Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
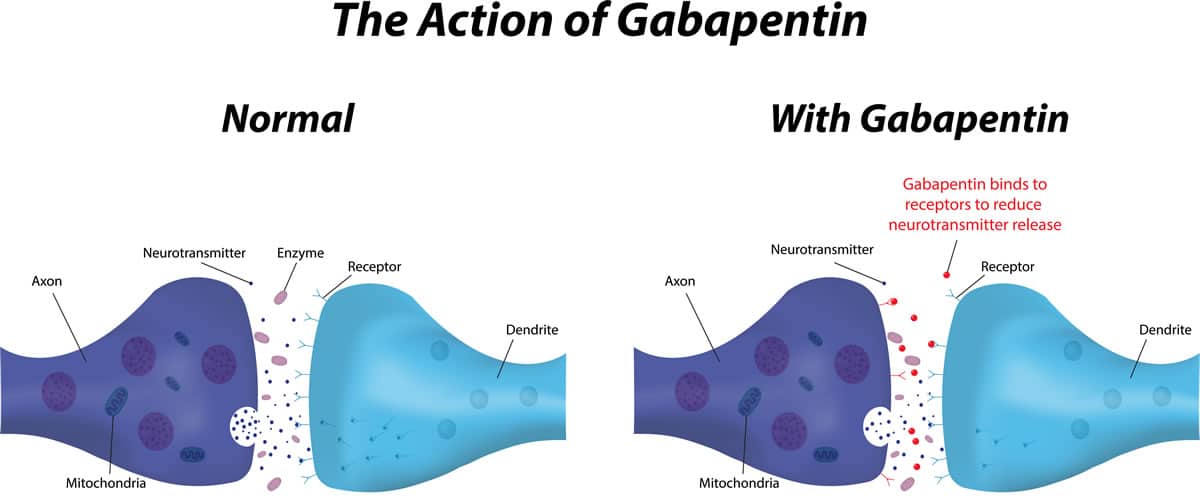
Gabapentin can be used long-term in cats with kidney disease, as long as it is monitored regularly by a veterinarian for any potential side effects or changes in kidney function. 5. Are there any side effects of gabapentin in cats with kidney disease? Common side effects of gabapentin in cats may include sedation, dizziness, and In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. However, when kidney function is impaired, gabapentin can accumulate in the body, leading to potential side effects like excessive sedation, dizziness, and confusion. Therefore, cautious dosing, usually significantly lower than what might be given to a cat with healthy kidneys, is essential. Overdosing on gabapentin, particularly with kidney disease, increases the risk of severe side effects like drowsiness, confusion, coordination problems, tremors, seizures, and even potentially more serious cardiovascular complications. This accumulation can increase the risk of side effects and potential toxicity. Therefore, anyone with stage 3 kidney disease considering gabapentin needs to do so under close medical supervision and with a carefully adjusted dosage. Never self-medicate with gabapentin, especially if you have kidney issues. Understanding Gabapentin and Kidney However, it is frequently used off-label to treat other pain conditions and psychological disorders, such as anxiety. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Gabapentin toxicity and side effects are well-known among nephrologists and fully described in the literature as myoclonic twitches, myopathy, neurotoxicity, etc., particularly in dialysis patients. 2,4. Rhabdomyolysis with associated acute renal failure is an uncommon side effect, but it has been described in earlier cases. 1,3 Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. Taper gabapentin and start to return to normal. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |