Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
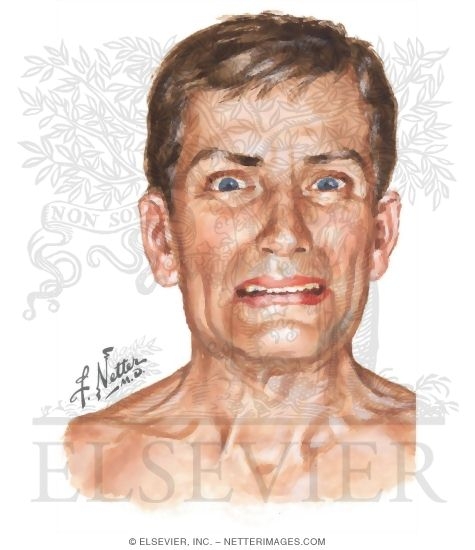
We report an unusual and rare case of an acute dystonic reaction caused by recreational gabapentin use. Get full text access Log in, subscribe or purchase for full access. Acute dystonia, sometimes called an acute dystonic reaction, can occur within hours or days of exposure to a dopamine blocking drug or, less commonly, after an increased dose of a dopamine blocking drug or decreased dose of a concurrent anticholinergic drug (e.g. benztropine). Although gabapentin is widely used and well tolerated, it can cause dystonic reactions, which are reversible after drug withdrawal. Discover the world's research 25+ million members The woman developed a dystonic reaction involving muscles of the neck and both arms that resolved rapidly after drug withdrawal. She was restarted on gabapentin with slow titration to 1800 mg daily, but the same dystonic reaction appeared, which led to definitive withdrawal of the drug. Background: Gabapentin (GBP)-induced movement disorders (MDs) are under-recognized adverse drug reactions. They are commonly not discussed with patients, and their sudden occurrence can lead to misdiagnosis. This literature review aims to evaluate the clinical–epidemiological profile, pathological mechanisms, and management of GBP-associated MD. A 68-year-old man suffered from dystonic reactions in both arms after 8 months of treatment with gabapentin 900 mg/day plus propranolol 80 mg/day for essential tremor. 8 Propranolol was added 2 days before the onset of dystonia. The dystonia disappeared when the dose of propranolol was cut by half, which suggests that propranolol interacts with Gabapentin, an analogue of GABA, was originally designed to be used as an anticonvulsant but gained popularity for reducing neuropathic pain. 47 The search strategy yielded no studies for the use of gabapentin for managing dystonia in individuals with CP. Despite this, it is increasingly being used in this population. We report an unusual and rare case of an acute dystonic reaction caused by recreational gabapentin use. A 26-year-old man presented to Accident & Emergency with his head rotated to the left and a clenched jaw, with visible intermittent involuntary spasmodic contractions of the neck and jaw musculature. The woman developed a dystonic reaction involving muscles of the neck and both arms that resolved rapidly after drug withdrawal. She was restarted on gabapentin with slow titration to 1800 mg daily, but the same dystonic reaction appeared, which led to definitive withdrawal of the drug. dystonic reactions presented within an hour of ingestion. The patient was a former intravenous drug user and was onprescriptionmethadone,buthadnootherpastmedical In this review, we will outline the few available pathogenesis-targeted therapies for specific dystonic disorders and will describe the current symptomatic pharmacologic options for treatment of dystonia. The etiology of acute dystonic reaction is thought to be due to dopaminergic-cholinergic imbalance in the basal ganglia. Reactions usually occur shortly after the initiation of an offending agent or an increased dose of a possible offending agent. 2024 EAN Congress 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting 2024 ACC Congress 2023 ESMO Congress 2023 EASD Congress 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting 2024 ACC Congress 2023 ESMO Congress 2023 EASD nomic instability with dystonia is increasingly recognized in children.12,30,31 Acute dystonic reactions (usually to drugs) arise dramatically and may cause severe dystonic symptoms (e.g. oculogyric crisis, jaw opening, or closing dystonia). Rhabdomyolysis, muscle rigidity, and stiffness from other causes warrant consideration (Table I).6,19,29 Gabapentin decreases the severity of dystonia at low doses in a genetic animal model of paroxysmal dystonic choreoathetosis. A 4-year-old girl with stereotyped episodes of inability to speak and dystonic posturing of the face and extremities lasting 20 minutes is presented with non-kinesigenic paroxysmal dySTONic choreoathetosis. A. Reeves E. J Emerg Med. 2014 Mar;46 (3):e89. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2013.08.024. Epub 2013 Sep 21. 1 York General Hospital, York, UK. 2 Accident & Emergency Department, James Cook University Hospital, Middlesbrough, UK. The effects of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-potentiating drug gabapentin (1-(aminomethyl) cyclohexaneacetic acid) on severity of dystonia were examined in a hamster model of idiopathic A significantly higher mean dose of 18.1 mg/kg/dose (SD: 13.3) for dystonia, compared to 7.61 mg/kg/dose (SD: 4.14) for pain relief without dystonia (z = -2.54, p = 0.011) was noted. Acute dystonic reactions most commonly occur in younger patients soon after taking to dopamine receptor blocking drugs, including antiemetics (e.g. metoclopramide or prochlorperazine) and antipsychotics. Acute sustained dystonic spasm of craniocervical muscles is typical, but oculogyric crises, truncal spasm causing opisthotonos, or limb The natural history of dystonia varies according to cause. Primary dystonias may plateau in severity. 6 Dopa-responsive dystonias can recover completely with levodopa treatment. 7 But for most children, dystonia exerts a significant, life-long reduction of activity and participation. 8, 9 A recent large, UK, supra-regional, demographic study of the management of hypertonus in children reported
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |