Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |
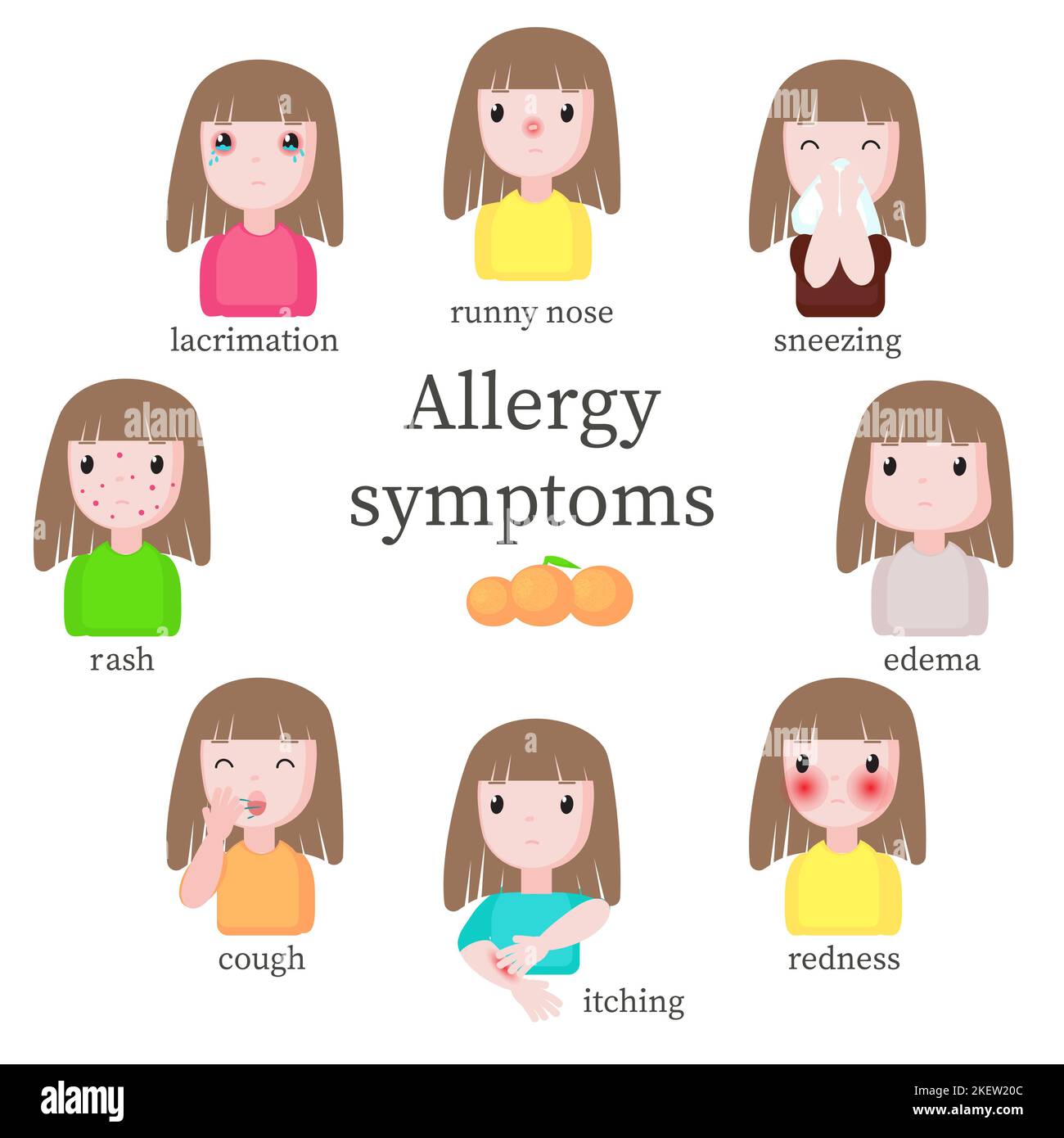
Edema is an established, but perhaps not widely known, side effect of gabapentinoids. Prior research has demonstrated that gabapentinoid initiation can lead to prescription of loop diuretics, a so-called “prescribing cascade” (NEJM JW Gen Med Dec 1 2021 and J Am Geriatr Soc 2021; 69:2842). Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Nervous system. Very common (10% or more): Somnolence (21%), dizziness (17%), ataxia (13%) Sorry to say, but my swelling lead to weight gain.I was prescribed Gabapentin for nerve pain. I started at 200 mgs once daily at bedtime. I couldn't stay on it for longer than two weeks. There has been one reported a case of gabapentin induced pitting edema in a 76-year-old male at a dose of 300 mg daily. Thus, the case discussed above describes a classic presentation of a patient developing bilateral pedal edema on a low dose of gabapentin and resolving upon its discontinuation. Seven days after the administration of the gabapentin, the patient complained from pain and edema and scaling and hyperesthesia in his lower extremities and pitting edema, pain and tenderness. The range of motion of the extremities was been increased. Edema is a well-described side effect of gabapentinoid drugs (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin). In this study from Ontario, Canada, researchers used provincial databases to examine whether gabapentinoid use was followed by diuretic prescriptions — a so-called “prescribing cascade” in which a drug is prescribed to treat an adverse effect of another drug. Furthermore, experimental data have shown an indirect inhibitory effect of gabapentinoids (ie, gabapentin, pregabalin) on the Cav1.2 channel pore of arterial myocytes, leading to vasodilatory effects and inhibition of the myogenic tone. 96-98 These data suggest that gabapentinoid-related peripheral edema 94, 95 may exhibit the same Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. It can also be prescribed off-label for other conditions, but it may cause serious side effects such as edema, rash, and suicidal thoughts. Gabapentin is a common medication-related cause of peripheral edema. This is when you experience swollen tissues in the body, often in the arms and legs. Up to 8% of people report edema with gabapentin clinical studies. But it’s more likely to occur in older adults. Gabapentin-induced edema is a common side effect that individuals should be aware of when taking this medication. Throughout this article, we have explored the causes, management tips, and prevention strategies for gabapentin edema. It is crucial to note that managing gabapentin-induced edema requires individualized medical advice and guidance. I take 600 mg of gabapentin, 300 mg twice daily. No swelling in my feet. I still get some cramping and stabbing. I hope everything is going well with others. The authors reported bilateral pretibial edema after 3 weeks of gabapentin 300 mg/d for neuropathic pain. Within 3 days of discontinuation of gabapentin, the edema resolved. When the patient was rechallenged with gabapentin, the edema returned after 5 days, suggesting the authors' suspicions of an adverse effect from gabapentin was likely correct. Medications are a common reason for swollen ankles and feet, also called pedal edema. Amlodipine (Norvasc), gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise), and pregabalin (Lyrica) can cause puffy legs and ankles. Birth control pills, certain over-the-counter pain medications, and steroids are a few other culprits. Gabapentin can cause edema: This medication may lead to swelling in some users. Dosage matters : Higher doses of gabapentin can increase the risk of edema. Monitor side effects : Regular checks for swelling are crucial during treatment. This is a case of painful, 4+ pitting bilateral edema with a probable association to gabapentin (Naranjo score 5) and a clear dose relationship in a patient with pervasive developmental disorder and schizoaffective disorder utilizing gabapentin for mood stabilization. The swelling associated with gabapentin isn't uniform across all users. Some might experience mild swelling in their extremities, while others could notice more significant changes. This variability often leads to questions about the duration and management of such side effects. Gabapentinoids can cause concentration-dependent peripheral edema of early onset. Reduced myogenic tone is the main mechanism of these non-cardiogenic edemas. In case of peripheral edema or heart failure, a drug etiology should be considered. We present a rare case of gabapentin induced bilateral 3+ pitting edema in a young man with sensorimotorpolyneuropathy, making it an unusual presentation. Gabapentinoids can cause concentration-dependent peripheral edema of early onset. The primary mechanism of non-cardiogenic peripheral edema is vasodilatory edema secondary to altered myogenic tone, independent of Ca v 1.2 blockade under the experimental conditions tested. I have swelling in my legs caused by lymphedema and have to wear compression socks but mine was not caused by a medication. I also would be concerned if it's been over 5 months since stopping gabapentin and the swelling and pain is still in the hands and feet.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |