Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
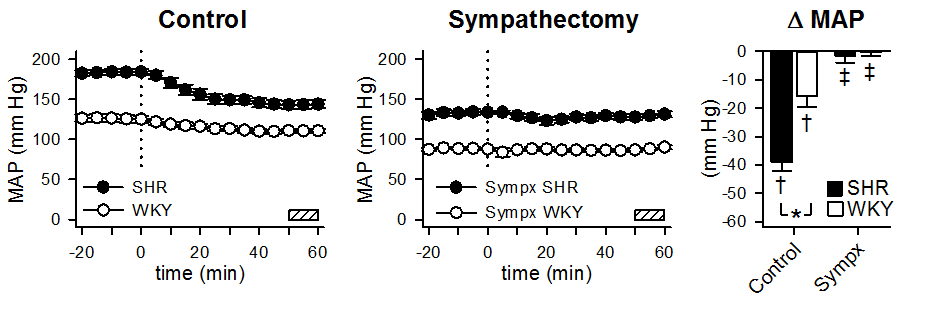 |  |
Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to What are the more common side effects of gabapentin? Common side effects of gabapentin include: Feeling tired. Dizziness. Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Fever. Difficulty speaking. Recurring infections. Memory loss. Weight gain. Movement problems: coordination problems, being unsteady, tremors, jerky movements. Here’s a question on gabapentin and blood pressure below. Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Well, gabapentin has several side effects, and high blood pressure isn’t directly one of them. But that doesn’t mean one can suffer high blood pressure when taking gabapentin. Here’s what happens. Research on rats has shown that gabapentin may lower blood pressure in those with high blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Behuliak et al. demonstrated that acute intravenous injections of GBP lowered blood pressure and heart rate by a sympatho-inhibitory mechanism in both SHR and normotensive rats (WKY), with more pronounced effects observed in the former. Chemical sympathectomy with guanethidine 30 mg/kg daily for 2 weeks prior to gabapentin administration abolished gabapentin’s blood pressure lowering effects, suggesting that gabapentin interfered with sympathetic nerve transmission. Importantly, oral, high-dose (1200 mg/kg daily) gabapentin had no effect on blood pressure over a 10-day period. Gabapentin has been shown to lower blood pressure acutely in hypertensive models, primarily through mechanisms involving the sympathetic nervous system and central nitric oxide signaling. However, its chronic use does not sustain these hypotensive effects and may even lead to adverse cardiovascular outcomes. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of gabapentin on high blood pressure, the available evidence suggests that it may be a useful treatment option for some patients. If you are considering taking gabapentin for high blood pressure, be sure to discuss the potential benefits and risks with your healthcare provider. Visits to the veterinary clinic can be a source of stress for both the feline patient and the caregiver. This can impact the welfare of the pet and the human–animal bond, and result in hesitancy to attend routine visits. 1,2 Palliating the patient’s stress level is important to make an accurate assessment of the patient’s health and perform procedures safely and effectively during Gabapentin can cause changes in blood pressure in some people, either increasing or decreasing it. Learn about the factors that may increase your risk, how to monitor your blood pressure, and how Statcare can help you manage your medication concerns. 1. Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension, a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. 2. Is gabapentin hard on the heart? The effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Cardiol Rev. 2011;19(4):184–191. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0b013e31821ddcf4. [Google Scholar] 10. •• Turtle EJ, Dear JW, Webb DJ. A systematic review of the effect of paracetamol on blood pressure in hypertensive and non-hypertensive subjects. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. We observed that unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS whether to change dose-related BP and HR. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome. It may have some effects on blood pressure, but this is not a common or primary side effect. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used for neuropathic pain and seizures, has been studied for its effects on blood pressure (BP) in various contexts. This article synthesizes research findings on how gabapentin influences BP, particularly during medical procedures and in hypertensive conditions. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: I suggest you contact your Dr. asap. Thanks! I will do that tomorrow! Brenda. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |