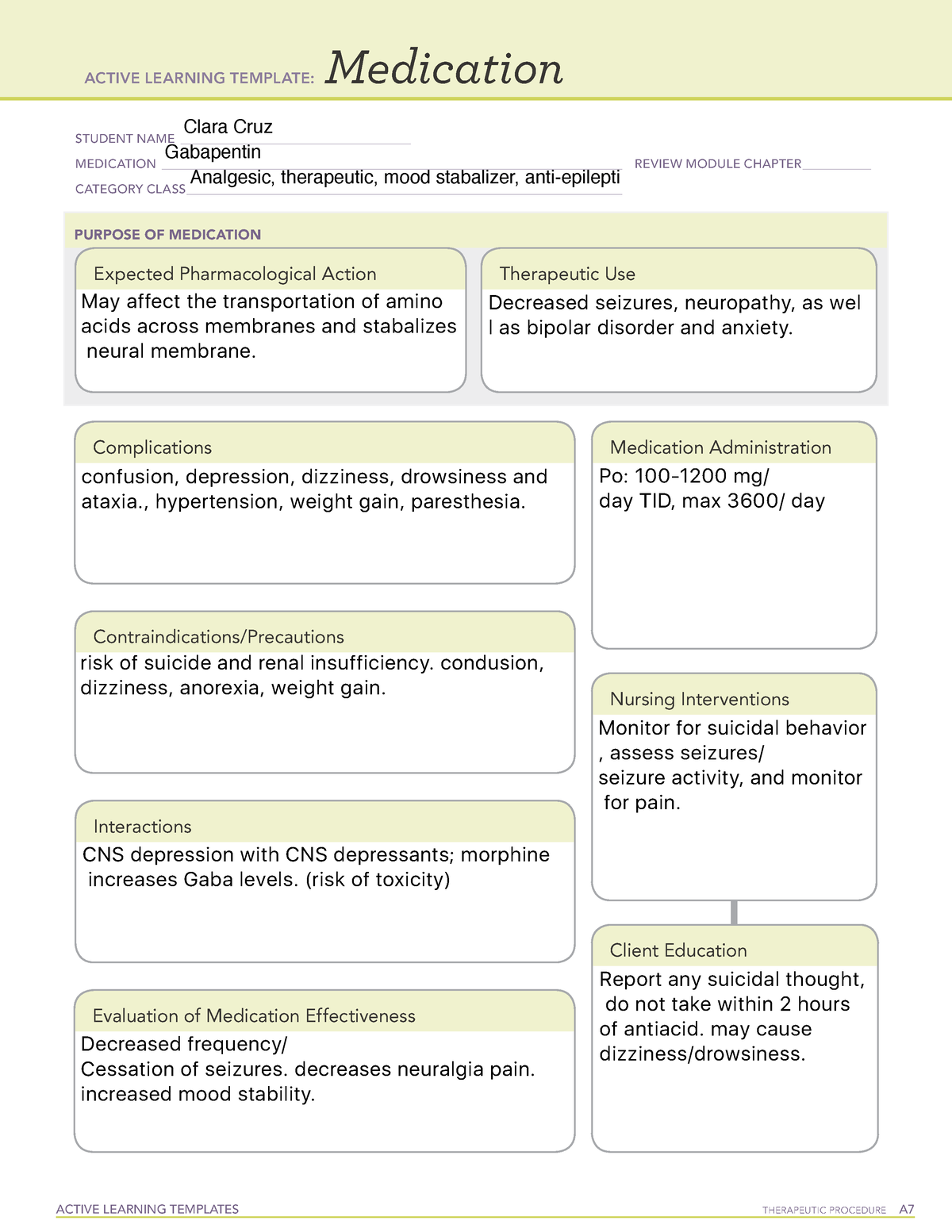
Gabapentin AUC exposure was less than dose-proportional in a PK study evaluating dose proportionality of Horizant® vs gabapentin AUC in blood after single oral doses. Gabapentin blood levels were shown to reach a maximum value independent of the dose. This is consistent with saturation of absorption. any relationship between gabapentin levels and other disease states, likely owing to the off-label nature of gabapentin prescribing. A closer look at the toxicology results of 104 postmortem patients found that gabapentin levels ranged from 1.1 to 59.2 mg/L with an average of 24.8 mg/L.26 Gaba- Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is most often dosed based on the patients renal (kidney) function. The prescribing information for the medication does not even mention therapeutic blood levels to watch for. Over time however, certain blood levels have been determined. Therapeutic Concentration appears to be around 5.9-21 mcg/mL (34.5-123 µmol/L). CUT-OFF AND TOXICITY LEVELS FOR DRUGS-OF-ABUSE TESTING This table summarizes information useful in the interpretation of drugs-of-abuse assays. It was originally developed by the late Daniel M. Baer, MD, and updated by Richard A. Paulson, MT(ASCP), supervisor of Chemistry and Toxicology, VA Medical Center, Portland, OR. The table has been updated A closer look at the toxicology results of 104 postmortem patients found that gabapentin levels ranged from 1.1 to 59.2 mg/L with an average of 24.8 mg/L. 26 Gabapentin levels that were not considered to be a direct causative or contributive factor to death ranged from 1.0 to 23.0 mg/L with an average of 10.6 mg/L. 26 Gabapentin blood Pharmacokinetics of gabapentin vary widely among patients, particularly those with compromised renal function. Adverse effects may include somnolence, dizziness, ataxia, and fatigue. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is an oral antiepileptic agent that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but it does not interact with GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it has properties in common with other anticonvulsant medications. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults, treating the pain of post herpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin belongs to a class of drugs known as anti-seizure drugs. Take gabapentin by mouth as directed by your doctor, usually once a day with the evening meal. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is effective in treating seizures, neuropathies, and a variety of neurological and psychological maladies. Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS . 7.1 Other Antiepileptic Drugs 7.2 Opioids . 7.3 Maalox ® (aluminum hydroxide, magn esium hydroxide) 7.4 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions . 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS . 8.1 Pregnancy . 8.2 Lactation 8.4 Pediatric Use . 8.5 Geriatric Use 8.6 Renal Impairment . 9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE . 9.1 Controlled Substance . 9.2 Order Code Order Code Name Order Loinc Result Code Result Code Name UofM Result LOINC; 790394: Gabapentin, Urine: 790443: Gabapentin, Urine: ug/mL: 59680-9: Order Code Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. For therapeutic drug monitoring, specimens should be drawn as trough levels. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is effective in treating seizures, neuropathies, and a variety of neurological and psychological maladies. Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. Gabapentin - Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug commonly used as adjunctive therapy to treat partial seizures. Therapeutic drug monitoring is useful to optimize dose and to avoid toxicity. Draw sample 2 hours after last dose. Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Gabapentin is an inexpensive drug used to control partial seizures in adults with epilepsy.It is also used to treat certain types of nerve pain.This drug is more popular than comparable drugs. Drug Monitoring, Gabapentin, Quantitative, Urine - Gabapentin is used as an anticonvulsant in the management of neuropathic pain in adults and as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures in patients with epilepsy. The test is a definitive assay using liquid chromatography mass spectroscopy (LC/MS/MS) methodology.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |